Abstract
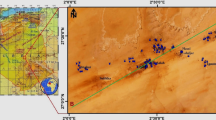
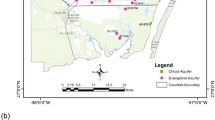
A study has been carried out in crystalline hard rock aquifers of Madurai district, Tamil Nadu, to identify the spatial and temporal variations and to understand sources responsible for hydrogeochemical processes in the region. Totally, 216 samples were collected for four seasons [premonsoon (PRM), southwest monsoon (SWM), northeast monsoon (NWM), and postmonsoon (POM)]. The Na and K ions are attributed from weathering of feldspars in charnockite and fissile hornblende gneiss. The results also indicate that monsoon leaches the U ions in the groundwater and later it is reflected in the 222Rn levels also. The statistical relationship on the temporal data reflects the fact that Ca, Mg, Na, Cl, HCO3, and SO4 form the spinal species, which are the chief ions playing the significant role in the geochemistry of the region. The factor loadings of the temporal data reveal the fact that the predominant factor is anthropogenic process and followed by natural weathering and U dissolution. The spatial analysis of the temporal data reveals that weathering is prominent in the NW part and that of distribution of U and 222Rn along the NE part of the study area. This is also reflected in the cluster analysis, and it is understood that lithology, land use pattern, lineaments, and groundwater flow direction determine the spatial variation of these ions with respect to season.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akpah, F. A., Ishaku, J. M., & Ameh, E. G. (2013). Statistical Investigation of groundwater system in Itakpe area, Kogi State. International Research Journal of Geology and Mining, 3(8), 282–290.
Alberto, WD., Del, PDM., Valeria, AM., Fabiana, PS, Cecilia, HA, De Los Angeles, BM. (2001). Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquıa River Basin (Cordoba-Argentina). Water Research, 35, 2881–2894.
Alther, G. A. (1979). A simplified statistical sequence applied to routine water quality analysis: a case history. Ground Water, 17, 556–561.
APHA. (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 19th Edn., APHA, Washington D.C., USASS.
Avtar, R., Kumar, P., Singh, C. K., Sahu, N., Verma, R. L., Thakur, J. K., & Mukherjee, S. (2013). Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality of Bundelkhand, India using statistical approach. . Water Quality, Exposure and Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-013-0094-2.
Brindha, K., Elango, L., & Nair, N. R. (2011). Spatial and temporal variation of uranium in a shallow weathered rock aquifer in southern India. Journal of Earth System Science, 120, 911–920.
Brindha, K., Rajesh, R., Murugan, R., & Elango, L. (2012). Fluoride contamination in groundwater in parts of Nalgonda district Andhra Pradesh India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 481–492.
Campbell, J. (1996). Introduction to remote sensing (2 ed., p. 622). New York:The Guilford Press.
CGWB (2007). Ground water resources and development prospects in Madurai region. Central groundwater board. Madurai district: District Groundwater Brochure. pp.6-9.
Chapelle, F. H., & Knobel, L. L. (1983). Aqueous geochemistry and the exchangeable cation composition of glauconite in the Aquia Aquifer, Maryland. Ground Water, 21, 343–352.
Chapelle, F. H., Zelibor, J. L., Grimes, D. J., & Knobel, L. L. (1987). Bacteria in deep coastal plain sediments of Maryland: a possible source of CO2 to ground water. Water Resources Research, 23, 1625–1632.
Chen, S., Fu, X. F., Gui, H. R., & Sun, L. H. (2013). Multivariate statistical analysis of the hydro-geochemical characteristics for Mining groundwater: a case study from Baishan mining, northern Anhui Province, China. Water Practice Technology, 8, 131–141.
Cheong, JY., Hamm, SY., Lee, JH., Lee, KS, Woo, NC. (2012). Groundwater nitrate contamination and risk assessment in an agricultural area, South Korea. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66,1127–1136.
Chidambaram, S. (2000). Hydrogeochemical studies of groundwater in Periyar district, Tamilnadu, India. Unpublished Ph.D thesis, Department of Geology, Annamalai University.
Chidambaram, S., Ramanathan, AL., Prasanna, MV., Anandhan, P., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vasudevan, S. (2007). Identification of hydrogeochemically active regimes in groundwaters of Erode district, Tamilnadu—a statistical approach. Asian Journal of Water, Environment and Pollution 5 (3), 93–102.
Chidambaram, S., Ramanathan, AL., Anandhan, P., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Prasanna, MV, Vasudevan, S. (2008). A statistical approach to identify the hydrogeochemically active regimes in ground waters of Erode district, Tamilnadu. Asian Journal of Water, Environment and Pollution, 5(3), 123–135.
Chidambaram, S., Bala Krishna Prasad, M., Manivannan, R., Karmegam, U., Singaraja, C., Anandhan, P., Prasanna, M. V., & Manikandan, S. (2013). Environmental hydrogeochemistry and genesis of fluoride in groundwaters of Dindigul district, Tamilnadu (India). Environmental Earth Sciences, 68, 333–342.
Chung, SY., Venkatramanan, S., Park, N., Rajesh, R., Ramkumar, T, Kim, BW. (2015). An Assessment of selected hydrochemical parameter trend of the Nakdong River water in South Korea, using time series analyses and PCA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(4192), 1–13.
Dillon, M. E., Carter, G. L., Arora, R., & Kahn, B. (1991). Radon concentrations in groundwater of Georgia piedmont. Health Physics, 60, 229–236.
Drever IJ. (1988).The geochemistry of natural waters, 2nd edn.Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, p 388.
Farnham, I. M., Stetzenbach, K. J., Singh, A. K., & Johannesson, K. H. (2000). Deciphering groundwater flow systems in Oasis Valley, Nevada, using trace element chemistry, multivariate statistics, and geographical information system. Mathematical Geology, 32, 943–968.
Farnham, I. M., Johannesson, K. H., Singh, A. K., Hodge, V. F., & Stetzenbach, K. J. (2003). Factor analytical approaches for evaluating groundwater trace element chemistry data. Analytical Chimica Acta, 490, 123–138.
GSI (Geological Survey of India) (1995). Geological and mineral map of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Miscellaneous Publication No. 30 Compiled by T.N. Rajan and P.S.Anil Kumar Geologists (Sr), pp.1-93.
Gui, H. R., & Chen, L. W. (2007). Hydrogeochemistric evolution and discrimination of groundwater in mining district. Beijing:Geological Publishing House..
Guo, H., & Wang, Y. (2004). Hydrogeochemical processes in shallow quaternary aquifers from the northern part of the Datong Basin, China. Applied Geochemistry, 19(1), 19–27.
Kacaroglu, F., & Gunay, G. (1997). Groundwater nitrate pollution in an alluvium aquifer, Eskisehir urban area and its vicinity, Turkey. Environmental Geology, 31, 178–184.
Kavitha, K., Prakasam, C., & Shanthakumari, A. (2012). Land use land cover change detection in Madurai district, Tamilnadu, India: using satellite remote. IJPSS Sensing, 2(8).
Mabee, S., Hardcastle, K., & Wise, D. (1994). A method of collecting and analyzing lineaments for regional scale fractured bedrock aquifer studies. Groundwater, 32(6), 884–894..
Manikandan, S., Chidambaram, S., Ramanathan, AL., Prasanna, MV., Karmegam, U., Singaraja, C., Paramaguru, P., & Jainab, L. (2012) A study on the high fluoride concentration in the magnesium-rich water of hard rock aquifer in Krishnagiri district, Tamilnadu, India, Arab.Journal of Geosciences, DOI 10.1007/s12517-012-0752-x
Melloul, A., & Collin, M. (1992). The ‘principal components’ statistical method as a complementary approach to geochemical methods in water quality factor identification; application to the Coastal Plain aquifer of Israel. Journal of Hydrology, 140, 49–73.
Meng, S. X., & Maynard, J. B. (2001). Use of statistical analysis to formulate conceptual models of geochemical behavior: water chemical data from Butucatu aquifer in Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Journal of Hydrology, 250, 78–97.
Mohapatra, P. K., Vijay, R., Pujari, P. R., Sundaray, S. K., & Mohanty, B. P. (2011). Determination of processes affecting groundwater quality in the coastal aquifer beneath Puri city, India: a multivariate statistical approach. Water Science and Technology, 64(4), 809–817. doi:10.2166/wst.2011.605.
Narmatha, T., Jeyaseelan, A., Mohan, SP, & Ram Mohan, V. (2011). Integrating multivariate statistical analysis with GIS for groundwater in Pambar Sub Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 2(2).
Olobaniyi, S. B., & Owoyemi, F. B. (2006). Characterization by factor analysis of the chemical facies of groundwater in the deltaic plain-sands aquifer of Warri, Western Niger Delta Nigeria. African Journal of Science and Technology, 7(1), 73–81.
Otwoma, D., & Mustapha, A. O. (1998). Measurement of 222Rn concentration in Kenyan groundwater. Health Physics, 74(1), 91–95.
Pandey, U K, & Krishnamurthy, P. (1995). Uranium and thorium abundances in some graphite-bearing Precambrian rocks of India and implications. Current Science, 68(8).
Panno, S.V, Hackley, K.C., & Greenberg, S.E. (1999a). A possible technique for determining the origin of sodium and chloride in natural waters: preliminary results from a site in northeastern Illinois. [Abstract] In Environmental Horizons 2000, Conference Proceedings, March 27–28, 2000. pp. 57.
Porcelli, D., & Swarzenski, P W. (2003). The behavior of U- and Th-series nuclides in groundwater. 317–361 in Uranium-Series Geochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 52.
Prabu, P., & Rajagopalan, B. (2013) Mapping of lineaments for groundwater targeting and sustainable water resource management in hard rock hydrogeological environment using RS-GIS, INTECH publications, http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/55702.
Prasanna, M. V., Chidambaram, S., & Srinivasamoorthy, K. (2010). Statistical analysis of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in hard and sedimentary aquifers system of Gadilam river basin, South India. Journal of King Saud University Science, 22(3), 133–145.
Ramesh, R., & Anbu, M. (1996). Chemical methods for environmental analysis—water and sediments (p. 161). India:Macmillan Publisher.
Ranjana, U. K., & Naverathna, M. P. C. (2011). River sand mining in southern Sri-Lanka and its effect on environment. 11th International River symposium on “A Future of extremes” Brisbane, Australia.
Schot, P. P., & Van der Wal, J. (1992). Human impact on regional groundwater composition through intervention in natural flow patterns and changes in land use. Journal of Hydrology, 134, 297–313.
Singaraja, C., Chidambaram, S., Anandhan, P., Prasanna, MV., Thivya, C., Thilagavathi, R., & Sarathidasan, J. (2013). Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region and its repercussion on quality, a case study—Thoothukudi district, Tamilnadu. India. Arab Journal of Geosciences, doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0794-0.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vasanthavigar, M., Chidambaram, S., Anandhan, P., & Sarma, V. S. (2011). Characterization of groundwater chemistry in an eastern coastal area of Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu. Journal of Geological Society of India, 78, 549–558.
Steinhorst, R. K., & Williams, R. E. (1985). Discrimination of groundwater sources using cluster analysis, MANOVA, canonical analysis and discriminant analysis. Water Resources Research, 21, 1149–1156.
Stetzenbach, K. J., Hodge, V. F., Guo, C., Farnham, I. M., & Johannesson, K. H. (2001). Geochemical and statistical evidence of deep carbonate groundwater within overlying volcanic rock aquifers/aquitards of southern Nevada, USA. Journal of Hydrology, 243, 254–271.
Subramani, T., Rajmohan, N., & Elango, L. (2009). Groundwater geochemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock region, Southern India. Environment Monitoring Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0781-4.
Thivya, C. (2013). Study on uranium in groundwater of Madurai district. Unpublished thesis. Department of Earth Sciences. Annamalai University.
Thivya, C., Chidambaram, S., Singaraja, C., Thilagavathi, R., Prasanna, M. V., & Jainab, I. (2013a). A study on the significance of lithology in groundwater quality of Madurai district, Tamil Nadu (India). Environment, Development and Sustainability. doi:10.1007/s10668-013-9439-z.
Thivya, C., Chidambaram, S., Thilagavathi, R., Prasanna, M. V., Singaraja, C., Nepolian, M., & Sundararajan, M. (2013b). Identification of the geochemical processes in groundwater by factor analysis in hard rock aquifers of Madurai District, South India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1065-4.
Thomas, M. A. A. (1987). Connecticut radon study using limited water sampling and a statewide ground based gamma survey to help guide an indoor air testing program. A progress report. In G. Barbara (Ed.), Radon, radium and other radioactivity in airborne contamination. Proceedings of a conference, National water well association (pp. 347–362). Ann Arbor: Lewis Publishers.
Usunoff, E. J., & Guzman-Guzman, A. (1989). Multivariate analysis in hydrochemistry: an example of the use of factor and correspondence analyses. Ground Water, 27, 27–34.
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., & Prasanna, M. V. (2012). Evaluation of groundwater suitability for domestic, irrigational, and industrial purposes: a case study from Thirumanimuttar river basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 405–420.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping methods to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58, 235–344.
Williams, R. E. (1982). Statistical identification of hydraulic connections between the surface of a mountain and internal mineralized sources. Groundwater, 20, 466–478.
Wu, E. M. Y., & Kuo, S. (2012). Applying a multivariate statistical analysis model to evaluate the water quality of a watershed. Water Environment Research, 84(12), 2075–2085.
Yidana, SM., Ophori, D, & Banoeng-Yakubo, B. (2008b). A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry—the Ankobra Basin, Ghana. Environmental Management, 86:80–87.
Zelensky, A. V., Buzinny, M. G., & Los, I. P. (1993). Measurements of 226Ra and 222Rn and uranium in Ukrainian groundwater using ultra-low-level liquid scintillation counting. In J. E. Noakes, F. Schoenhofer, H. A. Polach (Eds.), Liquid scintillation spectrometry, 1992 (pp. 405–411). Radiocarbon.
Zhang, X., Qian, H., Chen, J., & Qiao, L. (2014). Assessment of groundwater chemistry and status in a heavily used semi-arid region with multivariate statistical analysis. Water, 2014(6), 2212–2232.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their sincere thanks to University Grants Commission (UGC), India, for providing the necessary financial support to carry out this study with vide reference to UGC letter No. F: 39-143/2010 (SR) dated 27 December 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thivya, C., Chidambaram, S., Thilagavathi, R. et al. A multivariate statistical approach to identify the spatio-temporal variation of geochemical process in a hard rock aquifer. Environ Monit Assess 187, 552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4738-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4738-5