Abstract
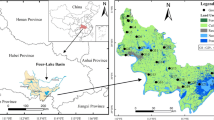
In this study, the hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater were analyzed to get insight into the factors affecting groundwater quality in a typical agricultural dominated area of the North China Plain. Forty-four shallow groundwater samples were collected for chemical analysis. The water type changes from Ca·Na-HCO3 type in grass land to Ca·Na-Cl (+NO3) type and Na (Ca)-Cl (+NO3+SO4) type in construction and facility agricultural land, indicating the influence of human activities. The factor analysis and geostatistical analysis revealed that the two major factors contributing to the groundwater hydrochemical compositions were the water-rock interaction and contamination from sewage discharge and agricultural fertilizers. The major ions (F, HCO3) and trace element (As) in the shallow groundwater represented the natural origin, while the nitrate and sulfate concentrations were related to the application of fertilizer and sewage discharge in the facility agricultural area, which was mainly affected by the human activities. The values of pH, total dissolved solids, electric conductivity, and conventional component (K, Ca, Na, Mg, Cl) in shallow groundwater increased from grass land and cultivated land, to construction land and to facility agriculture which were originated from the combination sources of natural processes (e.g., water-rock interaction) and human activities (e.g., domestic effluents). The study indicated that both natural processes and human activities had influences on the groundwater hydrochemical compositions in shallow groundwater, while anthropogenic processes had more contribution, especially in the reclaimed water irrigation area.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amadi, A. N., Olasehinde, P. I., Yisa, J., Okosun, E. A., Nwankwoala, H. O., & Alkali, Y. B. (2012). Geostatistical assessment of groundwater quality from coastal aquifers of Eastern Niger Delta, Nigeria. Geosciences, 2(3), 51–59.
Andrade, E. M., Palácio, H. A. Q., Souza, I. H., de Oliveira Leão, R. A., & Guerreiro, M. J. (2008). Land use effects in groundwater composition of an alluvial aquifer (Trussu River, Brazil) by multivariate techniques. Environmental Research, 106(2), 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2007.10.008.
Arslan, H. (2013). Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of groundwater quality in seawater intrusion area in Bafra Plain, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(3), 2439–2452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2722-x.
Barth, J. A. C., Grathwohl, P., Fowler, H. J., Bellin, A., Gerzabek, M. H., Lair, G. J., et al. (2009). Mobility, turnover and storage of pollutants in soils, sediments and waters: achievements and results of the EU project AquaTerra—a review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 29(1), 161–173. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2007060.
Bhuiyan, M. A. H., Bodrud-Doza, M., Islam, A. R. M. T., Rakib, M. A., Rahman, M. S., & Ramanathan, A. L. (2016). Assessment of groundwater quality of Lakshimpur district of Bangladesh using water quality indices, geostatistical methods, and multivariate analysis. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(12), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5823-y.
Bing, Z., Song, X., Zhang, Y., Han, D., Tang, C., Yu, Y., et al. (2012). Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Research, 46(8), 2737–2748.
Cai, X. (2008). Water stress, water transfer and social equity in Northern China—implications for policy reforms. Journal of Environmental Management, 87(1), 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.12.046.
Choi, B.-Y., Yun, S.-T., Kim, K.-H., Kim, J.-W., Kim, H. M., & Koh, Y.-K. (2014). Hydrogeochemical interpretation of South Korean groundwater monitoring data using self-organizing maps. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 137, 73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.12.001.
Compton, J. E., & Boone, R. D. (2000). Long-term impacts of agriculture on soil carbon and nitrogen in New England forests. Ecology, 81(8), 2314–2330.
Currell, M., Cartwright, I., Raveggi, M., & Han, D. (2011). Controls on elevated fluoride and arsenic concentrations in groundwater from the Yuncheng Basin, China. Applied Geochemistry, 26(4), 540–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.01.012.
Currell, M. J., Han, D., Chen, Z., & Cartwright, I. (2012). Sustainability of groundwater usage in northern China: dependence on palaeowaters and effects on water quality, quantity and ecosystem health. Hydrological Processes, 26(26), 4050–4066.
Devic, G., Djordjevic, D., & Sakan, S. (2014). Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in Serbia. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 933–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.011.
Dinnes, D. L., Karlen, D. L., Jaynes, D. B., Kaspar, T. C., Hatfield, J. L., Colvin, T. S., et al. (2002). Review and interpretation: nitrogen management strategies to reduce nitrate leaching in tile-drained Midwestern soils. Agronomy Journal, 94(1), 153–171. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2002.0153.
Griffioen, J. (2001). Potassium adsorption ratios as an indicator for the fate of agricultural potassium in groundwater. Journal of Hydrology, 254(1–4), 244–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00503-0.
Guo, Q., Wang, Y., Ma, T., & Ma, R. (2007). Geochemical processes controlling the elevated fluoride concentrations in groundwaters of the Taiyuan Basin, Northern China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 93(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2006.07.001.
Gurunadha Rao, V. V. S., Tamma Rao, G., Surinaidu, L., Mahesh, J., Mallikharjuna Rao, S. T., & Mangaraja Rao, B. (2013). Assessment of geochemical processes occurring in groundwaters in the coastal alluvial aquifer. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(10), 8259–8272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3171-x.
Han, D., Xing, L., Currell, M. J., Song, X., Chen, Z., Jin, M., et al. (2010). Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater systems in Daying and Qicun geothermal fields, Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi, China. Hydrological Processes, 24(22), 3157–3176.
Hounslow, A. (1995). Water quality data: analysis and interpretation. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Huan, H., Wang, J. S., Zhai, Y. Z., Zheng, J. Q., Sciences, C. O. W., University, B. N, et al. (2011). Chemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Yongding River Alluvial Fan of Beijing Plain. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 32(3), 357–366.
Huang, G., Chen, Z., Liu, F., Sun, J., & Wang, J. (2014). Impact of human activity and natural processes on groundwater arsenic in an urbanized area (South China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 21(22), 13043–13054.
Jiang, Y., Wu, Y., Groves, C., Yuan, D., & Kambesis, P. (2009). Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 109(1–4), 49–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2009.08.001.
Jiang, Y., Zhang, C., Yuan, D., Zhang, G., & He, R. (2008). Impact of land use change on groundwater quality in a typical karst watershed of southwest China: a case study of the Xiaojiang watershed, Yunnan Province. Hydrogeology Journal, 16(4), 727–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-007-0259-9.
Kouras, A., Katsoyiannis, I., & Voutsa, D. (2007). Distribution of arsenic in groundwater in the area of Chalkidiki, Northern Greece. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147(3), 890–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.124.
Liu, C., & Xia, J. (2004). Water problems and hydrological research in the Yellow River and the Huai and Hai River basins of China. Hydrological Processes, 18(12), 2197–2210. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.5524.
Mondal, N. C., Prasad, R. K., Saxena, V. K., Singh, Y., & Singh, V. S. (2009). Appraisal of highly fluoride zones in groundwater of Kurmapalli watershed, Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh (India). Environmental Earth Sciences, 59(1), 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0004-x.
Mondal, N. C., Saxena, V. K., & Singh, V. S. (2008). Occurrence of elevated nitrate in groundwaters of Krishna delta, India. African Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 2(9), 265–271.
Mondal, N. C., & Singh, V. P. (2011). Hydrochemical analysis of salinization for a tannery belt in Southern India. Journal of Hydrology, 405(3), 235–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.058.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, S., & Singh, V. S. (2011). Hydrochemical characteristic of coastal aquifer from Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175(1), 531–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1549-6.
Mondal, N. C., Singh, V. P., Singh, V. S., & Saxena, V. K. (2010). Determining the interaction between groundwater and saline water through groundwater major ions chemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 388(1), 100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.04.032.
Niu, Y., Yin, S., Liu, H., Wu, W., & Li, B. (2015). Use of geostatistics to determine the spatial variation of groundwater quality: a case study in Beijing’s reclaimed water irrigation area. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 24(2), 611–618.
Ouyang, Y., Zhang, J.-E., & Parajuli, P. (2013). Characterization of shallow groundwater quality in the Lower St. Johns River Basin: a case study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(12), 8860–8870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1864-x.
Papaioannou, A., Dovriki, E., Rigas, N., Plageras, P., Rigas, I., Kokkora, M., et al. (2010). Assessment and modelling of groundwater quality data by environmetric methods in the context of public health. Water Resources Management, 24(12), 3257–3278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9605-0.
Singh, E. J. K., Gupta, A., & Singh, N. R. (2013). Groundwater quality in Imphal West district, Manipur, India, with multivariate statistical analysis of data. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(4), 2421–2434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1127-2.
Stumm, W., & Morgan, J. J. (1996). Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. Cram101 Textbook Outlines to Accompany, 179(11), A277.
Teikeu, W. A., Meli’i, J. L., Njandjock Nouck, P., Tabod, T. C., Enyegue, A., Nyam, F., & Aretouyap, Z. (2015). Assessment of groundwater quality in Yaoundé area, Cameroon, using geostatistical and statistical approaches. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4779-7.
Wang, S., Tang, C., Song, X., Yuan, R., Han, Z., & Pan, Y. (2016). Factors contributing to nitrate contamination in a groundwater recharge area of the North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 30(13), 2271–2285. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10778.
Wang, G., & Cheng, G. (2001). Fluoride distribution in water and the governing factors of environment in arid north-west China. Journal of Arid Environments, 49(3), 601–614. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2001.0810.
Wang, S. (2013). Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the Yanqi Basin of Xinjiang Province, Northwest China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(9), 7469–7484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3113-7.
Xiao, Y., Gu, X., Yin, S., Shao, J., Cui, Y., Zhang, Q., et al. (2016). Geostatistical interpolation model selection based on ArcGIS and spatio-temporal variability analysis of groundwater level in piedmont plains, northwest China. Spring, 5(1), 1–15.
Yang, Z., Dou, Y., & Wang, Z. (2010). Analysis on the reasons of the decline of ground water level in the primary water supply source area of Beijing and the countermeasures. China Water Resources, 38, 455–471.
Zhai, Y., Wang, J., Teng, Y., & Zuo, R. (2013). Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater evolution and recharge in aquifers in Beijing Plain, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(7), 2167–2177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2045-9.
Zhou, Y., Dong, D., Liu, J., & Li, W. (2013). Upgrading a regional groundwater level monitoring network for Beijing Plain, China. Geoscience Frontiers, 4(1), 127–138.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (nos. 2652016020 and 2652016022), the fundamental research funds for Central Public Research Institutes (YYWF201626), and the Ministry of Water Resources Public Projects (201101051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Xiao, Y., Yin, S. et al. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the shallow groundwater quality in a typical irrigation area with reclaimed water, North China Plain. Environ Monit Assess 189, 514 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6229-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6229-3