Abstract
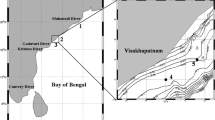
In this study, the water quality of the Coruh River Basin, which is located in the Eastern Black Sea Region of Turkey, was evaluated. The water quality data measurement results obtained by the State Hydraulic Works 26th Regional Directorate from four different sites over a course of 4 years between the years 2011 and 2014 in the Coruh River Basin were used as the data. In this study, the water quality was evaluated by using the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environmental Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) method and discriminant analysis (DA). The water quality of the Coruh River Basin was calculated as 30.4 and 71.35 by using the CCME WQI and classified as “poor,” “marginal,” and “fair”. These values show that the water of the Coruh River Basin is degraded and under threat and its overall quality is not close to natural or desired levels. The monitoring sites were divided into two groups by the cluster analysis (CA). DA is a multivariate analysis technique used to divide individuals or objects into different groups and assign them into predetermined groups. As a result of DA, calcium (Ca) and sulfate (SO4) were determined to be significant parameters in the determination of the water quality of the Coruh River Basin. The success of DA depends on the percentage of correct classification. As a result of the analysis, 23% of the parameters in the first measurement point, 69.2% of the parameters in the second and third measurement points, and 76.9% of the parameters in the fourth measurement point were classified correctly. Since the second measurement point is the discharge point of a copper mine, it can be said that the water quality parameters measured may provide accurate results in detecting pollution at this point.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, T., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Water-Quality Indices. In Water quality indices. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Akkoyunlu, A., & Akiner, M. E. (2012). Pollution evaluation in streams using water quality indices: a case study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin. Ecological Indicators, 18, 501–511.
Alexakis, D., Tsihrintzis, V. A., Tsakiris, G., & Gikas, G. D. (2016). Suitability of water quality indices for application in lakes in the mediterranean. Water Resource Management, 30(5), 1621–1633.
Bengraine, K., & Marthaba, T. F. (2003). Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 100, 179–195.
Bilgin, A. (2015a). An assessment of water quality in the Coruh Basin (Turkey) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(11), 721.
Bilgin, A. (2015b). Evaluation of Borcka Reservoir water quality by a multivariate statistical method. Celal Bayar University Journal of Science, 11(2), 287–293.
Bilgin, A., & Konanç, M. U. (2016). Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal pollution of Coruh River Basin (Turkey) by multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(1029), 1–18.
Bordalo, A. A., Nilsumranchit, W., & Chalermwat, K. (2001). Water quality and uses of the Bangpakon river (Eastern Thailand). Water Research, 35(15), 3635–3642.
Boyacıoğlu, H., & Boyacıoğlu, H. (2010). Detection of seasonal variations in surface water quality using discriminant analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 162, 15–20.
Boyacıoğlu, H., Gündogdu, V. & Boyacıoğlu, H. (2013). Investigation of priorities in water quality management based on correlations and variations. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 69, 48-54.
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). Water quality index-do we dare? Water Sewage Works., 117(10), 339–343.
CCME (2001). Canadian environmental quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life, CCME water quality index: technical report, 1.0.
Damo, R., & Icka, P. (2013). Evaluation of water quality index for drinking water. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 22(4), 1045–1051.
Espejo, L., Kretschmer, N., Oyarzún, J., Meza, F., Núñez, J., Maturana, H., Soto, G., Oyarzo, P., Garrido, M., Suckel, F., Amezaga, J., & Oyarzún, R. (2012). Application of water quality indices and analysis of the surface water quality monitoring network in semiarid North-Central Chile. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(9), 5571–5588.
Horton, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal-Water Pollution Control Federation, 37(3), 300–305.
House, M. A. (1989). A water quality index for river management. Water and Environment Journal, 3(4), 336–344.
Huang, G. H., & Xia, J. (2001). Barriers to sustainable water-quality management. Journal of Environmental Management, 61(1), 1–23.
Johnson, E.D. (1998). Applied multivariate methods for the data analysis. Duxbury press, 407.
Kalaycı, Ş. (2009). SPSS Uygulamalı çok değişkenli istatistik teknikleri. Asil Yayın Dağıtım (in Turkish).
Kankal, N. C., Indurkar, M. M., Gudadhe, S. K., & Wate, S. R. (2012). Water quality index of surface water bodies of Gujarat, India. Asian Journal of Experimental Sciences, 26(1), 39–48.
Khan, A. A., Paterson, R., & Khan, H. (2003). Modification and application of the CCME WQI for the communication of drinking water quality data in Newfoundland and Labrador. In Proceedings of the 38th central symposium on water quality research, Canadian association on water quality. Burlington: Canada.
Khan, A. A., Tobin, A., Paterson, R., Khan, H., & Warren, R. (2005). Application of CCME procedures for deriving site-specific water quality guidelines for the CCME water quality index. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 40(4), 448–456.
Lumb, A., Halliwell, D., & Sharma, T. (2006). Application of CCME water quality index to monitor water quality: a case of the Mackenzie river basin, Canada. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 113, 411–429.
Massart, D. L., & Kaufman, L. (1983). The ınterpretation of analytical chemical data by the use of cluster analysis. New York: Wiley.
Mohebbi, M. R., Saeedi, R., Montazeri, A., Vaghefia, K. A., Labbaf, S., Oktaie, S., Abtahi, M., & Mohagheghian, A. (2013). Assessment of water quality in groundwater resources of Iran using a modified drinking water quality index (DWQI). Ecological Indicators, 30, 28–34.
Mostafaei, A. (2014). Application of multivariate statistical methods and water quality index to evaluation of water quality in the Kashkan River. Environmental Management, 53(4), 865–881.
Najapour, S., Alkarkhi, A. F. M., Kadir, M. O. A., & Najapour, G. D. (2008). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in river water quality. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2(4), 349–358.
Ouyang, Y. (2005). Evaluation of river water quality monitoring station by principal component analysis. Water Research, 39, 2621–2635.
Ouyang, Y., Nkedi-kizza, P., Wu, Q. T., Shinde, D., & Huang, C. H. (2006). Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Research, 40, 3800–3810.
Otto, M. (1998). Multivariate methods. In R. Kellner, J. M. Mermet, M. Otto, & H. M. Widmer (Eds.), Analytical chemistry (p. 916). Weinheim: Wiley/VCH.
Sharma, D., & Kansal, A. (2011). Water quality analysis of River Yamuna using water quality index in the national capital territory, India (2000–2009). Applied Water Science, 1(3–4), 147–157.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modeling & Software, 22, 464–475.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India): a case study. Water Research, 38, 3980–3992.
Sophocleous, M. (2002). Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science. Hydrogeology Journal, 10, 52–67.
Sucu, S., & Dinç, T. (2008). Çoruh havzası projeleri. TMMOB II. Ulusal Su Politikaları Kongresi, 20–22 Mart. Ankara (in Turkish).
SWQMR (2015). Turkish surface water quality management regulations. Official Gazette 15.04.2015 and numbered 29327.
SWQMR (2016). Turkish surface water quality management regulations. Official Gazette 10.08.2016 and numbered 29797.
Taner, M. U., Ustun, B., & Erdinçler, A. (2011). A simple tool for the assessment of water quality in polluted lagoon systems: a case study for Kücük Çekmece Lagoon, Turkey. Ecological Indicators, 11, 749–756.
Tatlıdil, H. (1996). Uygulamalı cok değiskenli istatistiksel analiz, 2. Baskı, Ankara, 424. (in Turkish).
Terrado, M., Barceló, D., Tauler, R., Borrell, E., Campos, S. D., & Barceló, D. (2010). Surface-water-quality indices for the analysis of data generated by automated sampling networks. TrAC, Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 29(1), 40–52.
TSE-266 (2005) Turkish standards organization. Ankara: Turkey Standard Institute.
Tyagi, S., Sharma, B., Singh, P., & Dobhal, R. (2013). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. American Journal of Water Resources, 1, 34–38.
Uddin, M. G., Moniruzzaman, M., & Khan, M. (2017). Evaluation of groundwater quality using CCME water quality index in the Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant Area, Ishwardi, Pabna, Bangladesh. American Journal of Environmental Protection, 5(2), 33–43.
Varol, M., Gökot, B., Bekleyen, A., & Sen, B. (2012). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Tigris River (Tukey) using, multivariate statistical techniques a case study. River Research and Applications, 28, 1428–1438.
Vega, M., Pardo, R., Barrado, E., & Deban, L. (1998). Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32, 3581–3592.
Voutsa, D., Zachariadis, G., Samara, C., & Kouimtzis, T. (2008). Evaluation of chemical parameters in Aliakmon river in Northers Greece. 2. Dissolved and particulate heavy metals. Journal of Environmental Science Health. Part A. Environmental Science and Engineering, 30, 1–13.
Yan, F., Qiao, D., Qian, B., Ma, L., Xing, X., Zhang, Y., & Wang, X. (2016). Improvement of CCME WQI using grey relational method. Journal of Hydrology, 543, 316–323.
Wang, X., Cai, Q., Ye, L., & Qu, X. (2012). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in stream water quality by multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Xiangxi River basin, China. Quaternary International, 282, 137–144.
Wenning, R. J., & Erickson, G. A. (1994). Interpretation and analysis of complex environmental data using chemometric methods. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 13, 446–457.
Willet, P. (1987). Similarity and clustering in chemical information systems. Research studies press, Wiley, New York.
Acknowledgments
The author is thankful to the State Hydraulic Works 26th Regional Directorate (Artvin, Turkey) for providing the data. The author is thankful to Assoc. Prof. Dr. Halil Akıncı for drawing and mapping.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgin, A. Evaluation of surface water quality by using Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment Water Quality Index (CCME WQI) method and discriminant analysis method: a case study Coruh River Basin. Environ Monit Assess 190, 554 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6927-5