Abstract
The study evaluates Hermetia illucens larvae’s ability to decrease direct methane emissions and nutrients from cattle and swine manure. Hermetia illucens larvae were put into fresh cattle and swine manure, and the same conditions, without larvae, for the control treatment were established. The methane emissions were measured until the first prepupae appeared. The methane emissions from the bioconversion of animal manure by Hermetia illucens larvae were up to 86% lower than in the control treatments (conventional storage). The cumulative methane emissions from cattle and swine manure bioconversion were 41.4 ± 10.5 mg CH4 kg−1 and 134.2 ± 17.3 mg CH4 kg−1, respectively. Moreover, Hermetia illucens larvae could reduce 32% of dry matter, 53% nitrogen, 14% phosphorus, and 42% carbon in swine manure. Meanwhile, in cattle manure, reductions of 17% of dry matter, 5% of nitrogen, 11% of phosphorus, and 15% of carbon and pH reductions in both swine and cattle manure were found. Thus, the production of larvae was higher in swine manure than cattle manure. Furthermore, the larvae frass from swine manure was appropriate for agricultural use, unlike the larvae frass from cattle manure requiring further processing. These results reveal the ability of Hermetia illucens larvae to mitigate methane emissions from animal manure and show it to be a promising technology for manure treatment, with great potential to promote a circular economy in the livestock sector.
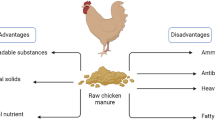
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article.
References
Abdoli, M. A., Omrani, G., Safa, M., & Samavat, S. (2019). Comparison between aerated static piles and vermicomposting in producing co-compost from rural organic wastes and cow manure. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(3), 1551–1562.
Abu Hasan, H., & Leong, K. P. (2018). Growth of Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) and Sarcophaga dux (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) larvae in poultry and livestock manures: Implication for animal waste management. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 21(3), 880–884.
Almeida, C., Rijo, P., & Rosado, C. (2020). Bioactive compounds from Hermetia illucens larvae as natural ingredients for cosmetic application. Biomolecules, 10(7), 976.
Barragan-Fonseca, K. B., Dicke, M., & van Loon, J. J. (2017). Nutritional value of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) and its suitability as animal feed–A review. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 3(2), 105–120.
Bava, L., Jucker, C., Gislon, G., Lupi, D., Savoldelli, S., Zucali, M., & Colombini, S. (2019). Rearing of Hermetia illucens on different organic by-products: Influence on growth waste reduction and environmental impact. Animals, 9(6), 289.
Beard, R. L., & Sands, D. C. (1973). Factors affecting degradation of poultry manure by flies. Environmental Entomology, 2(5), 801–806.
Bernal, M. P., Paredes, C., Sanchez-Monedero, M. A., & Cegarra, J. (1998). Maturity and stability parameters of composts prepared with a wide range of organic wastes. Bioresource Technology, 63(1), 91–99.
Biagini, D., & Lazzaroni, C. (2018). Eutrophication risk arising from intensive dairy cattle rearing systems and assessment of the potential effect of mitigation strategies. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 266, 76–83.
Bloukounon-Goubalan, A. Y., Saïdou, A., Chrysostome, C. A. A. M., Kenis, M., Amadji, G. L., Igué, A. M., & Mensah, G. A. (2019). Physical and chemical properties of the agro-processing by-products decomposed by larvae of Musca domestica and Hermetia illucens. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 1–9.
Bosch, G., Oonincx, D. G. A. B., Jordan, H. R., Zhang, J., van Loon, J. J. A., van Huis, A., Tomberlin, J. K. (2019). Standardisation of quantitative resource conversion studies with black soldier fly larvae. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 6 (2):95-109
Broucek, J. (2014). Production of methane emissions from ruminant husbandry: A review. Journal of Environmental Protection, 5(15), 1482.
Cai, M., Hu, R., Zhang, K., Ma, S., Zheng, L., Yu, Z., & Zhang, J. (2018). Resistance of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae to combined heavy metals and potential application in municipal sewage sludge treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(2), 1559–1567.
Cammack, J. A., & Tomberlin, J. K. (2017). The impact of diet protein and carbohydrate on select life-history traits of the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects, 8(2), 56.
Chadwick, D., Sommer, S., Thorman, R., Fangueiro, D., Cardenas, L., Amon, B., & Misselbrook, T. (2011). Manure management: Implications for greenhouse gas emissions. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 166, 514–531.
Chan, Y. C., Sinha, R. K., & Wang, W. (2011). Emission of greenhouse gases from home aerobic composting, anaerobic digestion and vermicomposting of household wastes in Brisbane (Australia). Waste Management & Research, 29(5), 540–548.
Chen, H., Awasthi, S. K., Liu, T., Duan, Y., Ren, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019). Effects of microbial culture and chicken manure biochar on compost maturity and greenhouse gas emissions during chicken manure composting. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 121908.
Chen, J., Hou, D., Pang, W., Nowar, E. E., Tomberlin, J. K., Hu, R., et al. (2019). Effect of moisture content on greenhouse gas and NH3 emissions from pig manure converted by black soldier fly. Science of The Total Environment, 697, 133840.
Cheng, J. Y., Chiu, S. L., & Lo, I. M. (2017). Effects of moisture content of food waste on residue separation, larval growth and larval survival in black soldier fly bioconversion. Waste Management, 67, 315–323.
Czepiel, P., Douglas, E., Harriss, R., & Crill, P. (1996). Measurements of N2O from composted organic wastes. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(8), 2519–2525.
Diener, S., Zurbrügg, C., & Tockner, K. (2009). Conversion of organic material by black soldier fly larvae: Establishing optimal feeding rates. Waste Management & Research, 27(6), 603–610.
Dzepe, D., Nana, P., Fotso, A., Tchuinkam, T., & Djouaka, R. (2020). Influence of larval density, substrate moisture content and feedstock ratio on life history traits of black soldier fly larvae. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 6(2), 133–140.
Erickson, M. C., Islam, M., Sheppard, C., Liao, J., & Doyle, M. P. (2004). Reduction of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis in chicken manure by larvae of the black soldier fly. Journal of Food Protection, 67(4), 685–690.
Ermolaev, E., Lalander, C., & Vinnerås, B. (2019). Greenhouse gas emissions from small-scale fly larvae composting with Hermetia illucens. Waste Management, 96, 65–74.
EU No 2017/893. (2017). Commission regulation (EU) 2017/893 of 24 May 2017 amending annexes I and IV to regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European parliament and of the council and annexes X XIV and XV to commission regulation (EU) No 142/2011 as regards the provisions and processed animal protein.
Font-Palma, C. (2019). Methods for the treatment of cattle manure-A review. Journal of Carbon Research, 5(2), 27.
Gerber, P. J., Hristov, A. N., Henderson, B., Makkar, H., Oh, J., Lee, C., et al. (2013a). Technical options for the mitigation of direct methane and nitrous oxide emissions from livestock: A review. Animal, 7(s2), 220–234.
Gerber, P. J., Mottet, A., Opio, C. I., Falcucci, A., & Teillard, F. (2015). Environmental impacts of beef production: Review of challenges and perspectives for durability. Meat Science, 109, 2–12.
Gerber, P. J., Steinfeld, H., Henderson, B., Mottet, A., Opio, C., Dijkman, J., et al. (2013). Tackling climate change through livestock: A global assessment of emissions and mitigation opportunities. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
Grossi, G., Goglio, P., Vitali, A., & Williams, A. G. (2018). Livestock and climate change: Impact of livestock on climate and mitigation strategies. Animal Frontiers, 9(1), 69–76.
Guo, G., Chen, Y., Tian, F., Gao, Z., Zhu, C., & Liu, C. (2018). Effects of livestock manure properties and temperature on the methanogen community composition and methane production during storage. Environmental Technology, 41(2), 131–140.
Guo, H., Jiang, C., Zhang, Z., Lu, W., & Wang, H. (2021). Material flow analysis and life cycle assessment of food waste bioconversion by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Science of The Total Environment, 750, 141656.
Harvey, R. J., Davis, D. D., Shishkoff, N., & Pecchia, J. (2019). Survival of lab grown Calonectria pseudonaviculata microsclerotia during small-scale composting. Compost Science & Utilization, 27(1), 24–34.
Hristov, A.N., Oh, J., Lee, C., Meinen, R., Montes, F., Ott, T., Firkins, J., Rotz, A., Dell, C., Adesogan, A., Yang, W., Tricarico, J., Kebreab, E., Waghorn, G., Dijkstra, J. & Oosting, S. (2013). Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions in livestock production – A review of technical options for non-CO2 emissions. Edited by Pierre J. Gerber, Benjamin
Hua, L., Wu, W., Liu, Y., McBride, M. B., & Chen, Y. (2009). Reduction of nitrogen loss and Cu and Zn mobility during sludge composting with bamboo charcoal amendment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16(1), 1–9.
Hwang, H. Y., Kim, S. H., Kim, M. S., Park, S. J., & Lee, C. H. (2020). Co-composting of chicken manure with organic wastes: Characterization of gases emissions and compost quality. Applied Biological Chemistry, 63(1), 1–10.
Iqbal, M. K., Shafiq, T., & Ahmed, K. (2010). Characterization of bulking agents and its effects on physical properties of compost. Bioresource Technology, 101(6), 1913–1919.
Ishak, S., & Kamari, A. (2019). Biodiesel from black soldier fly larvae grown on restaurant kitchen waste. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(2), 1143–1150.
Iwasa, M., Moki, Y., & Takahashi, J. (2015). Effects of the activity of coprophagous insects on greenhouse gas emissions from cattle dung pats and changes in amounts of nitrogen carbon and energy. Environmental Entomology, 44(1), 106–113.
Kavanagh, I., Burchill, W., Healy, M. G., Fenton, O., Krol, D. J., & Lanigan, G. J. (2019). Mitigation of ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from stored cattle slurry using acidifiers and chemical amendments. Journal of Cleaner Production, 237, 117822.
Kim, J. K., Lee, D. J., Ravindran, B., Jeong, K. H., Wong, J. W. C., Selvam, A., et al. (2017). Evaluation of integrated ammonia recovery technology and nutrient status with an in-vessel composting process for swine manure. Bioresource Technology, 245, 365–371.
Kim, S. Y., Pramanik, P., Bodelier, P. L., & Kim, P. J. (2014). Cattle manure enhances methanogens diversity and methane emissions compared to swine manure under rice paddy. PLoS One, 9(12).
Lalander, C. H., Fidjeland, J., Diener, S., Eriksson, S., & Vinnerås, B. (2015). High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 35(1), 261–271.
Lalander, C., Diener, S., Magri, M. E., Zurbrügg, C., Lindström, A., & Vinnerås, B. (2013). Faecal sludge management with the larvae of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens)—From a hygiene aspect. Science of the Total Environment, 458, 312–318.
Lalander, C., Diener, S., Zurbrügg, C., & Vinnerås, B. (2019). Effects of feedstock on larval development and process efficiency in waste treatment with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). Journal of Cleaner Production, 208, 211–219.
Li, H., & Xin, H. (2010). Lab-scale assessment of gaseous emissions from laying-hen manure storage as affected by physical and environmental factors. Transactions of the ASABE, 53(2), 593–604.
Li, Q., Zheng, L., Qiu, N., Cai, H., Tomberlin, J. K., & Yu, Z. (2011). Bioconversion of dairy manure by black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for biodiesel and sugar production. Waste Management, 31(6), 1316–1320.
Liu, C., Guo, T., Chen, Y., Meng, Q., Zhu, C., & Huang, H. (2018). Physicochemical characteristics of stored cattle manure affect methane emissions by inducing divergence of methanogens that have different interactions with bacteria. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 253, 38–47.
Liu, Q., Tomberlin, J. K., Brady, J. A., Sanford, M. R., & Yu, Z. (2008). Black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae reduce Escherichia coli in dairy manure. Environmental Entomology, 37(6), 1525–1530.
Liu, T., Awasthi, M. K., Chen, H., Duan, Y., Awasthi, S. K., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Performance of black soldier fly larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for manure composting and production of cleaner compost. Journal of environmental management, 251, 109593.
Loyon, L., Guiziou, F., & Saint Cast, P. (2008). Impact of manure management of different livestock on gaseous emissions: Laboratory study. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 48(2), 128–131.
Ly, P., Jensen, L. S., Bruun, T. B., & de Neergaard, A. (2013). Methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from the system of rice intensification (SRI) under a rain-fed lowland rice ecosystem in Cambodia. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 97(1–3), 13–27.
Ma, J., Lei, Y., Rehman, K. U., Yu, Z., Zhang, J., Li, W., et al. (2018). Dynamic effects of initial pH of substrate on biological growth and metamorphosis of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Environmental Entomology, 47(1), 159–165.
Maeda, K., Hanajima, D., Morioka, R., Toyoda, S., Yoshida, N., & Osada, T. (2013). Mitigation of greenhouse gas emission from the cattle manure composting process by use of a bulking agent. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 59(1), 96–106.
Majlessi, M., Eslami, A., Saleh, H. N., Mirshafieean, S., & Babaii, S. (2012). Vermicomposting of food waste: Assessing the stability and maturity. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 9(1), 25.
Majumdar, D., Patel, J., Bhatt, N., & Desai, P. (2006). Emission of methane and carbon dioxide and earthworm survival during composting of pharmaceutical sludge and spent mycelia. Bioresource Technology, 97(4), 648–658.
Massé, D. I., Masse, L., Claveau, S., Benchaar, C., & Thomas, O. (2008). Methane emissions from manure storages. Transactions of the ASABE, 51(5), 1775–1781.
Mathur, S. P., Owen, G., Dinel, H., & Schnitzer, M. (1993). Determination of compost biomaturity. I. Literature review. Biological Agriculture & Horticulture, 10(2), 65–85.
Maulini-Duran, C., Artola, A., Font, X., & Sánchez, A. (2014). Gaseous emissions in municipal wastes composting: Effect of the bulking agent. Bioresource Technology, 172, 260–268.
Meda, B., Hassouna, M., Aubert, C., Robin, P., & Dourmad, J. Y. (2011). Influence of rearing conditions and manure management practices on ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from poultry houses. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 67(3), 441–456.
Mertenat, A., Diener, S., & Zurbrügg, C. (2019). Black soldier fly biowaste treatment–Assessment of global warming potential. Waste Management, 84, 173–181.
Ministério da Agricultura., & Pecuária e Abastecimento. (2017). Manual de métodos analíticos oficiais para fertilizantes minerais orgânicos organominerais e corretivos. MAPA.
Miranda, C. D., Cammack, J. A., & Tomberlin, J. K. (2019). Life-history traits of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.)(Diptera: Stratiomyidae), reared on three manure types. Animals, 9(5), 281.
Miranda, C. D., Cammack, J. A., & Tomberlin, J. K. (2020). Life-history traits of house fly Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae) reared on three manure types. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 6(1), 81–90.
Miranda, C. D., Crippen, T. L., Cammack, J. A., & Tomberlin, J. K. (2021). Black soldier fly Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), and house fly Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae) larvae reduce livestock manure and possibly associated nutrients: An assessment at two scales. Environmental Pollution, 282, 116976.
Montes, F., Meinen, R., Dell, C., Rotz, A., Hristov, A. N., Oh, J., et al. (2013). Special topics—Mitigation of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from animal operations: II. A review of manure management mitigation options. Journal of animal science, 91(11), 5070–5094.
Myers, H. M., Tomberlin, J. K., Lambert, B. D., & Kattes, D. (2014). Development of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae fed dairy manure. Environmental Entomology, 37(1), 11–15.
Nguyen, T. T., Tomberlin, J. K., & Vanlaerhoven, S. (2013). Influence of resources on Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larval development. Journal of Medical Entomology, 50(4), 898–906.
Nigussie, A., Bruun, S., de Neergaard, A., & Kuyper, T. W. (2017). Earthworms change the quantity and composition of dissolved organic carbon and reduce greenhouse gas emissions during composting. Waste Management, 62, 43–51.
Noble, R., & Roberts, S. J. (2004). Eradication of plant pathogens and nematodes during composting: A review. Plant Pathology, 53(5), 548–568.
Nordentoft, S., Fischer, C., Bjerrum, L., Heckmann, L. H., & Hald, B. (2017). Reduction of Escherichia coli, Salmonella Enteritidis and Campylobacter jejuni in poultry manure by rearing of Musca domestica fly larvae. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 3(2), 145–153.
Oonincx, D. G. A. B., Van Huis, A., & Van Loon, J. J. A. (2015a). Nutrient utilisation by black soldier flies fed with chicken, pig, or cow manure. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 1(2), 131–139.
Oonincx, D. G., Van Broekhoven, S., Van Huis, A., & van Loon, J. J. (2015b). Feed conversion, survival and development, and composition of four insect species on diets composed of food by-products. PLoS One, 10(12).
Pang, W., Hou, D., Chen, J., Nowar, E. E., Li, Z., Hu, R., et al. (2020). Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing carbon and nitrogen conversion in food wastes by the black soldier fly. Journal of Environmental Management, 260, 110066.
Pardo, G., Moral, R., Aguilera, E., & del Prado, A. (2015). Gaseous emissions from management of solid waste: A systematic review. Global Change Biology, 21(3), 1313–1327.
Parodi, A., De Boer, I. J., Gerrits, W. J., Van Loon, J. J., Heetkamp, M. J., Van Schelt, J., Bolhuis, J.E., & Van Zanten, H. H. (2020). Bioconversion efficiencies, greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions during black soldier fly rearing–A mass balance approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 122488.
Parodi, A., Gerrits, W. J., Van Loon, J. J., De Boer, I. J., Aarnink, A. J., & Van Zanten, H. H. (2021). Black soldier fly reared on pig manure: Bioconversion efficiencies, nutrients in the residual material, greenhouse gas and ammonia emissions. Waste Management, 126, 674–683.
Parra-Paz, A. S., Carrejo, N. S., & Rodríguez, C. H. G. (2015). Effects of larval density and feeding rates on the bioconversion of vegetable waste using black soldier fly larvae Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Waste and Biomass Valorization, 6(6), 1059–1065.
Qasim, W., Lee, M. H., Moon, B. E., Okyere, F. G., Khan, F., Nafees, M., & Kim, H. T. (2018). Composting of chicken manure with a mixture of sawdust and wood shavings under forced aeration in a closed reactor system. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 7(3), 261–267.
Rajendran, A., Fox, T., Reis, C. R., Wilson, B., & Hu, B. (2018). Deposition of manure nutrients in a novel mycoalgae biofilm for nutrient management. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 14, 120–128.
Ravindran, B., & Mnkeni, P. N. S. (2016). Bio-optimization of the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio for efficient vermicomposting of chicken manure and waste paper using Eisenia fetida. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(17), 16965–16976.
Saggar, S., Bolan, N. S., Bhandral, R., Hedley, C. B., & Luo, J. (2004). A review of emissions of methane, ammonia, and nitrous oxide from animal excreta deposition and farm effluent application in grazed pastures. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 47(4), 513–544.
Salomone, R., Saija, G., Mondello, G., Giannetto, A., Fasulo, S., & Savastano, D. (2017). Environmental impact of food waste bioconversion by insects: Application of life cycle assessment to process using Hermetia illucens. Journal of Cleaner Production, 140, 890–905.
Sanchez Matos, J., Barberino, A. T. M. S., de Araujo, L. P., Lôbo, I. P., & de Almeida Neto, J. A. (2020). Potentials and limitations of the bioconversion of animal manure using fly larvae. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 1–24.
Santos, A., Bustamante, M. A., Tortosa, G., Moral, R., & Bernal, M. P. (2016). Gaseous emissions and process development during composting of pig slurry: The influence of the proportion of cotton gin waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 81–90.
Sefeedpari, P., Vellinga, T., Rafiee, S., Sharifi, M., Shine, P., & Pishgar-Komleh, S. H. (2019). Technical, environmental and cost-benefit assessment of manure management chain: A case study of large scale dairy farming. Journal of Cleaner Production, 233, 857–868.
Shumo, M., Khamis, F. M., Tanga, C. M., Fiaboe, K. K., Subramanian, S., Ekesi, S., et al. (2019). Influence of temperature on selected life-history traits of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) reared on two common urban organic waste streams in Kenya. Animals, 9(3), 79.
Ur Rehman, K., Cai, M., Xiao, X., Zheng, L., Wang, H., Soomro, A. A., et al. (2017a). Cellulose decomposition and larval biomass production from the co-digestion of dairy manure and chicken manure by mini-livestock (Hermetia illucens L.). Journal of Environmental Management, 196, 458–465.
Ur Rehman, K., Rehman, A., Cai, M., Zheng, L., Xiao, X., Somroo, A. A., et al. (2017b). Conversion of mixtures of dairy manure and soybean curd residue by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Journal of Cleaner Production, 154, 366–373.
Ur Rehman, K., Rehman, R. U., Somroo, A. A., Cai, M., Zheng, L., Xiao, X., et al. (2019). Enhanced bioconversion of dairy and chicken manure by the interaction of exogenous bacteria and black soldier fly larvae. Journal of Environmental Management, 237, 75–83.
van Huis, A. (2020). Insects as food and feed, a new emerging agricultural sector: A review. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 1–18.
Vasco-Correa, J., Khanal, S., Manandhar, A., & Shah, A. (2018). Anaerobic digestion for bioenergy production: Global status, environmental and techno-economic implications, and government policies. Bioresource Technology, 247, 1015–1026.
Wang, H., Wang, S., Li, H., Wang, B., Zhou, Q., Zhang, X., et al. (2016). Decomposition and humification of dissolved organic matter in swine manure during housefly larvae composting. Waste Management & Research, 34(5), 465–473.
Wang, J. Z., Hu, Z. Y., Zhou, X. Q., An, Z. Z., Gao, J. F., Liu, X. N., et al. (2012). Effects of reed straw, zeolite, and superphosphate amendments on ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from stored duck manure. Journal of Environmental Quality, 41(4), 1221–1227.
Wang, J., Hu, Z., Xu, X., Jiang, X., Zheng, B., Liu, X., et al. (2014). Emissions of ammonia and greenhouse gases during combined pre-composting and vermicomposting of duck manure. Waste Management, 34(8), 1546–1552.
Wang, X., Cui, H., Shi, J., Zhao, X., Zhao, Y., & Wei, Z. (2015). Relationship between bacterial diversity and environmental parameters during composting of different raw materials. Bioresource Technology, 198, 395–402.
Wang, X., Wang, W., Gao, Q., Wang, X., Lei, C., & Zhu, F. (2018). Chrysomya megacephala larvae feeding favourably influences manure microbiome, heavy metal stability and greenhouse gas emissions. Microbial Biotechnology, 11(3), 498–509.
Wu, J., He, S., Liang, Y., Li, G., Li, S., Chen, S., et al. (2017). Effect of phosphate additive on the nitrogen transformation during pig manure composting. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(21), 17760–17768.
Xiao, X., Mazza, L., Yu, Y., Cai, M., Zheng, L., Tomberlin, J. K., et al. (2018). Efficient co-conversion process of chicken manure into protein feed and organic fertilizer by Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae and functional bacteria. Journal of Environmental Management, 217, 668–676.
Yang, F., Li, G. X., Yang, Q. Y., & Luo, W. H. (2013). Effect of bulking agents on maturity and gaseous emissions during kitchen waste composting. Chemosphere, 93(7), 1393–1399.
Zhang, X., Zhang, J., Jiang, L., Yu, X., Zhu, H., Zhang, J., et al. (2021). Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae significantly change the microbial community in chicken manure. Current Microbiology, 78(1), 303–315.
Zhou, F., Tomberlin, J. K., Zheng, L., Yu, Z., & Zhang, J. (2013). Developmental and waste reduction plasticity of three black soldier fly strains (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) raised on different livestock manures. Journal of Medical Entomology, 50(6), 1224–1230.
Zhu, F. X., Wang, W. P., Hong, C. L., Feng, M. G., Xue, Z. Y., Chen, X. Y., et al. (2012). Rapid production of maggots as feed supplement and organic fertilizer by the two-stage composting of pig manure. Bioresource Technology, 116, 485–491.
Zhu, F. X., Yao, Y. L., Wang, S. J., Du, R. G., Wang, W. P., Chen, X. Y., et al. (2015). Housefly maggot-treated composting as sustainable option for pig manure management. Waste Management, 35, 62–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matos, J.S., de Aráujo, L.P., Allaman, I.B. et al. Evaluation of the reduction of methane emission in swine and bovine manure treated with black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Environ Monit Assess 193, 480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09252-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09252-2