Abstract
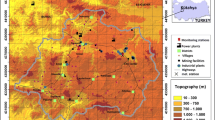
In this study, SO2 dispersion over İzmit Gulf is simulated by California Puff (CALPUFF) model for three air pollution cases, which occurred on January 28, February 12, and February 26, 1997. These days are generally characterized by dominant high-pressure systems – pressure values reaching 1032 mb, low wind speeds and sometimes calm conditions, and low temperatures with a minimum of 0°C. Hourly simulations during those critical cases were carried out and results revealed very high concentrations of SO2 transported to the downwind regions of Tüpraş and Gebze, and values sometimes exceeded 1,000 μg/m3. Nighttime and morning simulations associated with inversion produced considerably higher values of SO2 than the afternoon simulations associated with breeze. Model verification was conducted by comparing the measured daily average values of eight stations with the model predicted values at the same receptor points. Results showed that the model well predicted the values at station Gebze in all three cases. The model sometimes underestimated and sometimes overestimated the concentrations at other receptor stations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anbar, A., Saka, K., & Kupcu, M. (2003). Modeling air pollution dispersion by RIMPUFF over Gebze Kocaeli region, Graduation thesis, Marmara University, Istanbul.
Barna, M. G., & Gimson, N. R. (2002). Dispersion modelling of a wintertime particulate pollution episode in Christchurch, New Zealand. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 3531–3544.
Chang, J. C., Franzese, P., Chayantrakom, K., & Hanna, S. R. (2003). Evaluations of CALPUFF, HPAC, and VLSTRACK with two mesoscale field datasets. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 42, 453–466.
Cohen, J., Cook, R., Bailey, C. R., & Carr, E. (2005). Relationship between motor vehicle emissions of hazardous pollutants, roadway proximity, and ambient concentrations in Portland, Oregon. Environmental Modelling & Software, 20, 7–12.
Elbir, T. (2004). A GIS based decision support system for estimation, visualization and analysis of air pollution for large Turkish cities. Atmospheric Environment, 38, 4509–4517.
Gürcan, T. (2002). A study on preparing an emission inventory for Gebze–Kocaeli industrial region. Graduation thesis, Marmara University, Istanbul.
Jiang, G., Lamb, B., & Westberg, H. (2003). Using back trajectories and process analysis to investigate photochemical ozone production in the Puget Sound region. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 1489–1502.
Levy, J. I., Greco, S. L., & Spengler, J. D. (2002). The importance of population susceptibility for air pollution risk assessment: A case study of power plants, Washington, DC. Environmental Health Perspectives, 110, 1253–1260.
Levy, J. I., Spengler, J. D., Hlinka, D., Sullivan, D., & Moon, D. (2002). Using CALPUFF to evaluate the impacts of power plant emissions in Illinois: Model sensitivity and implications. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 1063–1075.
Lopez, M. T., Zuk, M., Garibay, V., Tzintzun, G., Iniestra, R., & Fernandez, A. (2005). Health impacts from power plant emissions in Mexico. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 1199–1209.
Scire, J. S., Robe F. R., Fernau, M. E., & Yarmartino, R. J. (2000). A User’s Guide for the CALMET Meteorological Model (Version 5). Concord, MA: Earth Tech Inc., 332 pp.
Scire, J. S., Strimaitis, D. G., & Yarmartino, R. J. (2000). A User’s Guide for the CALPUFF Dispersion Model (Version 5.0). Concord, MA: Earth Tech Inc., 521 pp.
Villasenor, R., Lopez-Villegas, M. T., Eidels-Dubovoi, S., Quintanar, A., & Gallardo, J. C. (2003). A mesoscale modeling study of wind blown dust on the Mexico City Basin. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 2451–2462.
Zhou, Y., Levy, J. I., Hammitt, J. K., & Evans, J. S. (2003). Estimating population exposure to power plant emissions using CALPUFF: A case study in Beijing, China. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 815–826.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tayanç, M., Berçin, A. SO2 modeling in İzmit Gulf, Turkey during the winter of 1997: 3 cases. Environ Model Assess 12, 119–129 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-006-9056-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-006-9056-4