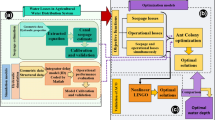
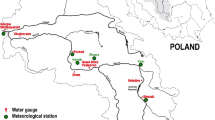
Abstract
The systematic and integrative approach to optimum watershed management couples a watershed simulation model and an efficient optimization algorithm for evaluating great number of “what if” scenarios in the search domain. This study integrates a multi-objective Non-dominated Archiving Ant Colony Optimization (NA-ACO) algorithm as an optimization tool with Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) as the simulation module for optimum management of total suspended solids (TSS) loading to downstream water bodies. The resulting NA-ACO–SWAT model is computationally and experimentally expensive because of the large number of required function evaluations which demands repetitive execution of SWAT simulation model. To increase the computational efficiency of the watershed simulation model, the SWAT model is replaced by a trained artificial neural network (ANN) model to form a hybrid NA-ACO–SWAT–ANN model to efficiently develop the set of optimum non-dominated solutions for configuration and design of detention ponds in basin scale. The applicability of the proposed method is evaluated at Gharesou watershed in the northwest of Iran. The outcomes of the proposed approach is further analyzed and compared in terms of their quality of solutions and computational efficiencies. Results show that the proposed hybrid approach may reduce the computational time by 90 % while keeping the accuracy of the results in the same order.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour, K. C., Schulin, R., & Genuchten, M. T. V. (2001). Estimating unsaturated soil hydraulic parameters using ant colony optimization. Advances in Water Resources, 24(8), 827–841.
Abbaspour, K. C., Yang, J., Maximov, I., Siber, R., Bogner, K., Mieleitner, J., Zobrist, J., & Srinivasan, R. (2007). Modelling hydrology and water quality in the pre‐alpine/alpine thur watershed using SWAT. Journal of Hydrology, 333(2–4), 413–430.
Afshar, M. H., Afshar, A., Marino, M. A., & Darbandi, A. A. S. (2006). Hydrograph-based storm sewer design optimization by genetic algorithm. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 33(3), 319–325.
Afshar, M. H., & Marino, M. A. (2006). Application of an ant algorithm for layout optimization of tree networks. Engineering Optimization, 38(3), 353–369.
Afshar, A., Sharifi, F., & Jalali, M. R. (2009). Non-dominated archiving multi-colony ant algorithm for multi-objective optimization: application to multi-purpose reservoir operation. Engineering Optimization, 41(4), 313–325.
Afshar, A., & Kazemi, H. (2012). Multi objective calibration of large scaled water quality model using a hybrid particle swarm optimization and neural network algorithm. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Environmental Engineering, 16(6), 913–918.
Arabi, M., Govindaraju, R. S., Hantush, M. M., & Engel, B. A. (2006). Role of watershed subdivision on modeling the effectiveness of best management practices with SWAT. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 42(2), 513–528.
Arnold, J. G., Srinisvan, R., Muttiah, R. S., & Williams, J. R. (1998). Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment, part I: model development. Journal of American Water Resource Association, 34(1), 73–89.
Back, A. D., & Trappenberg, T. P. (2001). Selecting inputs for modeling using normalized higher order statistics and independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions in Neural Networks, 12(3), 612–617.
Baran, B., Schaerer M., (2003). A multi-objective ant colony system for vehicle routing problem with time windows. Twenty first IASTED International Conference on Applied Informatics, Insbruck, Austria, February 10–13, pp. 97–102.
Barton, R. R., (1998). SIMULATION METAMODELS. Proceedings of the 1998 Winter Simulation Conference, Medeiros, D.J., Watson, E.F., Carson, J.S., and Manivannan, M.S. as editors. pp. 167–174.
Bozorg Haddad, O., Afshar, A., & Marino, M. A. (2006). Honey-bees mating optimization (HBMO) algorithm: a new heuristic approach for water resources optimization. Water Resources Management, 20(5), 661–680.
Bracmort, K. S., Arabi, M., Frankenberger, J. R., Engel, B. A., & Arnold, J. G. (2006). Modeling long‐term water quality impact of structural BMPs. Transactions American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 49(2), 367–374.
Broad, D., Dandy, G. C., & Maier, H. R. (2005). Water distribution systems optimization using metamodels. Water Resources Planning and Management, ASCE, 131(3), 172–180.
Chu, T. W., & Shirmohammadi, A. (2004). Evaluation of the SWAT model’s hydrology component in the piedmont physiographic region of Maryland. Transaction of ASAE, 47(4), 1057–1073.
Deb, K. (2001). Multi objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms. New York: Wiley.
Demirel, M. C., Venancio, A., & Kahya, E. (2009). Flow forecast by SWAT model and ANN in pracana basin, Portugal. Advances in Engineering Software, 40(7), 467–473.
Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V., & Colorni, A. (1996). The ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating ants. IEEE Transaction on System Management Cybernetics, 26(1), 29–41.
Doerner, K., Gutjahr, W. J., Hartl, R. F., Strauss, C., & Stummer, C. (2004). Pareto ant colony optimization: a meta-heuristic approach to multi-objective portfolio selection. Annals of Operations Research, 131(1–4), 79–99.
Elliot, A. H. (1998). Model for preliminary catchment scale planning of urban storm water quality controls. Journal of Environmental Management, 52(3), 273–288.
Gassman, P. W., Reyes, M. R., Green, C. H., & Arnold, J. G. (2007). The soil and water assessment tool: historical development, applications and future research directions. Invited Review Series, American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 50(4), 364–381.
Harrell, L. J., & Ranjithan, S. R. (2003). Detention pond design and land Use planning for watershed management. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 129(2), 98–106.
Jalali, M. R., Afshar, A., & Marino, M. A. (2007). Multi-colony ant algorithm for continuous multi-reservoir operation optimization problem. Water Resources Management, 21(9), 1429–1447.
Johnson, V. M., & Rogers, L. L. (2000). Accuracy of neural network approximators in simulation-optimization. Water Resources Planning and Management, ASCE, 126(2), 48–56.
Karamouz, M., Taheriyoun, M., Baghvand, A., Tavakolifar, H., & Emami, F. (2010). Optimization of watershed control strategies for reservoir eutrophication management. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 136(12), 847–861.
Kaini, P., Artita, K., & Nicklow, J. W., (2009). Generating different scenarios of BMP designs in a watershed scale by combining NSGA-II with SWAT. World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2009: Great Rivers, ASCE.,1-9.
Kaur, R., Singh, O., Srinivasan, R., Das, S. N., & Mishra, K. (2004). Comparison of a subjective and a physical approach for identification of priority areas for soil and water management in a watershed: a case study of Nagwan watershed in Hazaribagh District of Jharkhand, India. Environmental Modelling and Assessment, 9(2), 115–127.
Madadgar, S., & Afshar, A. (2009). An improved continuous Ant algorithm for optimization of water resources problems. Water Resources Management, 23(10), 2119–2139.
Maier, H. R., Simpson, A. R., Zecchin, A. C., Foong, W. K., Phang, K. Y., Seah, H. Y., & Tan, C. L. (2003). Ant colony optimization for the design of water distribution systems. Journal of Water Resources and Planning Management, 129(3), 200–209.
Mousavi, S. J., Ponnambalam, K., & Karray, F. (2007). Inferring operating rules for reservoir operation using fuzzy regression and ANFIS. Fuzzy Sets Systems, 158(10), 1064–1082.
Ostadrahimi, L., Marino, M. A., & Afshar, A. (2012). Multi-reservoir operation rules: multi-swarm PSO-based optimization approach. Water Resources Management, 26(2), 407–427.
Qi, H., & Altinakar, M. S. (2011). A conceptual framework of agricultural land use planning with BMP for integrated watershed management. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(1), 149–55.
Qi, H., & Altinakar, M. S. (2011). Vegetation buffer strips design using an optimization approach for Non-point source pollutant control, of an agricultural watershed. Water Resources Management, 25(2), 565–578.
Ranjithan, S., Eheart, J. W., & Garrett, J. H. (1993). Neural network based screening for groundwater reclamation uncertainty. Water Resources Research, 29(3), 563–574.
Rogers, L. L., & Dowla, F. U. (1994). Optimization of groundwater remediation using artificial neural networks with parallel solute transport modeling. Water Resources Research, 30(2), 457–481.
Rostamian, R., Jaleh, A., Afyuni, M., Mousavi, S. F., Heidarpour, M., Jalalian, A., & Abbaspour, K. C. (2008). Application of a SWAT model for estimating runoff and sediment in two mountainous basins in central Iran. Hydrological Sciences-Journal, 53(5), 977–988.
Sadeghi, S., (2010). Identifying and prioritizing causing erosion areas in the Gharesou Watershed. M.S. Dissertation, Department of civil engineering of Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch, Iran, Tehran.
Santhi, C., Arnold, J. G., Williams, J. R., Dugas, W. A., Srinivasn, R., & Hauck, L. M. (2001). Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 37(5), 1169–1188.
Santhi, C., Srinivasan, R., Arnold, J. G., & Williams, J. R. (2006). A modeling approach to evaluate the impacts of water quality management plans implemented in a watershed in Texas. Environmental Modelling and Software, 21(8), 1141–1157.
Shepherd, B., Harper, D., & Millington, A. (1999). Modeling catchment-scale nutrient transport to watercourses in the UK. Hydrobiologia, 395–396, 227–238.
Shourian, M., Mousavi, S. J., Menhaj, M., & Jabbari, E. (2008). Neural network‐based simulation optimization model for optimal water allocation planning at basin scale. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 10(4), 331–343.
Sindelar, R., & Babuska, R. (2004). Input selection for nonlinear regression models. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 12(5), 688–696.
Emami Skardi, M. J., (2011). Design of detention ponds for watersheds, using ant colony algorithm (AC) and SWAT model; a cooperative game theory approach, MS Dissertation, Afshar, A., as Advisor, Iran University of Science and Technology.
Skardi, M. J., Afshar, A., & Sandoval Solis, S. (2013). Simulation-optimization model for Non-point source pollution management in watersheds: application of cooperative game theory. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 17(6), 1232–1240.
Smith, J., & Eli, R. N. (1995). Neural network models for rainfall runoff Process. Water Resources Planning and Management, ASCE, 121(6), 499–508.
Spruill, C. A., Workman, S. R., & Taraba, J. L. (2000). Simulation of daily and monthly stream discharge from small watersheds using the SWAT model. Transaction of ASAE, 43(6), 1431–1439.
Sureerattanan, S., & Phein, H. N., (1997). Back propagation networks for daily stream flow forecasting. Water Resources Research, C/195, 1–7.
Tolson, B. A., & Shoemaker, C. A., (2004). Watershed modeling of the Cannonsville Basin using SWAT2000: model development, calibration and validation for the prediction of flow, sediment and phosphorus transport to the Cannonsville Reservoir. Technical Report, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Cornell University., Ithaca, N. Y.
Vaché, K. B., Eilers, J. M., & Santelman, M. V. (2002). Water quality modeling of alternative agricultural scenarios in the U.S. Corn Belt. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 38(2), 773–787.
Wagner, B. J. (1995). Sampling design methods for groundwater modeling under uncertainty. Water Resources Research, 31(10), 2581–2591.
Wang, G. G., & Shan, S. (2006). Review of meta‐modeling techniques in support of engineering design optimization. Journal of Mechanical Design, 76(5), 34–56.
Yan, S., & Minsker, B., (2006). Optimal groundwater remediation design using an adaptive neural network genetic algorithm. Water Resources Research, 42(5), 1–14. W05407.
Zecchin, A. C., Maier, H. R., Simpson, A. R., Roberts, A. J., Berrisford, M. J., & Leonard, M., 2003. Max-min ant system applied to water distribution system optimization. International Congress on Modeling Simulation (MODSIM), Vol. 2, Townsville, Australia, pp. 795–800.
Zhang, X., Srinivasan, R., Debele, B., & Hao, F. (2008). Runoff simulation of the headwaters of the yellow river using the swat model with three snowmelt algorithms. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 44(1), 48–61.
Zhang, X., Srinivasan, R., & Van Liew, M. (2009). Approximating SWAT model using artificial neural network and support vector machine. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 45(2), 460–474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emami Skardi, M.J., Afshar, A., Saadatpour, M. et al. Hybrid ACO–ANN-Based Multi-objective Simulation–Optimization Model for Pollutant Load Control at Basin Scale. Environ Model Assess 20, 29–39 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-014-9413-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-014-9413-7