Abstract
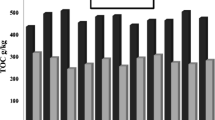
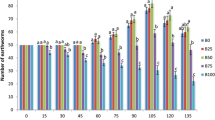
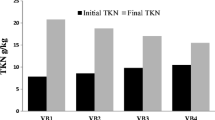
In India, millions of tones of livestock excreta are produced. Our study explores the potential of an epigeic earthworm Eisenia foetida to compost different livestock excreta (cow, buffalo, horse, donkey, sheep, goat and camel) into value added product (vermicompost) at the laboratory scale. Vermicomposting resulted in lowering of pH, electrical conductivity, potassium and C:N ratio and increase in nitrogen and phosphorus contents. Total K was lower in the final cast than in the initial feed. C:N ratios of the vermicomposts ranged from 16.2 ± 2.17 to 75.4 ± 6.84. Microbial activity measured as dehydrogenase activity in buffalo, donkey and camel wastes increased with time up to day 90. But in sheep and goat wastes, maximum dehydrogenase activity was recorded on day 60 and decreased thereafter. The cocoons and hatchlings production by Eisenia foetida in different excreta were also investigated. The greatest number and biomass of hatchlings was recorded in horse excreta followed by cow, goat and sheep excreta. Thus, cow, horse, sheep and goat excreta show potential as good substrates in vermicomposting using Eisenia foetida, although further research is required to explore the feasibility of use of buffalo, donkey and camel excreta in combination with cow/sheep/goat excreta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atiyeh, R.M., Dominguez, J., Subler, S., and Edwards, C.A.: 2000, ‘Changes in Biochemical Properties of Cow Manure During Processing by Earthworms (Eisenia andrei Bouche) and the Effects on Seedling Growth,’ Pedobiologia, 44, 709–724.
Bansal, S. and Kapoor, K.K.: 2000, ‘Vermicomposting of Crop Residues and Cattle Dung with Eisenia foetida,’ Biores. Technol. 73, 95–98.
Benitez, E., Nogales, R., Elvira, C., Masciandaro, G., and Ceccanti, B.: 1999, ‘Enzyme Activities as Indicators of the Stabilization of Sewage Sludge Composting with Eisenia foetida,’ Biores. Technol. 67, 297–303.
Bremner, J.M. and Mulvaney, R.G.: 1982, ‘Nitrogen Total,’ in: A.L. Page, R.H. Miller, and D.R. Keeney, (eds.), Method of Soil Analysis, American Society of agronomy, Madison, pp. 575–624.
Casida Jr., L.E., Klevin, D.A., and Santoro, T.: 1964, ‘Soil Dehydrogenase Activity,’ Soil Sci. 93, 371–376.
Chan, L.P.S. and Griffiths, D.A.: 1988, ‘The Vermicomposting of Pre-Treated Pig Manure,’ Biol. Wastes 24, 57– 69.
Crawford, J.H.: 1983, ‘Review of Composting,’ Process Biochem. 18, 14–15.
Delgado, M., Bigeriego, M., Walter, I., and Calbo, R.: 1995, ‘Use of California Red Worm in Sewage Sludge Transformation,’ Turrialba 45, 33–41.
Datar, M.T., Rao, M.N., and Reddy, S.: 1997, ‘Vermicomposting- a Technological Option for Solid Waste Management’, J. Solid Waste Technol. Mgt. 24(2), 89–93.
Diaz-Burgos, M.A., Ceccanti, B., and Polo, A.: 1992, ‘Monitoring Biochemical Activity during Sewage Sludge Composting,’ Biol. Fertil. Soil 16, 145–150.
Edwards, C.A.: 1988, ‘Breakdown of Animal, Vegetable and Industrial Organic Wastes by Earthworms’, in: C.A. Edwards and E.F. Neuhauser (eds.), Earthworms in Waste and Environmental Management, SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, pp. 21–31.
Edwards, C.A., Dominguez, J., and Neuhauser, E.F.: 1998, ‘Growth and Reproduction of Parionyx excavatus (Perr.) (Megascolecidae) as Factors in Organic Waste Management’, Biol. Fertil. Soils 27, 155–161.
Edwards, C.A. and Lofty, J.R.: 1972, Biology of Earthworms, Chapman and Hall, London.
Elvira, C., Sampedro, L., Benitez, E., and Nogales, R.: 1998, ‘Vermicomposting of Sludges from Paper Mill and Dairy Industries with Eisenia andrei: A Pilot Scale Study,’ Biores. Technol. 63, 205-211.
Garcia, C. Hernandez, T., and Costa, F.: 1997, ‘Potential use of Dehydrogenase Activity as an Index of Microbial Activity in Degraded Soils,’ Commun. Soil Sci. Plant An. 28, 123–134.
Ghosh, M., Chattopadhyay, G.N., and Baral, K.: 1999, ‘Transformation of Phosphorus During Vermicomposting,’ Biores. Technol. 69, 149–154.
Gunadi, B. and Edwards, C.A.: 2003, ‘The Effect of Multiple Applications of Different Organic Wastes on the Growth, Fecundity and Survival of Eisenia foetida (Savigny) (Lumbricidae),’ Pedobiologia 47(4), 321–330.
Hartenstein, R.: 1981, ‘Production of Earthworms as a Potentially Economic Source of Protein,’ Biotechnol. Bioengg. 23, 1797–1811.
Hartenstein, R. and Hartenstein, F.: 1981, ‘Physico-Chemical Changes Affected in Activated Sludge by the Earthworm Eisenia foetida,’ J. Environ. Quality 10, 377–382.
Hartenstein, R., Neuhauser, E.F., and Kaplan, D.L.: 1979, ‘Reproductive Potential of the Earthworm Eisenia foetida’, Oecologia 43, 329–340
Kale, R.D., Bano, K., and Krishnamoorthy, R.V.: 1982, ‘Potential of Perionyx excavatus for Utilization of Organic Wastes,’ Pedobiologia 23, 419–425.
Kale, R.D.: 2000, ‘An Evaluation of the Vermitechnology Process for the Treatment of Agro, Sugar and Food Processing Wastes,’ Technology Appreciation Programme on Evaluation of Biotechnological Approaches to Waste Management held on 26th October, 2000. Industrial Association-Ship of IIT, Madras, 15–17.
Kaviraj and Sharma, S.: 2003, ‘Municipal Solid Waste Management Through Vermicomposting Employing Exotic and Local Species of Earthworms,’ Biores. Technol 90, 169–173.
Kemppainnen, E.: 1989, ‘Nutrient Content and Fertilizer Value of Live Stick Manure with Special Reference to Cow Manure,’ Ann. Agric. Fenn. 28, 163–284.
Levi-Minzi, R., Riffaldi, R., and Saviozzi, A.: 1986, ‘Organic Matter and Nutrients in Fresh and Mature Farmyard Manure,’ Agricul. Wastes 16, 225–236.
Loh, T.C., Lee, Y.C., Liang, J.B., and Tan, D.: 2004, ‘Vermicomposting of Cattle and Goat Manures by Eisenia foetida and their Growth and Reproduction Performance,’ Biores. Technol. 96, 111–114.
Mitchell, A.: 1997, ‘Production of Eisenia foetida and Vermicompost from Feedlot Cattle Manure,’ Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 763–766.
Ndegwa, P.M. and Thompson, S.A.: 2001, ‘Integrating Composting and Vermicomposting the Treatment and Bioconversion of Biosolids,’ Biores. Technol. 76, 107–112.
Ndegwa, P.M., Thompson, S.A., and Das, K.C.: 2000, ‘Effects of Stocking Sensity and Feeding Rate on Vermicomposting of Biosolids,’ Biores. Technol. 71, 5–12.
Nelson, D.W. and Sommers, L.E.: 1982, ‘Total Carbon and Organic Carbon and Organic Matter,’ in: A.L. Page, R.H. Miller and D.R. Keeney (eds.), Method of Soil Analysis, American Society of agronomy, Madison, pp. 539–579.
Orozco, F.H., Cegarra, J., Trujillo, L.M., and Roig, A.: 1996, ‘Vermicomposting of Coffee Pulp using the Earthworm Eisenia foetida: Effects on C and N Contents and the Availability of Nutrients,’ Biol. Fertil. Soil 22, 162–166.
Reinecke, A.J., Viljoen, S.A., and Saayman, R.J.: 1992, ‘The Suitability of Eudrilus eugeniae, Perionyx excavatus and Eisenia foetida (Oligochaeta) for Vermicomposting in Southern Africa in Terms of their Temperature Requirements,’ Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 1295–1307.
Sabine, J.R.: 1978, ‘The Nutritive Value of Earthworm Meals,’ in: R. Hartenstein (ed.), Utilization of soil organisms in sludge management, Syracuse, State University of New York, pp. 122–130.
Senapati, B.K., Dash, M.C., Rane, A.K., and Panda, B.K.: 1980, ‘Observation on the Effect of Earthworms in the Decomposition Process in Soil Under Laboratory Conditions,’ Comp. Physiol. Ecol. 5, 140–142.
Satchell, J.E. and Martin, K.: 1984, ‘Phosphate Activity in Earthworm Faeces,’ Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 191–194.
Senesi, N.: 1989, ‘Composted Materials as Organic Fertilizers,’ The Sci. Total Environ. 81/82, 521–524.
Tomati, U., Grappelli, A., and Gallii, E.: 1987, ‘The Presence of Growth Regulators in Earthworm-Worked Wastes,’ in: Proceedings of International Symposium on Earthworms, A.M. Bonvicini Paglioi and P. Omodeo (eds.), Unione Zoologica Italiana, 2, Mucchi, Modena, pp. 423–435.
Trevors, J.T.: 1984, ‘Dehydrogenase Activity in Soil,’ A Comparison Between the INT and TTC assay,’ Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 673–674.
Tripathi, G. and Bhardwaj, P.: 2004, ‘Comparative Studies on Biomass Production, Life Cycles and Composting Efficiency of Eisenia foetida (Savigny) and Lampito mauritii (Kinberg),’ Biores Technol. 92, 275–283.
Viel, M., Sayag, D., and Andre, L.: 1987, ‘Optimization of Agricultural, Industrial Waste Management through In-vessel Composting,’ in: M. de Bertoldi, (ed.), Compost: Production, Quality and Use. Elseiver Appl. Sci. Essex, pp. 230–237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, V.K., Yadav, Y.K., Sheoran, A. et al. Livestock excreta management through vermicomposting using an epigeic earthworm Eisenia foetida . Environmentalist 26, 269–276 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-006-8641-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-006-8641-z