Abstract
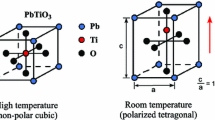
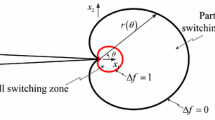
In this paper Mode I steady state crack growth in single crystal ferroelectric materials is investigated. Specifically, the fracture toughness enhancement due to domain switching near a steadily growing crack tip is analyzed. For this purpose, an incremental phenomenological constitutive law for single crystal ferroelectric materials is implemented within a finite element model to calculate the stress and remanent strain fields around the crack tip. Also, the ratio of the far field applied energy release rate to the crack tip energy release rate, i.e. the toughening, is calculated. The numerical computations are carried out for single crystal ferroelectric materials of tetragonal or rhombohedral structure with different switching hardening and irreversible remanent strain levels. Toughening levels for crack growth along different crystallographic directions and planes are obtained and compared. Results from numerical computations for the toughening anisotropy for both tetragonal and rhombohedral crystals are presented and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dean RH, Hutchinson JW (1980) Quasi-static steady crack growth in small scale yielding. In: Fracture mechanics, ASTM-STP 700, pp 383–405
Huber JE, Fleck NA, Landis CM, McMeeking RM (1999) A constitutive model for ferroelectric polycrystals. J Mech Phys Solids 47:1663–1697
Hutchinson JW (1974) On steady quasi-static crack growth. Harvard University Report, Division of Applied Sciences, DEAP S–8
Kreher WS (2002) Influence of domain switching zones on the fracture toughness of ferroelectrics. J Mech Phys Solids 50:1029–1050
Landis CM, McMeeking RM (1999) A phenomenological constitutive law for ferroelastic switching and a resulting asymptotic crack tip solution. J Intell Mater Systems Struct 10:155–163
Landis CM (2002) Uncoupled, asymmetric mode III and mode E crack tip solutions in non-linear ferroelectric materials. Eng Fract Mech 69:13–23
Landis CM (2003) On the fracture toughness of ferroelastic materials. J Mech Phys Solids 51:1347–1369
Landis CM (2004a) On the fracture toughness anisotropy of mechanically poled ferroelectric ceramics. Int J Fract 126:1–16
Landis CM (2004b) Energetically consistent boundary conditions for electromechanical fracture. Int J Solids Struct 41:6291–6315
Li FZ, Shih CF, Needleman A (1985) A comparison of methods for calculating energy release rates. Eng Fract Mech 21:405–421
Reece MJ, Guiu F (2002) Toughening produced by crack-tip-stress-induced domain reorientation in ferroelectric and/or ferroelastic materials. Philos Mag A 82:29–38
Wang J, Landis CM (2004) On the fracture toughness of ferroelectric ceramics with electric field applied parallel to the crack front. Acta Mater 52:3435–3446
Wang J, Landis CM (2006) Domain switch toughening in polycrystalline ferroelectrics. J Mater Res 21:13–20
Yang W, Zhu T (1998) Switching toughening of ferroelectrics subjected to electric fields. J Mech Phys Solids 46:291–311
Zhu T, Yang W (1997) Toughness variation of ferroelectrics by polarization switch under non-uniform electric field. Acta Mater 45:4659–4702
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, J., Landis, C.M. Toughening due to domain switching in single crystal ferroelectric materials. Int J Fract 143, 161–175 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-007-9056-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-007-9056-7