Abstract
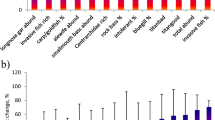
A number of biological approaches are commonly used to assess the ecological integrity of stream ecosystems. Recently, it is becoming increasingly common to use multiple organism groups in bioassessment. Advocates of the multiple organism approach argue that the use of different organism groups should strengthen inference-based models and ultimately result in lower assessment error, while opponents argue that organism groups often respond similarly to stress implying a high degree of redundancy. Using fish, macroinvertebrate, macrophyte and benthic diatom data, site-specific parameters (e.g., water chemistry and substratum) and catchment variables from European mountain (n = 77) and lowland (n = 85) streams we evaluated the discriminatory power and uncertainty associated with the use of a number of biological metrics commonly used in stream assessment. The primary environmental gradient for both streams types was land use and nutrient enrichment. Secondary and tertiary gradients were related to habitat quality or alterations in hydromorphology. Benthic diatom and macroinvertebrate metrics showed high discriminatory power (R2 values often >0.50) and low error (<30%) with the primary (nutrient) gradient, while both fish and macrophyte metrics performed relatively poorly. Conversely, both fish and macrophyte metrics showed higher response (high coefficients of determination) than either benthic diatom or macroinvertebrate metrics to the second (e.g., alteration in habitat/hydromorphology) gradient. However, the discriminatory power and error associated with individual metrics varied markedly, indicating that caution should be exercised when selecting the ‘best’ organism group or metric to monitor stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. D. Allan (1995) Stream Ecology. Structure and Function Of Running Waters Chapman and Hall London
P. D. Armitage D. Moss J. F. Wright M. T. Furse (1983) ArticleTitleThe performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites Water Research 17 333–347 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhtFegtLY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(83)90188-4
M. B. Bain J. T. Finn H. E. Booke (1988) ArticleTitleStreamflow regulation and fish community structure Ecology 69 382–392 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1940436
R. W. Battarbee R. J. Flower S. Juggins S. T. Patrick A. C. Stevenson (1997) ArticleTitleThe relationship between diatoms and surface water quality in the Hoylandet area of Nord-Trondelag, Norway Hydrobiologia 348 69–80 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtFait7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003085116632
A. Buffagni (1997) Mayfly community composition and the biological quality of streams P. Landolt M. Sartori (Eds) Ephemeroptera & Plecoptera: Biology-Ecology-Systematics MTL Fribourg 235–246
A. Buffagni (1999) ArticleTitlePregio naturalistico, qualità ecologica e integrità della comunità degli Efemerotteri. Un indice per la classificazione dei fiumi italiani Acqua & Aria 8 99–107
A. Buffagni S. Erba M. Cazzola J. L. Kemp (2004) ArticleTitleThe AQEM multimetric system for the southern Italian Apennines: assessing the impact of water quality and habitat degradation on pool macroinvertebrates in Mediterranean rivers Hydrobiologia 516 313–329 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025273.15958.6a
CEMAGREF, 1982. Etude des méthodes biologiques d’appréciation quantitative de la qualité des eaux. Rapport Q. E. Lyon A. F. Bassin Rhône-Méditérannée-Corse, 218 pp
E. Coring (1999) Situation and developments of algal (diatom)-based techniques for monitoring rivers in Germany J. Prygiel B. A. Whitton J. Bukowska (Eds) Use of Algae for Monitoring Rivers III Agence de l’Eau Artois-Picardie Douai 122–127
Dell’Uomo, A., 1996. Assessment of water quality of an Apennine river as a pilot study for diatom-based monitoring of Italian watercourses. In Whtitton, B. A. & E. Rott (eds), Use of Algae for Monitoring Rivers II, Institut für Botanik, Universität Innsbruck, 65–72
J. P. Descy M. Coste (1990) Utilisation des diatomées benthiques pour l’évaluation de la qualité des eaux courantes Rapport final, UNECED Namur, Cemagref, Bordeaux
H. Ellenberg H. E. Weber R. Düll V. Wirth W. Werner D. Paulißen (1992) ArticleTitleZeigerwerte von Pflanzen in Mitteleuropa Scripta Geobotanica 18 1–257
G. Englund (1997) ArticleTitleImportance of spatial scale and prey movements in predator caging experiments Ecology 78 2316–2325 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2265894
European Commission, 2000. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council – Establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Brussels, Belgium, 23 October 2000
L.S. Fore J. R. Karr R. W. Wisseman (1996) ArticleTitleAssessing invertebrate responses to human activities: evaluating alternative approaches Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15 212–231 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1467949
Furse, M. T., A. Schmidt-Kloiber, J. Strackbein, J. Davy-Bowker, A. Lorenz, J. van der Molen & P. Scarlett, 2004. Results of the sampling programme. A report to the European Commission. Framework V Project STAR (EVK1-CT-2001_00089)
O. T. Gorman J. R. Karr (1978) ArticleTitleHabitat structure and stream fish communities Ecology 59 507–515 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1936581
J. Haury M. C. Peltre M. Tremolieres J. Barbe G. Thiebaut I. Berne H. Daniel P. Chatenet S. Muller A. Dutartre C. Laplace-Treyture A. Cazaubon E. Lambert-Servien (2002) A method involving macrophytes to assess water trophy and organic pollution: the Macrophyte Biological Index for Rivers (IBMR) – application to different types of rivers and pollutions A. Dutartre M. H. Montel (Eds) Proceedings 11th EWRS Internat. Symp. Aquatic Weeds Moliets Et Maa France 247–250
D. Hering C. Meier C. Rawer-Jost C. K. Feld R. Biss A. Zenker A. Sundermann S. Lohse J. Böhmer (2004) ArticleTitleAssessing streams in Germany with benthic invertebrates: selection of candidate metrics Limnologica 34 398–415
Hering, D. & J. Strackbein, 2002. STAR stream types and sampling sites. A report to the European Commission. Framework V Project STAR (EVK1-CT-2001_00089)
A. G. Hildrew G. Woodward J. H. Winterbottom S. Orton (2004) ArticleTitleStrong density dependence in a predatory insect: large-scale experiments in a stream Journal of Animal Ecology 73 447–458 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0021-8790.2004.00819.x
H. Hirst I. Jüttern S. J. Ormerod (2002) ArticleTitleComparing the responses of diatoms and macroinvertebrates to metals in upland streams of Wales and Cornwall Freshwater Biology 47 1752–1765 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvVSrt7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00904.x
Hoffmann, G., 1999. Trophiebewertung von Seen anhand von Aufwuchsdiatomeen. Von Tümpling, W. & G. Friedrich (eds), Biologische Gewässeruntersuchung, 2. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena: 319–333
N. T. H. Holmes J. R. Newman S. Chadd K. J. Rouen L. Saint F. H. Dawson (1999) Mean Trophic Rank: A users manual R&D Technical Report No. E 38, Environment Agency Bristol, UK
R. K. Johnson (1998) ArticleTitleSpatio-temporal variability of temperate lake macroinvertebrate communities: detection of impact Ecological Applications 8 61–70 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2641311
R. K. Johnson T. Wiederholm D. M. Rosenberg (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring using individual organisms, populations and species assemblages of benthic macroinvertebrates D. M. Rosenberg V. H. Resh (Eds) Freshwater Biomonitoring and Benthic Macroinvertebrates Chapman and Hall New York 40–158
R. K. Johnson W. Goedkoop L. Sandin (2004) ArticleTitleSpatial scale and ecological relationships between the macroinvertebrate communities of stony habitats of streams and lakes Freshwater Biology 49 1179–1194 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01262.x
R. A. E. Knoben C. Roos M. C. M. Oirschot Particlevan (1995) Biological Assessment Methods for Watercourses UN/ECE Task Force on Monitoring and Assessment Lelystad
S. L. Kohler M. J. Wiley (1997) ArticleTitlePathogen outbreaks reveal large-scale effects of competition in stream communities Ecology 73 2164–2176 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2265953
R. Kolkwitz M. Marsson (1902) ArticleTitleGrundsätse für die biologische Beurteiling des Wassers nach seiner Flora und Fauna Mitt. Prüfungsanst. Wasserversorg. Abwasserreinig 1 33–72
P. S. Lake (2000) ArticleTitleDisturbance, patchiness, and diversity in streams Journal of North American Benthological Society 19 573–592 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1468118
C. LeCointe M. Coste J. Prygiel (1993) ArticleTitle“OMNIDIA” software for taxonomy, calculation of diatom indices and inventories management Hydrobiologia 269/270 509–513 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00028048
A. Lorenz D. Hering C. K. Feld P. Rolauffs (2004) ArticleTitleA new method for assessing the impact of morphological degradation on the benthic invertebrate fauna for streams in Germany Hydrobiologia 516 107–127 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025261.79761.b3
S. J. McNaughton (1967) ArticleTitleRelationships among functional properties of Californian grasslands Nature 216 168–169 Occurrence Handle10.1038/216168b0
J. L. Metcalfe (1989) ArticleTitleBiological water-quality assessment of running waters based on macroinvertebrate communities – history and present status in Europe Environmental Pollution 60 101–139 Occurrence Handle15092393 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXmtVWju7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0269-7491(89)90223-6
Noble, R. & I. Cowx, 2002. Development of a river-type classification system (D1); Compilation and harmonization of fish species classification (D2). Report of the EU funded project Development, Evaluation & Implementation of a Standardised Fish-based Assessment Method for the Ecological Status of European Rivers – A Contribution to the Water Framework Directive (FAME). Available from http://fame.boku.ac.at/downloads/D1_2_typology_and%20species_classification.pdf
S. J. Ormerod S. D. Rundle E. C. Lloyd A. A. Douglas (1993) ArticleTitleThe influence of riparian management on the habitat structure and macroinvertebrate communities of upland streams draining plantation forests Journal of Applied Ecology 30 13–24 Occurrence Handle10.2307/2404266
R. Paavola T. Muotka R. Virtanen J. Heino P. Kreivi (2003) ArticleTitleAre biological classifications of headwater streams concordant across multiple taxonomic groups? Freshwater Biology 48 1912–1923 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01131.x
Raven P. J., N. T. H. Holmes, F. H. Dawson, P. J. A. Fox, M. Everard, I. R. Fozzard & K. J. Rouen, 1998. River Habitat Quality – the physical character of rivers and streams in the UK and Isle of Man. River Habitat Survey Report Number 2, Bristol: Environment Agency, Stirling: Scottish Environment Protection Agency. Belfast: Environment and Heritage Service, 84
V. H. Resh A. V. Brown A. P. Covich M. E. Gurtz H. W. Li G. W. Minshall S. R. Reice A. L. Sheldon J. B. Wallace R. C. Wissmar (1988) ArticleTitleThe role of disturbance in stream ecology Journal of the North American Benthological Society 7 433–455 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1467300
T. B. Reynoldson R. H. Norris V. H. Resh K. E. Day D. M. Rosenberg (1997) ArticleTitleThe reference condition: a comparison of multimetric and multivariate approaches to assess water-quality impairment using benthic macroinvertebrates Journal of the North American Benthological Society 16 833–852 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1468175
C. Richards R. J. Haro L. B. Johnson G. E. Host (1997) ArticleTitleCatchment and reach-scale properties as indicators of macroinvertebrate species traits Freshwater Biology 37 219–230 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.d01-540.x
E. Rott G. Hofmann K. Pall P. Pfister E. Pipp (1997) Indikationslisten für Aufwuchsalgen. Teil 1: Saprobielle Indikation Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft Wien 73
E. Rott P. Pfister H. Dam Particlevan E. Pipp K. Pall N. Binder K. Ortler (1999) Indikationslisten für Aufwuchsalgen. Teil 2: Trophieindikation sowie geochemische Präferenz, taxonomische und toxikologische Anmerkungen Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft Wien 248
A. Rumeau M. Coste (1988) ArticleTitleInitiation à la systématique des diatomées d’eau douce pour l’utilisation pratique d’un indice diatomique générique Bulletin Francais de la Peche et de la Pisciculture 309 1–69
L. Sandin R. K. Johnson (2000) ArticleTitleStatistical power of selected indicator metrics using macroinvertebrates for assessing acidification and eutrophication of running waters Hydrobiologia 422/423 233–243 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1017082619481
L. Sandin J. Dahl R. K. Johnson (2004) ArticleTitleAssessing acid stress in Swedish boreal and alpine streams using benthic macroinvertebrates Hydrobiologia 516 129–148 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjvV2msL0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025262.98511.46
InstitutionalAuthorNameSAS (1994) JMP – Statistics Made Visual, Version 3.1 SAS Institute Inc Cary, North Carolina, USA
T. B. E. Southwood (1977) ArticleTitleHabitat, the template for ecological strategies? Journal of Animal Ecology 46 336–365 Occurrence Handle10.2307/3817
J. Schaumburg C. Schranz J. Foerster A Gutowski G. Hofmann P. Meilinger S. Schneider U. Schmedtje (2004) ArticleTitleEcological classification of macrophytes and phytobenthos for rivers in Germany according to the Water Framework Directive Limnologica 34 283–301
C. E. Shannon W. Weaver (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication University of Illinois Press Urbana
J. Skriver N. Friberg J. Kirkegaard (2001) ArticleTitleBiological assessment of running waters in Denmark: Introduction of the Danish Stream Fauna Index (DSFI) Verhandlungen der internationalen Vereineinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 27 1822–1830
C. Steinberg S. Schiefele (1988) ArticleTitleBiological indication of trophy and pollution of running waters Zeitschrift für Wasser- und Abwasser-Forschung 21 227–234 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhs1Sjsro%3D
H. Tremp A. Kohler (1995) ArticleTitleThe usefulness of macrophyte monitoring-systems, exemplified on eutrophication and acidification of running waters Acta Botanica Gallica 142 541–550
M. J. Wiley S. L. Kohler P. W. Seelbach (1997) ArticleTitleReconciling landscape and local views of aquatic communities: lessons from Michigan trout streams Freshwater Biology 37 133–148 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.00152.x
M. Zelinka P. Marvan (1961) ArticleTitleZur Präzisierung der biologischen Klassifikation der Reinheit fließender Gewässer Archiv für Hydrobiologie 57 389–407
Ziemann, H., 1999. Bestimmung des Halobienindex. Tümpling W. & G. Friedrich (eds), Biologische Gewässeruntersuchung. Methoden der Biologischen Gewässeruntersuchung, 2: 310–313
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, R.K., Hering, D., Furse, M.T. et al. Detection of ecological change using multiple organism groups: metrics and uncertainty. Hydrobiologia 566, 115–137 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0101-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0101-8