Abstract
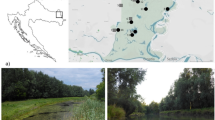
Zoobenthos is an essential part of shallow lake ecosystems, exerting a considerable impact upon their functioning. We studied 13 eutrophic, shallow, polymictic lakes from Northern Poland to find out which environmental factors influence taxonomic composition, abundance and biodiversity of their zoobenthos. The Canonical Correspondence Analysis allowed to distinguish three lake types: (1) macrophyte-dominated lakes, with high plant cover and well illuminated bottom, inhabited by abundant, diverse benthic taxa; (2) deeper phytoplankton-dominated lakes, with shaded bottom, high sediment oxygen demand (SOD) and rather sparse zobenthos community, dominated by Chironomus and Chaoborus larvae; (3) shallower phytoplankton-dominated lakes, with intermediate amount of light at the bottom and lower SOD values and comparatively diverse zoobenthos, but with lower number of taxa than in the first group. Apart from plant presence, distinguishing between macrophyte-dominated lakes and the other types, the most important variable in the CCA was amount of light reaching the bottom. Probably the impact of light on the bottom fauna was indirect: light stimulated development of macrophytes or phytobenthos (depending on its intensity) and thus improved food and oxygen conditions. Zoobenthos was also affected by oxygen conditions (mainly SOD), presumably by short-time oxygen depletions occurring in the deep phytoplankton-dominated lakes and preventing survival of some benthic taxa.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren, G., W. Goedkoop, H. Markensten, L. Sonesten & M. Boberg, 1997. Seasonal variation in food quality for pelagic and benthic invertebrates in Lake Erken – the role of fatty acids. Freshwater Biology 38: 555–570.
Armitage, P. D., P. S. Cranston & L. C. V. Pinder (eds), 1995. The Chironomidae: Biology and ecology of non-biting midges. Chapman & Hall.
Bayley, S .E. & C. M. Prather, 2003. Do wetland lakes exhibit alternative stable states? Submersed aquatic vegetation and chlorophyll in western boreal lakes. Limnology & Oceanography 48: 2335–2345.
Bostrom, B., J. M. Andersen, S. Fleischer & M. Jansson 1988. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 170: 229–244.
Chapman, P. M., B. Anderson, S. Carr, V. Engle, R. Green, J. Hameedi, M. Harmon, P. Haverland, J. Hyland, C. Ingersoll, E. Long, J. Rodgers Jr, M. Salazar, P. K. Sibley & H. Windom, 1997. General guidelines for using the sediment quality triad. Marine Pollution Bulletin 34: 368–372.
Clements, W. H. & P. M. Kiffney, 1993. Assessing contaminant effects at higher levels of biological organization. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 13: 357–359.
Covich, A. P., M. A. Palmer & T. A. Crowl, 1999. The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems. Bioscience 49: 119–127.
Dinsmore, W. P. & E. E. Prepas, 1997. Impact of hypolimnetic oxygenation on profundal macroinvertebrates in a eutrophic lake in central Alberta .1. Changes in macroinvertebrate abundance and diversity. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 54: 2157–2169.
Diehl, S. & R. Kornijów, 1997. Influence of submerged macrophytes on trophic interactions among fish and macroinvertebrates. In Jeppesen E., M. Sondergaard, M. Sondergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The structuring role of submerged macrophytes in lakes. Springer, 24–46.
Engel S., 1988. The role and interactions of submersed macrophytes in a shallow Wisconsin Lake USA. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 4: 329–342.
Fukuhara, H. & K. Yasuda, 1985. Phosphorus excretion by some zoobenthos in a eutrophic freshwater lake and its temperature dependency. The Japanese Journal of Limnology 46: 287–296.
Goedkoop, W. & R. K. Johnson, 1996. Pelagic-benthic coupling: profundal benthic community response to spring diatom deposition in mesotrophic Lake Erken. Limnology And Oceanography 41: 636–647.
Goedkoop, W., L. Sonesten, G. Ahlgren & M. Boberg, 2000. Fatty acids in profundal benthic invertebrates and their major food resources in Lake Erken, Sweden: Seasonal variation and trophic indications. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 57: 2267–2279.
Gong, Z., P. Xie & S. Wang, 2000. Macrozoobenthos in 2 shallow, mesotrophic Chinese lakes with contrasting sources of primary production. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 19: 709–724.
Gross, T. F., F. E. Werner & J. E. Eckman 1992. Numerical modeling of larval settlement in turbulent bottom boundary layers. Journal of Marine Research 50: 611–642.
Gullberg, K. R., W. Goedkoop & R. K. Johnson, 1997. The fate of diatom carbon within a freshwater benthic community – a microcosm study. Limnology & Oceanography 42: 452–460.
Hargeby, A., G. Andersson, I. Blindow & S. Johansson, 1994. Trophic web structure in a shallow eutrophic lake during a dominance shift from phytoplankton to submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 280: 83–90.
Heinis, F. & C. Davids, 1993. Factors governing the spatial and temporal distribution of chironomid larvae in the Maarsseveen lakes with special emphasis on the role of oxygen conditions. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 27: 21–34.
Hurlbert, S. M., 1971. The non-concept of species diversity: a critique and alternative parameters. Ecology 52: 577–586.
Jonasson, P. M. & C. Lindegaard, 1979. Zoobenthos and its contribution to the metabolism of shallow lakes. Archive Hydrobiology Beihefte Ergebnisse Limnology 13: 162–180.
Jones, S. E. & C. F. Jago, 1992. In situ assessment of modification of sediment properties by burrowing invertebrates. Marine Biology 115: 133–142.
Kelderman, P., 1984. Sediment-water exchange in Lake Grevelingen under different environmental conditions. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 18: 286–311.
Kohler, S. L., 1992. Competition and the structure of a benthic stream community. Ecological Monographs 62: 165–188.
Kornijów, R. & B. Moss, 2002. On the survival of benthic macroinvertebrates during night hypoxia in a shallow lake. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 28: 1–3.
Krantzberg, G., 1985. The influence of bioturbation on physical and biological parameters in aquatic environments; A review. Environmental Pollution 39: 99–122.
Lassen, C., N. P. Revsbech & O. Pedersen, 1997. Macrophyte development and resuspension regulate the photosyntesis and production of benthic microalgae. Hydrobiologia 350: 1–11.
Lindegaard, C., 1994. The role of zoobenthos in energy flow in two shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 275/276: 313–322.
MacKay, R. J., 1992. Colonization by lotic macroinvertebrates: a review of processes and patterns. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 49: 617–628.
Madsen, K. N., P. Nilson & K. Sundback 1993. The influence of benthic microalgae on the stability of a subtidal sediment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 170: 159–177.
Marsden, M. W., 1989. Lake restoration by reducing external phosphorus loading the influence of sediment phosphorus release. Freshwater Biology 21: 139–162.
Marsh, A. G. & K. R. Tenore, 1990. The role of nutrition in regulating the population dynamics of opportunistic, surface deposit feeders in a mesohaline community. Limnology & Oceanography 35: 710–724.
Meadows, P. S. & J. Tait, 1989. Modification of sediment permeability and shear strength by two burrowing invertebrates. Marine Biology (Berlin) 101: 75–82.
Phipps, G. L., V. R. Mattson & G. T. Ankley, 1995. Relative sensivity of three freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates to ten contaminants. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 28: 281–286.
Raspopov, I. M., T. D. Slepukhina, F. F. Vorontzov & O.N. Dotzenko, 1988. Wave effects on the bottom biocenosis in the Onega Lake bays (USSR). Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 112: 115–124.
Reynoldson, T. B., R. C. Bailey, K. E. Day & R. H. Norris, 1995. Biological guidelines for freshwater sediment based on BEnthic Assessment of SedimenT (BEAST) using a multivariate approach for predicting biological state. Australian Journal of Ecology 20: 198–219.
Risnoveanu, G., C. Postolache & A. Vadineanu, 2004. Ecological significance of nitrogen cycling by tubificid communities in shallow eutrophic lakes of the Danube Delta. Hydrobiologia 524: 193–202.
Scheffer, M., 1990. Multiplicity of stable states in freshwater systems. Hydrobiologia 200/201: 475–486.
Scheffer, M., S. H. Hosper, M. L. Meijer & B. Moss 1993. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology and Evolution: 275–279.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of shallow lakes. Chapman & Hall.
Shin, P. K. S., 1989. Natural disturbance of benthic infauna in the offshore waters of Hong Kong. Asian Marine Biology 6: 193–207.
Svensson, J. M. & L. Leonardson, 1996. Effects of bioturbation by tube-dwelling chironomids larvae on oxygen uptake and denitrification in eutrophic lake sediments. Freshwater Biology 35: 289–300.
Svensson, J. M., 1997. Influence of Chironomus plumosus larvae on ammonium flux and denitrification (measured by the acetylene blockage – and the isotope pairing-technique) in eutrophic lake sediment. Hydrobiologia 346: 157–168.
Svensson, J. M., 1998. Emission of N2O, nitrification and denitrification in a eutrophic lake sediment bioturbated by Chironomus plumosus. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 14: 289–299.
Sweerts, J-P R. A., 1990. Oxygen consumption processes, mineralization and nitrogen cycling at the sediment-water interface of north temperate lakes. Ph.D. Thesis.
Underwood, G. J. C. & D. M. Paterson, 1993. Recovery of intertidal benthic diatoms after biocide treatment and associated sediment dynamics. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the UK 73: 25–45.
van de Bund, W. J., W. Goedkoop & R. K. Johnson, 1994. Effects of deposit-feeder activity on bacterial production and abundance in profundal lake sediment. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 13: 532–539.
Van Den Berg, M. S., H. Coops, R. Noordhuis, J. Van Schie & J. Simons 1997. Macroinvertebrate communities in relation to submerged vegetation in two Chara-dominated lakes. Hydrobiologia 342/343: 143–150.
Vos, J. H., M. A. G. Ooijevaar, J. F. Postma & W. Admiraal, 2000. Interaction between food availability and food quality during growth of early instar chironomid larvae. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 19: 158–168.
Vos, J. H., E. T. H. M. Peeters, R. Gylstra, M. H. S. Kraak & W. Admiraal, 2004. Nutritional value of sediments for macroinvertebrate communities in shallow eutrophic waters. Archiv fuer Hydrobiologie 161: 469–487.
Weatherhead, M. A. & M. R. James, 2001. Distribution of macroinvertebrates in relation to physical and biological variables in the littoral zone of nine New Zealand lakes. Hydrobiologia 462: 115–129.
Wiśniewski, R., 1980a. Pseudolittoral of Gopło lake. Part I. Characteristics of the environment. Limnological Papers 12: 61–81.
Wiśniewski, R., 1980b. Pseudolittoral of Gopło lake. Part II. Biological characteristics. Limnological Papers 12: 83–116.
Wiśniewski, R., 1995. Role of sediment resuspension in aquatic ecosystems functioning (in Polish). Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Mikołaja Kopernika, Toruń.
Wolnomiejski, N. & E. Papis, 1974. Pseudolittoral of the Jeziorak Lake – a separate bottom zone of a strongly eutrophied water body. Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii 21: 343–353.
Wood, L. W., 1975. Role of oligochaetes in the circulation of water and solutes across the mud-water interface. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 19: 1530–1533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Żbikowski, J., Kobak, J. Factors influencing taxonomic composition and abundance of macrozoobenthos in extralittoral zone of shallow eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 584, 145–155 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0613-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0613-x