Abstract
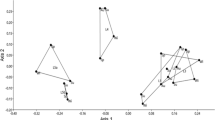
Regulation of lake water level for power production and flood control is among the major anthropogenic disturbances in boreal aquatic ecosystems. In Finland, over 300 lakes, representing one third of the total inland water area of the country, are artificially regulated. To study the effects of regulation on lake littoral macroinvertebrate communities, samples were taken from upper stony littoral and from lower soft bottom littoral habitats of 11 lakes with different regulation amplitudes (wintertime fall in water level 1.19–6.75 m). Twelve unregulated (wintertime fall in water level 0.11–0.55 m) lakes with otherwise similar characteristics were used as a reference. Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling ordinations showed that the composition of macroinvertebrate assemblages was strongly associated with the amplitude of water level regulation. Taxon richness also decreased with increasing intensity of regulation. Freezing and flushing of sediments in late winter are probably the most important factors leading to the impoverished littoral macroinvertebrate fauna. Invertebrates with long life cycle seem to be particularly vulnerable to unnatural water level fluctuation. Our results show that regulation of water level has a major impact on functionally significant lake littoral macroinvertebrates.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasaarela, E., S. Hellsten & P. Tikkanen, 1989. Ecological aspects of lake regulation in northern Finland. In Laikari, H. (ed.), River Basin Management–V. Pergamon, Oxford: 247–255.
Aroviita, J., H. Hämäläinen & I. J. Holopainen, 2006. Benthic macroinvertebrates in lakes affected by iron mining waste waters in Kostomuksha area, north-west Russia. Verhandlungen der internationalen Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 29: 2039–2044.
Benson, N. G. & P. L. Hudson, 1975. Effects of a reduced fall drawdown on benthos abundance in Lake Francis case. Transactions of the North American Fisheries Society 104: 526–528.
Coops, H., M. Beklioglu & T. L. Crisman, 2003. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems–workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506: 23–27.
Dufrêne, M. & P. Legendre, 1997. Species assemblages and indicator species: the need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecological Monographs 67: 345–366.
Dynesius, M. & C. Nilsson, 1994. Fragmentation and flow regulation of river systems in the northern third of the World. Science 266: 753–762.
European Commission, 2000. Establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Directive 2000/60/EC. October 2000.
France, R. L., 1995. Differentiation between littoral and pelagic food webs in lakes using stable carbon isotopes. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1310–1313.
Furey, P. C., R. N. Nordin & A. Mazumder, 2006. Littoral benthic macroinvertebrates under contrasting drawdown in a reservoir and a natural lake. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 19–31.
Gasith, A. & S. Gafny, 1990. Effects of Water Level Fluctuation on the Structure and Function of the Littoral Zone. In Tilzer, M. M. & C. Serruya (eds), Large Lakes Ecological Structure and Function. Springer-Verlag, Berlin: 156–171.
Grimås, U., 1961. The bottom fauna of natural and impounded lakes in northern Sweden (Ankarvattnet and Blåsjön). Institute of Freshwater Research Drottningholm 42: 183–237.
Hellsten, S., 2001. Effects of lake water level regulation on aquatic macrophyte stands in northern Finland and options to predict these impacts under varying conditions. Acta Botanica Fennica 171: 1–47.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1961. The effect of water-level fluctuations on littoral fauna. Verhandlungen der internationalen Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 16: 652–656.
Hynes, H. B. N. & U. R. Yadav, 1985. Three decades of post-impoundment data on the littoral fauna of Llyn Tegid, North Wales. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 104: 39–48.
Hynynen, J., A. Palomäki, H. Veijola, J. J. Meriläinen, P. Bagge & S. Bibiceanu, 1997. Life-Pihlajavesi 1995–1996: Phytoplankton, zooplankton and benthic invertebrates in the Pihlajavesi Basin of the Lake Saimaa complex, Finland. Research report no 166. Institute for Environmental Research, University of Jyväskylä. (in Finnish with English summary).
Johnson, R. K. & W. Goedkoop, 2002. Littoral macroinvertebrate communities: spatial scale and ecological relationships. Freshwater Biology 47: 1840–1854.
Keto, A., A. Tarvainen & S. Hellsten, 2006. The effect of water level regulation on species richness and abundance of aquatic macrophytes in Finnish lakes. Verhandlungen der internationalen Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 29: 2109–2114.
Liljaniemi, P., 1998. The use of benthic invertebrates in biomonitoring: the fauna of Lake Suuri-Onkamo, Lake Pieni-Onkamo and Lake Särkijärvi (North Carelia) in years 1990–1991. Regional Environmental Publications 73. North Carelia Environment Centre. (in Finnish with English abstract).
Marttunen, M. & S. Hellsten, 2003. Heavily modified waters in Europe: a case study of Lake Kemijärvi, Finland. The Finnish Enviroment 630: 1–60.
McCune, B. & J. B. Grace, 2002. Analysis of Ecological Communities. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, Oregon, USA.
McCune, B. & M. J. Mefford, 1999. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data. Version 4.0. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, Oregon, USA.
Mortsch, L. D. & F. H. Quinn, 1996. Climate change scenarios for the Great Lakes Basin ecosystem studies. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 903–911.
Palomäki, R., 1994. Response by macrozoobenthos biomass to water level regulation in some Finnish lake littoral zones. Hydrobiologia 286: 17–26.
Palomäki, R. & E. Koskenniemi, 1993. Effects of bottom freezing on macrozoobenthos in the regulated Lake Pyhäjärvi. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 128: 73–90.
Quennerstedt, N., 1958. Effect of water level fluctuation on lake vegetation. Verhandlungen der internationalen Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 13: 901–906.
Richter, B. D., D. P. Braun, M. A. Mendelson & L. L. Master, 1997. Threats to imperiled freshwater fauna. Conservation Biology 11: 1081–1093.
Särkkä, J., 1983. A quantitative ecological investigation of the littoral zoobenthos of an oligotrophic Finnish lake. Annales Zoologici Fennici 20: 157–178.
Smith, B. D., P. S. Maitland & S. M. Pennock, 1987. A comparative study of water level regimes and littoral benthic communities in Scottish lochs. Biological Conservation 39: 291–316.
SPSS Inc., 2003. SPSS for Windows, Rel. 12.0.1. Chicago.
Statzner, B., B. Bis, S. Doledec & P. Usseglio-Polatera, 2001. Perspectives for biomonitoring at large spatial scales: a unified measure for the functional composition on invertebrate communities in European running waters. Basic and Applied Ecology 2: 73–85.
Sutela, T. & T. Vehanen, 2008. Effects of water-level regulation on the nearshore fish community in boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-008-9468-z.
Tikkanen, P., L. Kantola, T. Niva, S. Hellsten & E. Alasaarela, 1989. Ecological aspects of lake regulation in northern Finland. Part 3. Macrozoobenthos and feeding of fish. VTT Research Notes 987. Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo. (in Finnish with English abstract).
Tolonen, K. T., H. Hämäläinen, I. J. Holopainen & J. Karjalainen, 2001. Influences of habitat type and environmental variables on littoral macroinvertebrate communities in a large lake system. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 152: 39–67.
Tolonen, K. T., H. Hämäläinen, H. Luotonen & J. Kotanen, 2003. Use of benthic macroinvertebrates in assessment and monitoring the ecological status of lakes. Evaluation of the usability and costs of methods in the Life Vuoksi Project. Regional Environmental Publications 328. North Carelia Regional Environment Centre. (in Finnish with English abstract).
Turner, M. A., D. B. Huebert, D. L. Findlay, L. L. Hendzel, W. A. Jansen, R. A. Bodaly, L. M. Armstrong & S. E. M. Kasian, 2005. Divergent impacts of experimental lake-level drawdown on planktonic and benthic plant communities in a boreal forest lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 991–1003.
Valdovinos, C., C. Moya, V. Olmos, O. Parra, B. Karrasch & O. Buettner, 2007. The importance of water-level fluctuation for the conservation of shallow water benthic macroinvertebrates: an example in the Andean zone of Chile. Biodiversity and Conservation 16: 3095–3109.
Virnes, A., 2005. The evaluation of state of two bays by macroinvertebrate communities in Lake Pyhäjärvi, in North Carelia, Finland. M.Sc. Thesis. University of Joensuu. (in Finnish with English abstract).
Acknowledgements
We thank the regional environmental centres of Kainuu (especially Pasi Toro), Lapland and North Carelia for help during the field trips. Olli Nousiainen and Petri Mäkinen (University of Jyväskylä) assisted in the field and the laboratory. We also thank Kimmo T. Tolonen and Ari Virnes for their unpublished macroinvertebrate data. This study has been a part of CENOREG-project (Classification and Environmental Objectives of Regulated Lakes), coordinated by SYKE, and has been financed by the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry in Finland. Also Graninge Kainuu provided financial support. Professor Roger I. Jones provided helpful comments and improved the language. Comments from Zoltan Csabai and an anonymous reviewer were helpful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: K. M. Wantzen, K.-O. Rothhaupt, M. Mörtl, M. Cantonati, L. G.-Tóth & P. Fischer
Ecological Effects of Water-level Fluctuations in Lakes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aroviita, J., Hämäläinen, H. The impact of water-level regulation on littoral macroinvertebrate assemblages in boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia 613, 45–56 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9471-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9471-4