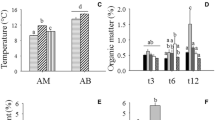
Abstract
Fluxes of nutrients across habitats are of paramount relevance in ecological studies due to the implication in primary production, trophic structure and biodiversity. This study analyses the role of sandy beaches in the processing of organic matter. Three beaches with different macroalgal inputs were sampled throughout the annual cycle. The standing stock of wrack macroalgae on the beach surface and the nutrient concentration in the intertidal pore water (IPW) and in the surf zone water were measured monthly. Mean concentration of dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphate in the IPW increased from the low to the very high subsidized beach. Seasonal coupling was observed between the wrack biomass and the nutrient concentration throughout the year. Among the nutrient species, a variable relationship was found between the NH4 +/NO x − ratio and the biomass of macroalgae deposited. These results provide evidences of the active role of sandy beaches in the processing of organic matter and in the nutrient cycling, remarking the feedback connectivity between sandy beaches and their neighbour ecosystems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Salgado, X., G. Rosón, F. Pérez, F. Figueiras & Y. Pazos, 1996. Nitrogen cycling in an estuarine upwelling system, the Ría de Arousa (NW Spain). I. Short-time-scale patterns of hydrodynamic and biogeochemical circulation. Marine Ecology Progress Series 135: 259–273.
Anderson, W. & G. Polis, 1999. Nutrient fluxes from water to land: seabirds affect plant nutrient status on Gulf of California islands. Oecologia 118: 324–332.
Anschutz, P., T. Smith, A. Mouret, J. Deborde, S. Bujan, D. Poirier & P. Lecroart, 2009. Tidal sands as biogeochemical reactors. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 84: 84–90.
Avery, G. B., R. J. Kieber & K. J. Taylor, 2008. Nitrogen release from surface sand of a high energy beach along the southeastern coast of North Carolina, USA. Biogeochemistry 89: 357–365.
Barreiro, F., M. Gómez, M. Lastra, J. López & R. de la Huz, 2011. Annual cycle of wrack supply to sandy beaches: effect of the physical environment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 433: 65–74.
Billerbeck, M., U. Werner, K. Bosselmann, E. Walpersdorf & M. Huettel, 2006. Nutrient release from an exposed intertidal sand flat. Marine Ecology Progress Series 316: 35–51.
Bode, A., M. Varela, E. Teira, E. Fernández, N. González & M. Varela, 2004. Planktonic carbon and nitrogen cycling off northwest Spain: variations in production of particulate and dissolved organic pools. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 37: 95–107.
Boudreau, B., M. Huettel, S. Forster, R. A. Jahnke, A. McLachlan, J. J. Middelburg, P. Nielsen, F. Sansone, G. Taghon, W. Van Raaphorst, I. Webster, J. M. Weslawski & P. Wiberg, 2001. Permeable marine sediments: overturning an old paradigm. Eos Transactions 82: 133–136.
Bourguès, S., I. Auby, R. Wit & P. J. Labourg, 1996. Differential anaerobic decomposition of seagrass (Zostera noltii) and macroalgal (Monostroma obscurum) biomass from Arcachon Bay (France). Hydrobiologia 329: 121–131.
Buchsbaum, R., I. Valiela, T. Swain, M. Dzierzeski & S. Allen, 1991. Available and refractory nitrogen in detritus of coastal vascular plants and macroalgae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 72: 131–143.
Burnett, W., H. Bokuniewicz, M. Huettel, W. Moore & M. Taniguchi, 2003. Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeochemistry 66: 3–33.
Cade, B. S. & B. R. Noon, 2003. A gentle introduction to quantile regression for ecologists. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 1(8): 412–420.
Catenazzi, A. & M. Donnelly, 2007. Role of supratidal invertebrates in the decomposition of beach-cast green algae Ulva sp. Marine Ecology Progress Series 349: 33–42.
Chapin, F., P. Matson & H. Mooney, 2002. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology. Springer, New York.
Chapman, A. R. O. & J. S. Craigie, 1977. Seasonal growth in Laminaria longicruris: relations with dissolved inorganic nutrients and internal reserves of nitrogen. Marine Biology 40: 197–205.
Corzo, A., S. van Bergeijk & E. García-Robledo, 2009. Effects of green macroalgal blooms on intertidal sediments: net metabolism and carbon and nitrogen contents. Marine Ecology Progress Series 380: 81–93.
Coupland, G. & J. McDonald, 2008. Extraordinarily high earthworm abundance in deposits of marine macrodetritus along two semi-arid beaches. Marine Ecology Progress Series 361: 181–189.
Coupland, G. T., C. M. Duarte & D. I. Walker, 2007. High metabolic rates in beach cast communities. Ecosystems 10: 1341–1350.
Dugan, J., D. M. Hubbard, M. D. McCrary & M. O. Pierson, 2003. The response of macrofauna communities and shorebirds to macrophyte wrack subsidies on exposed sandy beach of southern California. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 58: 25–40.
Dugan, J. E., D. M. Hubbard, H. M. Page & J. P. Schimel, 2011. Marine macrophyte wrack inputs and dissolved nutrients in beach sands. Estuaries and Coasts 34: 839–850.
Ehrenhauss, S. & M. Huettel, 2004. Advective transport and decomposition of chain-forming planktonic diatoms in permeable sediments. Journal of Sea Research 52: 179–197.
Emery, K., 1961. A simple method of measuring beach profiles. Limnology and Oceanography 6: 90–93.
Figueiras, F., U. Labarta & M. Fernández Reiriz, 2002. Coastal upwelling, primary production and mussel growth in the Rías Baixas of Galicia. Hydrobiologia 484: 121–131.
Folk, R., 1980. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks. Hemphill Publishing Company, Austin.
García-Robledo, E., A. Corzo, J. García de Lomas & S. van Bergeijk, 2008. Biogeochemical effects of macroalgal decomposition on intertidal microbenthos: a microcosm experiment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 356: 139–151.
Giere, O., A. Eleftheriou & D. Murinson, 1988. Abiotic factors. In Higgins, R. P. & H. Thiel (eds), Introduction to the Study of Meiofauna. Smithsonian Institution Press, London: 61–78.
Hanisak, M., 1993. Nitrogen release from decomposing seaweeds: species and temperature effects. Journal of Applied Phycology 5: 175–181.
Hardison, A., E. Canuel, I. Anderson & B. Veuger, 2010. Fate of macroalgae in benthic systems: carbon and nitrogen cycling within the microbial community. Marine Ecology Progress Series 414: 41–55.
Harrison, P., 1989. Detrital processing in seagrass systems: a review of factors affecting decay rates, remineralization and detritivory. Aquatic Botany 35: 263–288.
Hays, R. & W. Ullman, 2007a. Direct determination of total and fresh groundwater discharge and nutrient loads from a sandy beachface at low tide (Cape Henlopen, Delaware). Limnology and Oceanography 52: 240–247.
Hays, R. & W. Ullman, 2007b. Dissolved nutrient fluxes through a sandy estuarine beachface (Cape Henlopen, Delaware, USA): contributions from fresh groundwater discharge, seawater recycling, and diagenesis. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 710–724.
Hobday, A., 2000. Abundance and dispersal of drifting kelp Macrocystis pyrifera rafts in the Southern California Bight. Marine Ecology Progress Series 195: 101–116.
Horn, D., 2002. Beach groundwater dynamics. Geomorphology 48: 121–146.
Jickells, T. D. & J. E. Rae, 1997. Biogeochemistry of Intertidal Sediments. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Koop, K. & M. Lucas, 1983. Carbon flow and nutrient regeneration from the decomposition of macrophyte debris in a sandy beach microcosm. In McLachlan, A. & T. Erasmus (eds), Sandy Beaches as Ecosystems. Junk, The Hague: 249–263.
Koop, K., R. Newell & M. Lucas, 1982. Biodegradation and carbon flow based on kelp (Ecklonia maxima) debris in a sandy beach microcosm. Marine Ecology Progress Series 7: 315–326.
Lastra, M., R. de la Huz, A. G. Sánchez-Mata, I. F. Rodil, K. Aerts, S. Beloso & J. López, 2006. Ecology of exposed sandy beaches in northern Spain: environmental factors controlling macrofauna communities. Journal of Sea Research 55: 128–140.
Lastra, M., H. M. Page, J. E. Dugan, D. M. Hubbard & I. F. Rodil, 2008. Processing of allochthonous macrophyte subsidies by sandy beach consumers: estimates of feeding rates and impacts on food resources. Marine Biology 154: 163–174.
Mateo, M. A., 2010. Beach-Cast Cymodocea nodosa along the shore of a semienclosed bay: sampling and elements to assess its ecological implications. Journal of Coastal Research 262: 283–291.
McGwynne, L., A. McLachlan & J. Furstenberg, 1988. Wrack breakdown on sandy beaches – its impact on interstitial meiofauna. Marine Environmental Research 25: 213–232.
McLachlan, A., 1980. The definition of sandy beaches in relation to exposure: simple rating system. South African Journal of Science 76: 137–138.
McLachlan, A. & A. C. Brown, 2006. The Ecology of Sandy Shores, 2nd ed. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Mews, M., M. Zimmer & D. Jelinski, 2007. Species-specific decomposition rates of beach-cast wrack in Barkley Sound, British Columbia, Canada. Marine Ecology Progress Series 328: 155–160.
Moore, W. S., 1996. Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature 380: 612–614.
Nedzarek, A. & S. Rakusa-Suszczewski, 2004. Decomposition of macroalgae and the release of nutrient in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Polar Bioscience 17: 26–35.
Page, H., R. Petty & D. Meade, 1995. Influence of watershed runoff on nutrient dynamics in a southern California salt marsh. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 41: 163–180.
Pearse, A., H. Humm & G. Wharton, 1942. Ecology of sand beaches at Beaufort, N.C. Ecological Monographs 12: 135–190.
Polis, G., W. Anderson & R. Holt, 1997. Toward an integration of landscape and food web ecology: the dynamics of spatially subsidized food webs. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 28: 289–316.
Prego, R., M. A. D. C. Barciela & M. Varela, 1999. Nutrient dynamics in the Galician coastal area (Northwestern Iberian Peninsula): do the Rias Bajas receive more nutrient salts than the Rias Altas? Continental Shelf Research 19: 317–334.
Rauch, M., L. Denis & J.-C. Dauvin, 2008. The effects of Phaeocystis globosa bloom on the dynamics of the mineralization processes in intertidal permeable sediment in the Eastern English Channel (Wimereux, France). Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 1284–1293.
Rocha, C., 2008. Sandy sediments as active biogeochemical reactors: compound cycling in the fast lane. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 53: 119–127.
Rocha, C., J. Ibanhez & C. Leote, 2009. Benthic nitrate biogeochemistry affected by tidal modulation of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) through a sandy beach face, Ria Formosa, Southwestern Iberia. Marine Chemistry 115: 43–58.
Rodil, I., C. Olabarria, M. Lastra & J. López, 2008. Differential effects of native and invasive algal wrack on macrofaunal assemblages inhabiting exposed sandy beaches. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 358: 1–13.
Rossi, F. & A. Underwood, 2002. Small-scale disturbance and increased nutrients as influences on intertidal macrobenthic assemblages: experimental burial of wrack in different intertidal. Marine Ecology Progress Series 241: 29–39.
Rusch, A., M. Huettel, C. Wild & C. E. Reimers, 2006. Benthic oxygen consumption and organic matter turnover in organic-poor, permeable shelf sands. Aquatic Geochemistry 12: 1–19.
Sassi, R., M. Kutner & G. F. Moura, 1988. Studies on the decomposition of drift seaweed from the northeast Brazilian coastal reefs. Hydrobiologia 192: 187–192.
Stenton-Dozey, J. M. E. & C. L. Griffiths, 1983. The fauna associated with kelp stranded on a sandy beach. In McLachlan, A. & T. Erasmus (eds), Sandy Beaches as Ecosystems. Junk, The Hague: 557–568.
Strauss, E. A. & G. A. Lamberti, 2000. Regulation of nitrification in aquatic sediments by organic carbon. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1854–1859.
Strayer, D. L. & S. E. G. Findlay, 2010. Ecology of freshwater shore zones. Aquatic Sciences 72: 127–163.
Sundby, B., C. Gobeil, N. Silverberg & A. Mucci, 1992. The phosphorus cycle in coastal marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 1129–1145.
Swarzenski, P. W. & J. A. Izbicki, 2009. Coastal groundwater dynamics off Santa Barbara, California: combining geochemical tracers, electromagnetic seepmeters, and electrical resistivity. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 83: 77–89.
Tenore, K. R. & R. B. Hanson, 1980. Availability of detritus of different types and ages to a polychaete macroconsumer, Capitella capitata. Limnology and Oceanography 25: 553–558.
Uchiyama, Y., K. Nadaoka, P. Rolke, K. Adachi & H. Yagi, 2000. Submarine groundwater discharge into the sea and associated nutrient transport in a sandy beach. Water Resources Research 36: 1467–1479.
Ullman, W., B. Chang, C. D. Miller & J. A. Madsen, 2003. Groundwater mixing, nutrient diagenesis, and discharges across a sandy beachface, Cape Henlopen, Delaware (USA). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 57: 539–552.
Urban-Malinga, B. & D. Burska, 2009. The colonization of macroalgal wrack by the meiofauna in the Arctic intertidal. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 85: 666–670.
Waska, H. & G. Kim, 2011. Submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) as a main nutrient source for benthic and water-column primary production in a large intertidal environment of the Yellow Sea. Journal of Sea Research 65: 103–113.
Williams, S., 1984. Decomposition of the tropical macroalga Caulerpa cupressoides (West) C. Agardh: field and laboratory studies. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 80: 109–124.
Wilson, A. M., M. Huettel & S. Klein, 2008. Grain size and depositional environment as predictors of permeability in coastal marine sands. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 80: 193–199.
Wooster, W., A. Bakun & D. McLain, 1976. The seasonal upwelling cycle along the eastern boundary of the North Atlantic. Journal of Marine Research 34: 131–141.
Yin, K. & P. Harrison, 2000. Influences of flood and ebb tides on nutrient fluxes and chlorophyll on an intertidal flat. Marine Ecology Progress Series 196: 75–85.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank L. Soliño, L. García, J. Hernández and I. Rodil for help with field work. Thanks are also due to E. Cacabelos for valuable comments and advice on statistical techniques. We are very grateful to 2 anonymous reviewers for their insightful and constructive comments. This research was supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (BFU2010-16080), Xunta de Galicia (10PXIB312152PR) and the Universidade de Vigo (C505122F64102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Pierluigi Viaroli
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barreiro, F., Gómez, M., López, J. et al. Coupling between macroalgal inputs and nutrients outcrop in exposed sandy beaches. Hydrobiologia 700, 73–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1220-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1220-z