Abstract
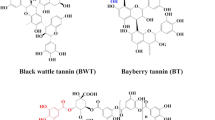
The inhibitory effect of tannins was investigated using, among others, potentiodynamic polarizations and Mössbauer spectroscopy. These techniques confirmed that the nature, pH and concentration of tannic solution are of upmost importance in the inhibitory properties of the solutions. It is observed that at low tannin concentration or pH, both, hydrolizable and condensed tannins, effectively inhibit iron corrosion, due to the redox properties of tannins. At pH ≈ 0, Mössbauer spectra of the frozen aqueous solutions of iron(III) with the tannin solutions showed that iron is in the form of a monomeric species [Fe(H2O)6]3 + , without coordination with the functional hydroxyl groups of the tannins. The suspended material consisted of amorphous ferric oxide and oxyhydroxides, though with quebracho tannin partly resulted in complex formation and in an iron (II) species from a redox process. Other tannins, such as chestnut hydrolysable tannins, do not complex iron at this low pH. Tannins react at high concentrations or pH (3 and 5) to form insoluble blue–black amorphous complexes of mono-and bis-type tannate complexes, with a relative amount of the bis-ferric tannate generally increasing with pH. Some Fe2 + in the form of hydrated polymeric ferrous tannate could be obtained. At pH 7, a partially hydrolyzed ferric tannate complex was also formed. The latter two phases do not provide corrosion protection. Tannin solutions at natural pH react with electrodeposited iron films (approx. 6 μm) to obtain products consisting only on the catecholate mono-complex of ferric tannate. Some aspects of the mechanism of tannins protection against corrosion are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lahodny-Šark, O., Kapor, F.: Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in the near neutral media by blends of tannin and calcium gluconate. Mater. Corros. 53, 264–268 (2002)
Rahim, A.A., Rocca, E., Steinmetz, J., Jain Kassim, M.: Inhibitive action of mangrove tannins and phosphoric acid on pre-rusted steel via electrochemical methods. Corros. Sci. 50, 1546–1550 (2008)
Ocampo, L.M, Margarit, I.C.P., Mattos, O.R., Córdoba-de-Torresi, S.I., Fragata, F.L.: Performance of rust converter based in phosphoric and tannic acids. Corros. Sci. 46, 1515–1525 (2004)
Hornus Sack, S., Romagnoli, R., Vetere, V.F., Elsner, C.I., Pardini, O., Almalvy, J.I., Di Sarli, A.R.: Evaluation of steel/primer based on chestnut tannin/paint film systems by EIS. J. Coat. Technol. 74(3), 63–69 (2002)
Singh, DDN., Yadav, S.: Role of tannic acid based rust converter on formation of passive film on zinc rich coating exposed in simulated concrete pore solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 202, 1526–1542 (2008)
Al-Mayouf, A.M.: Inhibitors for chemical cleaning of iron with tannic acid. Desalination 121, 173–182 (1999)
Chinchón, S., García, J., López-Atalaya, M., Linares, A., Vera, R.: Cement paste colouring in concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 34, 1987–1991 (2004)
Gust, J., Suwalski, J.: Use of Mössbauer spectroscopy to study reaction products of polyphenols and iron compounds. Corrosion 50(5), 355–365 (1994)
Iglesias, J., García de Saldaña, E., Jaén, J.A.: On the tannic acid interaction with metallic iron. Hyperfine Interact. 134, 109–114 (2001)
Jaén, J.A., Araúz, E.Y., Iglesias, J., Delgado, Y.: Reactivity of tannic acid with common corrosion products and its influences on the hydrolysis of iron in alkaline solutions. Hyperfine Interact. 148–149, 199–209 (2003)
Jaén, J.A., González, L., Vargas, A., y Olave, G.: Gallic acid, ellagic acid and pyrogallol reaction with metallic iron. Hyperfine Interact. 148–149, 227–235 (2003)
Martinez, S., Štern, I.: Ferric-tannate formation and anticorrosive properties of mimosa tannin in acid solutions. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 13(4), 191–199 (1999)
Martinez, S., Štern, I.: Inhibitory mechanism of low-carbon steel corrosion by mimosa tannin in sulphuric acid solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 31(9), 973–978 (2001)
Martinez, S., Štern, I.: Thermodynamic characterization of metal dissolution and inhibitor adsorption processes in the steel/mimosa tannin/sulfuric acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 199(1–4), 83–89 (2002)
Rahim, A.A. Rocca, E., Steinmentz, J. Kassim, M.J., Adnan, R., Sani Ibrahim, M.: Mangrove Tannins and their flavanoid monomers as alternative steel corrosion inhibitors in acidic medium. Corros. Sci. 49, 402–417 (2007)
Pardini, O.R., Amalvy, J.I., Di Sarli, A.R., Romagnoli, R., Vetere, V.F.: Formulation and testing of a waterborne primer containing chestnut tannin. J. Coat. Technol. 73(913), 99–106 (2001)
Matamala, G., Smeltzer, W., Droguett, G.: Use of tannin anticorrosive reaction primer to improve traditional coating systems. Corrosion 50, 270–275 (1994)
Morcillo, M., Feliu, S., Simancas, J., Bastidas, J.M., Galván, J.C., Feliu Jr., S., Almeida, E.M.: Corrosion of rusted steel in aqueous solutions of tannic acid. Corrosion 48(12), 1032–1039 (1992)
Barrero, C.A., Ocampo, L.M., Arroyave, C.E.: Possible improvements in the action of some rust converters. Corros. Sci. 43, 1003–1018 (2001)
Ocampo, L.M., Margarit, I.C.P., Mattos, O.R., Córdoba-Torresi, S.I., Fragata, F.L.: Performance of rust converter based in phosphoric and tannic acids. Corros. Sci. 46, 1515–1525 (2004)
Caballero, L., Felloni, L., Trabanelli, G., Pulidori, F.: The anodic dissolution of the behaviour of some corrosion inhibitors investigated by the potentiodynamic method. Electrochim. Acta 9(5), 485–494 (1964)
Jaén, J.A., García de Saldaña, E., Hernández, C.: Characterization of reaction products of iron and iron salts and aqueous plant extracts. Hyperfine Interact. 122, 139–145 (1999)
Jaén Osorio, J.A., Adames, I.M.: Evidencias espectroscópicas de la reacción de acomplejamiento y reducción de algunos productos de corrosión por el ácido gálico y el pirogalol. Rev. Cubana de Química (ISSN 0258-5595) XIX(1) (2007)
Jaén, J. A., Navarro, C.: Mössbauer and infrared spectroscopy as a diagnostic tool for the characterization of ferric tannates. Hyperfine Interact. 192(1), 61–67 (2009)
Hider, R.C., Howlin, B., Miller, J.R., Rahim Mohd-Nor, A., Silver, J.: Model compounds for microbial iron-transport compounds. IV: further solution chemistry and Mössbauer studies on iron (II) and iron (III) catechol complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 80, 51–56 (1983)
Murad, E., Johnston, J.H.: Iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. In: Long, G.J. (ed.) Mössbauer Applied to Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 2, pp. 507–582. Plenum Pub Co, New York–London (1987)
Vértes, A., Czakó-Nagy, I.: Mössbauer spectroscopy and its application to corrosion studies. Electrochim. Acta. 34(6), 721–758 (1989)
Coey, J.M.D., Readman, P.W.: Characterisation and magnetic properties of natural ferric gel. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 21(1), 45–51 (1973)
Jambor J.L., Dutrizac, J.E.: Occurrence and constitution of natural and synthetic ferrihydrite, a wide spread iron oxyhydroxide. Chem. Rev. 98, 2549–2585 (1998)
Raman, A., Kuban, B., Razvan, A.: The application of infrared spectroscopy to the study of atmospheric rust systems. Corr. Sci. 32(12), 1295–1306 (1991)
Cornell, R.M., Schwertmann, U.: The Iron Oxides, Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH (2003)
Carlson, L., Schwertmann, U.: Natural occurrence of feroxyhite (δ’-FeOOH). Clay Miner. 28(4), 272–280 (1980)
Kahani, S.A., Jafari, M.: A new method for preparation of magnetite from iron oxyhydroxide or iron oxide and ferrous salt in aqueous solution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1951–1954 (2009)
Miller, F.A., Wilkins, C.H.: Infrared spectra and characteristics frequencies of inorganic ions. Anal. Chem. 24(8), 1253–1294 (1952)
Vértes, A., Parak, F.: A study of the relationship between the spin relaxation and certain chemical properties of paramagnetic iron (III)-salt solutions by Mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2062–2068 (1972). doi:10.1039/DT9720002062
Chavez, F.A.B., Garg, V.K.: Mössbauer frozen solution studies of Fe(III) nitrate and Fe(III) perchlorate. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 37, 2283–2285 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaén, J.A., De Obaldía, J. & Rodríguez, M.V. Application of Mössbauer spectroscopy to the study of tannins inhibition of iron and steel corrosion. Hyperfine Interact 202, 25–38 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-011-0337-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-011-0337-1