Abstract
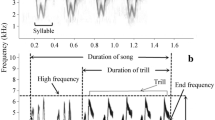
Gibbons are characterized by their species-specific calls, or songs. There are few studies of songs of Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus). To study the sound spectrum characteristics and test for intergroup differences in Hainan gibbon song, we studied the singing behavior of Hainan gibbons in Bawangling National Nature Reserve, Hainan Province, China, intermittently from August 2002 to February 2013, collecting 184 recordings. Our results show that: 1) Hainan gibbon song bouts occur mainly 0–4 h after dawn. 2) The songs of adult males living in groups are composed mainly of one to three short notes and one to five long notes, while solitary adult male songs consist only of long frequency modulated notes and no short or single notes. 3) The song chorus is dominated by adult males, while females add a great call. Males do not have a great call, unlike those in other gibbon species. There are no female solos. 4) The sound spectrum frequency is similar in adult males living in two different groups, but the duration of the first long note differed significantly between the groups. The sonic frequencies of male and female songs are lower than those of other gibbons: no more than 2 kHz. Hainan gibbon sound structure is simple, although females participate in the chorus, reflecting their primitive status among gibbon species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brockelman, W. Y., & Ali, R. (1987). Methods of surveying and sampling forest primate populations. In C. W. Marsh & R. A. Mittermerier (Eds.), Primate conservation in the tropical rain forest (pp. 23–62). New York: Alan R. Liss.
Brockelman, W. Y., & Srikosamatara, S. (1993). Estimation of density of gibbon groups by use of loud songs. American Journal of Primatology, 29, 93–108.
Caro, T. M. (1995). Pursuit-deterrence revisited. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 500–503.
Carpenter, C. R. (1940). A field study in Siam of the behavior and social relations of the gibbon (Hylobates lar). Comparative Psychology Monographs, 16, 1–212.
Chivers, D. J. (1977). The lesser apes.In Prince Rainier III of Monaco. In G. H. Bourne (Ed.), Primate conservation (pp. 539–598). London and New York: Academic Press.
Chivers, D. J. (2001). The swinging singing apes:Fighting for food and family in far-east forests.The apes:Challenges for the 21st century (pp. 1–28). Brookfield: Chicago Zoological Society.
Cowlishaw, G. (1992). Song function in gibbons. Behaviour, 121, 131–153.
Fan, P. F., Huang, B., Guan, Z. H., & Jiang, X. L. (2010). Singing behavior before and after male replacement in a western black crested gibbon group in Wuliang Mountain, Yunnan. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 30(2), 139–143.
Fan, P. F., Liu, C. M., Luo, W. S., & Jiang, X. L. (2007). Can a group elicit duets from its neighbours? A field study on the black crested gibbon (Nomascus concolor jingdongensis) in Central Yunnan, China. Folia Primatologica, 78(3), 186–195.
Fan, P. F., Xiao, W., Huo, S., & Jiang, X. L. (2009). Singing behavior and singing functions of black crested gibbons (Nomascus concolor jingdongensis) at Mt. Wuliang, Central Yunnan, China. American Journal of Primatology, 71, 539–547.
Haimoff, E. H. (1984a). The organization of song in the agile gibbon (Hylobates agilis). Folia Primatologica, 42, 42–61.
Haimoff, E. H. (1984b). The organization of song in the Hainan black gibbon (Hylobates Concolor hainanus). Primates, 25, 225–235.
Haimoff, E. H., Yang, X. J., He, S. J., et al. (1986). Census and survey o f wild black-crested gibbons (Hylobates concolor concolor ) in Yunnan Province, People’s Republic of China. Folia Primatologica, 46, 205–214.
Geissmann, T. (1993). Evolution of communication in gibbons (Hylobatidae). In Anthropological Institute, Philosoph. Faculty II, Zürich University.
Geissmann, T. (2000). Gibbon songs and human music in an evolutionary perspective. In N. L. Wallin & B. S. Merker (Eds.), The origins of music (pp. 103–123). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Geissmann, T. (2002). Duet-splitting and the evolution of gibbon songs. Biological Reviews, 77, 57–76.
Geissmann, T., Dang, N., Lormée, N., & Momberg, F. (2000). Vietnam primate conservation status review 2000–Part 1: Gibbons. Indochina Programme, Hanoi: Fauna and Flora International.
Gittins, S. P. (1984). Territorial advertisement and defence in gibbons. In H. Preuschoft, D. J. Chivers, W. Y. Brockelman, & N. Creel (Eds.), The lesser apes: evolutionary and behavioural biology (pp. 420–424). Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Groves, C. P. (1972). Systematics and phylogeny of gibbons. In D. M. Rumbaugh (Ed.), Gibbon and siamang (pp. 1–89). Basel & New York: Karger.
Groves, C. P. (2004). Taxonomy and biogeography of primates in Vietnam and neighbouring regions.In. In T. Nadler, U. Streicher, & H. T. Long (Eds.), Conservation of primates in Vietnam (pp. 15–22). Hanoi: Frankfurt Zoological Society, Vietnam Primate Conservation Programme, Endangered Primate Rescue Center, Cuc Phuong National Park.
Kappeler, M. (1984). Vocal bouts and territorial maintenance in the moloch gibbon. In H. Preuschoft, D. J. Chivers, W. Y. Brockelman, & N. Creel (Eds.), The lesser apes (pp. 376–389). Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Konrad, R., & Geissmann, T. (2006). Vocal diversity and taxonomy of Nomascus in Cambodia. International Journal of Primatology, 27, 713–745.
Marshall, J. T., & Marshall, E. R. (1976). Gibbons and their territorial songs. Science, 193, 235–237.
Rajpurohit, L. S., & Sommer, V. (1991). Sex differences in mortality among langurs (Presbytis enteilus) of Jodhpur, Rajasthan. Folia Primatologica, 56, 17–27.
Rawson, B. (2004). Vocalization patterns in the yellow-cheeked crested gibbon (Nomascus gabriellae). In T. Nadler, U. Streicher, & H. T. Long (Eds.), Conservation of primates in Vietnam (pp. 130–136). Hanoi: Frankfurt Zoological Society, Vietnam Primate Conservation Programme, Endangered Primate Rescue Center, Cuc Phuong National Park.
Ruppell, J. (2010). Vocal diversity and taxonomy of Nomascus in central Vietnam and southern Laos. International Journal of Primatology, 31(1), 73–96.
Su, B., Kressirer, P., Monda, K., Wang, W., Jiang, X. L., Wang, Y. X., et al. (1996). The research of genetic diversity and molecule system of black gibbons of China, Non-invasive sampling DNA sequence analysis. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 26(5), 414–419.
Tenaza, R. R. (1976). Songs, choruses and counter singing of kloss’ gibbons (Hylobatesk lossii) in Siberut Island. Zeit Tierpsychologie, 40, 37–52.
Van Gulik, R. H. (1967). The gibbon in China: An essay in Chinese animal lore. Leiden: E. J. Brill.
Wang, Y. X., Jiang, X. L., & Feng, Q. (2000). Distribution, status and conservation of black-crested gibbon (Hylobates concolor) in China. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 19(2), 138–147.
Zhang, Y. P. (1997). Mitochondrial DNA sequence evolution and phylogenetic relationships of Gibbons. Acta Genetica Sinica, 24(3), 231–237.
Zhou, J. (2008). The ecology and behavior traits of Hainan black-crested gibbon (Nomascus hainanus). Unpublished Ph.D. dissertation, Northeast Normal University, Jilin, China.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a 2011 grant from the National Nature Science Funds to the project “The nutrition and ecologic strategy of Hainan gibbons” (No. 31170365). This research was conducted with the help of students Xiaofeng Gao, Yun Liu, and Wenyong Li, and other staff of the Bawangling Nature Reserve. We thank them for their support. We also thank the reviewers and editors for their constructive and positive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, H., Zhou, J. & Yang, Y. Sound Spectrum Characteristics of Songs of Hainan Gibbon (Nomascus hainanus). Int J Primatol 35, 547–556 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-014-9767-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-014-9767-3