Abstract
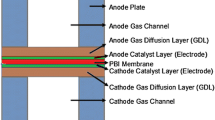
Accurate information on the temperature field and associated heat transfer rates is particularly important for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) and PEM electrolyzers. An important parameter in fuel cell and electrolyzer performance analysis is the effective thermal conductivity of the gas diffusion layer (GDL) which is a solid porous medium. Usually, this parameter is introduced in modeling and performance analysis without taking into account the dependence of the GDL thermal conductivity λ (in W · m−1 · K−1) on mechanical compression. Nevertheless, mechanical stresses arising in an operating system can change significantly the thermal conductivity and heat exchange. Metrology allowing the characterization of the GDL thermal conductivity as a function of the applied mechanical compression has been developed in this study using the transient hot-wire technique (THW). This method is the best for obtaining standard reference data in fluids, but it is rarely used for thermal-conductivity measurements in solids. The experiments provided with Quintech carbon cloth indicate a strong dependence (up to 300%) of the thermal conductivity λ on the applied mechanical load. The experiments have been provided in the pressure range 0 < p < 8 MPa which corresponds to stresses arising in fuel cells. All obtained experimental results have been fitted by the equation λ = 0.9log(12p + 17)(1 − 0.4e−50p) with 9% uncertainty. The obtained experimental dependence can be used for correct modeling of coupled thermo/electro-mechanical phenomena in fuel cells and electrolyzers. Special attention has been devoted to justification of the main hypotheses of the THW method and for estimation of the possible influence of the contact resistances. For this purpose, measurements with a different number of carbon cloth layers have been provided. The conducted experiments indicate the independence of the measured thermal conductivity on the number of GDL layers and, thus, justify the robustness of the developed method and apparatus for this type of application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vielstich, W., Lamm, A., Gasteiger, H.A. (eds): Handbook of Fuel Cell Fundamentals, Technology and Application. Wiley, Chichester, UK (2003)
Grigoriev S.A., Porembsky V.I., Fateev V.N.: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 31, 171 (2006)
Escribano S., Blachot J.F., Etheve M., Morin A., Mosdale R.: J. Power Sources 156, 8 (2006)
Kleemann J., Finsterwalder F., Tillmetz W.: J. Power Sources 190, 92 (2009)
Zong Y., Zhou B., Sobiesiak A.: J. Power Sources 161, 143 (2006)
Wen C., Lin Y., Lu C.: J. Power Sources 189, 1100 (2009)
Kandlikar S.G., Lu Z.: Appl. Therm. Eng. 29, 1276 (2009)
Bograchev D., Gueguen M., Grandidier J.C., Martemianov S.: J. Power Sources 180, 393 (2008)
Martemianov S., Gueguen M., Grandidier J.C., Bograchev D.: J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2, 49 (2009)
Kusoglu A., Karlssona A.M., Santare M.H., Cleghorn S., Johnson W.B.: J. Power Sources 161, 987 (2006)
Bograchev D., Gueguen M., Grandidier J.C., Martemianov S.: Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 33, 5703 (2008)
Ge J., Higier A., Liu H.: J. Power Sources 159, 922 (2006)
Zhou P., Wu C.W., Ma G.J.: J. Power Sources 163, 874 (2007)
Zhang L., Liu Y., Shuxin Wang H.S., Zhou Y., Jack Hub S.: J. Power Sources 162, 1165 (2006)
Zhou P., Wu C.W., Ma G.J.: J. Power Sources 159, 1115 (2006)
Zhou P., Wu C.W.: J. Power Sources 170, 93 (2007)
Cindrella L., Kannan A.M., Lin J.F., Saminathan K., Hoc Y., Lind C.W., Wertze J.: J. Power Sources 194, 146 (2009)
Su Z.Y., Liu C.T., Chang H.P., Li C.H., Huang K.J., Sui P.C.: J. Power Sources 183, 182 (2008)
Ramousse J., Didierjean S., Lottin O., Maillet D.: Int. J. Therm. Sci. 47, 1 (2008)
Karimi G., Li X., Teertstra P.: J. Electrochim. Acta 55, 1619 (2010)
Djilali N., Lu D.: Int. J. Therm. Sci. 41, 29 (2002)
Vie P.J.S., Kjelstrup S.: J. Electrochim. Acta 49, 1069 (2004)
Nguyen P.T., Berning T., Djilali N.: J. Power Sources 130, 149 (2004)
Ju H., Meng H., Wang C.Y.: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 1303 (2005)
Khandelwal M., Mench M.M.: J. Power Sources 161, 1106 (2006)
Toray Industries Inc., Toray Carbon Paper, Toray Industries Inc., Advanced Composites Department (2001)
Healy J.J., De Groot J.J., Kestin J.: Physica C (Amsterdam) 82, 392 (1976)
Nagasaka Y., Nagashima A.: J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 14, 1435 (1981)
Alloush A., Gosney W.B., Wakeham W.A.: Int. J. Thermophys. 3, 225 (1982)
Perkins R.A., Ramires M.L.V., Nieto De Castro C.A.: J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 105, 221 (2000)
Beirao S.G.S., Ramires M.L.V., Dix M., Nieto De Castro C.A.: Int. J. Thermophys. 27, 1018 (2006)
Bilek J., Atkinson J., Wakeham W.A.: Int. J. Thermophys. 27, 1626 (2006)
Bilek J., Atkinson J., Wakeham W.A.: Int. J. Thermophys. 28, 496 (2007)
Garnier J.P., Maye J.P., Saillard J., Thévenot G., Kadjo A., Martemianov S.: Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 468 (2008)
Kadjo A., Garnier J.P., Maye J.P., Martemianov S.: Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 1267 (2008)
Carslaw H.S., Jaeger J.C.: Conduction of Heat in Solids. Oxford University Press, London (1959)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamour, M., Garnier, J.P., Grandidier, J.C. et al. Thermal-Conductivity Characterization of Gas Diffusion Layer in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers Under Mechanical Loading. Int J Thermophys 32, 1025–1037 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-011-0964-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-011-0964-4