Abstract
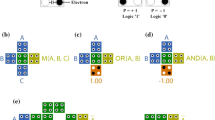
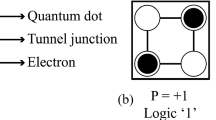
Quantum-dot cellular automata is a new technology to design the efficient combinational and sequential circuits at the nano-scale. This technology has many desirable advantages compared to the CMOS technology such as low power consumption, less occupation area and low latency. These features make it suitable for use in flip-flop design. In this paper, with knowing the characteristics of reversible logic, we design new structures for flip-flops. The operations of these structures are evaluated with QCADesigner Version 2.0.3 simulator. In addition, we calculate the power dissipation of these structures by QCAPro tool. The results illustrated that proposed structures are efficient compared to the previous ones.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 October 2017
The authors want to add two references in the original version of this article.
References
Goyal, D., Sharma, V.: VHDL implementation of reversible logic gate. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Res. (IJATER), 2(3) (2012). ISSN NO: 2250-3536
Compano, R., Molenkamp, L., Paul, D.J.: Technology Roadmap for Nanoelec-Tronics Proceedings of the European Commission IST Programme, Future Emerging Technology (1999)
Tougaw, P.D., Lent, C.S.: Logical devices implemented using quantum cellular automata. Appl. Phys. 75, 1818–1824 (1994)
Kianpour, M., Sabbaghi-Nadooshan, R.: A conventional design and sim500 ulation for CLB implementation of an FPGA quantum-dot cellular automata. Microprocess. Microsyst. 38, 1046–1062 (2014)
Hashemi, S., Navi, K.: Reversible multiplexer design in quantum-dot cellular automata. Quantum Matter 3, 523–528 (2014)
Cho, H., Swartzlander, E.: Adder and multiplier design in quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 58(6), 721–727 (2009)
Ali, B., Hossin, M., Ullah, E.: Design of reversible sequential circuit using reversible logic synthesis. International Journal of VLSI Design &, Communication Systems (VLSICS) vol. 2, no. 4 (2011)
Saravanan, P., Kalpana, P.: A novel and systematic approach to implement reversible gates in quantum dot cellular automata. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 12, 307–316 (2013)
Thapliyal, H., Ranganathan, N.: Reversible logic-based concurrently testable latches for molecular QCA. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 9, 62–69 (2010)
Moustafa, A., Younes, A., Hassan, Y.F.: A customizable quantum-dot cellular automata building block for the synthesis of classical and reversible circuits. Sci. World J. doi:10.1155/2015/705056 (2015)
Navi, K., Sayedsalehi, S., Farazkish, R., Rahimi Azghadi, M.: Five-input majority gate, a new device for quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 7, 1546–1553 (2010)
Navi, K., Farazkish, R., Sayedsalehi, S., Rahimi Azghadi, M.: A new quantum-dot cellular automata full-adder. Microelectron. J. 41, 820–826 (2010). (Elsevier)
Mukhopadhyay, D., Dutta, P.: A study on energy optimized 4 dot 2 electron two dimensional quantum dot cellular automata logical reversible flip-flops. J. 46, 519–530 (2015). (Elsevier)
Blair, E.P., Liu, M., Lent, C.S.: Signal energy in quantum-dot cellular automata bit packets. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 8, 972–983 (2011)
Timler, J., Lent, C.S.: Power gain and dissipation in quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 823–831 (2002)
Himanshu, T., Srinivas, M.B.: A beginning in the reversible logic synthesis of sequential circuits having features of online testability, SPIE Microelectronics, MEMS, and Nanotechnology Symposium, Brisbane, Australia (2005)
Ali, B., Hossin, M., Ullah, E.: Design of reversible sequential circuit using reversible logic synthesis. International Journal of VLSI design and Communication Systems (VLSICS) vol. 2, no. 4 (2011)
Walus, K., Dysart, T.J., Jullien, G.A., Budiman, R.A.: QCADEsigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 3(1) (2004)
Srivastava, S., Asthana, A., Bhanja, S., Sarkar, S.: QCAPro-An Error Power Estimation Tool for QCA Circuit Design Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium Circuits System, pp 2377–2380 (2011)
Heikalabad, S.R., Navin, A.H., Hosseinzadeh, M.: Midpoint memory: a special memory structure for Data-Oriented models implementation. J. Circuits, Syst. Comput. 24(5) (2015)
Heikalabad, S.R., Navin, A.H., Hosseinzadeh, M.: Content addressable memory cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. Eng. 163, 140–150 (2016)
Karkaj, E.T., Heikalabad, S.R.: Binary to gray and gray to binary converter in quantum-dot cellular automata. Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, vol. 130. doi:10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.11.087 (2017)
Karkaj, E.T., Heikalabad, S.R.: A testable parity conservative gate in quantum-dot cellular automata. Superlattices Microstruct. doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2016.08.054 (2017)
Asfestani, M.N., Heikalabad, S.R.: A unique structure for the multiplexer in quantum-dot cellular automata to create a revolution in design of nanostructures. Phys. B Condens. Matter 512, 91–99 (2017). doi:10.1016/j.physb.2017.02.028
Barughi, Y.Z., Heikalabad, S.R.: A Three-Layer Full Adder/Subtractor Structure in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. doi:10.1007/s10773-017-3453-0 (2017)
Asfestani, M.N., Heikalabad, S.R.: A novel multiplexer-based structure for random access memory cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Phys. B Condens. Matter 521, 162–167 (2017). doi:10.1016/j.physb.2017.06.059
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3575-4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rad, S.K., Heikalabad, S.R. Reversible Flip-Flops in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. Int J Theor Phys 56, 2990–3004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3466-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3466-8