Abstract
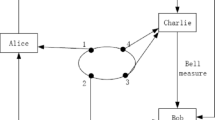
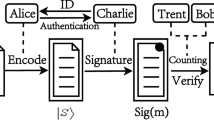
As an important topic of quantum cryptography, quantum voting has attracted more and more attentions recently. However, with our analysis, it can be seen that there exist some serious problems in a particular quantum voting model. Firstly, the voter does not have the ability to vote as his own. Secondly, the voter may be dishonest and can deny some corresponding voting results. Furthermore, some improvements will be presented to solve the loopholes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jan, J.K., Tai, C.C.: A secure electronic voting protocol with ic cards. J. Syst. Softw. 39(2), 93–101 (1997)
Ku, W.C., Wang, S.D.: A secure and practical electronic voting scheme. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V(22), 279–286 (1999)
Tian, J.H.: A quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine four-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(2), 809–816 (2016)
Shao, A.X., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A quantum multi-proxy multi-blind-signature scheme based on genuine six-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(12), 5216–5224 (2016)
Khodambashi, S., Zakerolhosseini, A.: A sessional blind signature based on quantum cryptography. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(1), 121–130 (2014)
Naseri, M., Gong, L.H., Houshmand, M., Matin, L.F.: An anonymous surveying protocol via greenberger-horne-zeilinger states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(10), 4436–4444 (2016)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Comput. 26(5), 1484–1509 (1997)
Grover, L.K.: Fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. Twenty-eighth Amc Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219 (1996)
Hillery, M., Ziman, M., Bužek, V., et al.: Towards quantum-based privacy and voting. Phys. Lett. A 349(1-4), 75–81 (2006)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A. 75(1), 10064–10070 (2005)
Horoshko, D., Kilin, S.: Quantum anonymous voting with anonymity check. Phys. Lett. A 375(8), 1172–1175 (2011)
Bonanome, M., et al.: Toward protocols for quantum-ensured privacy and secure voting. Phys. Rev. A 84(2), 290–296 (2011)
Hillery, M.: Quantum voting and privacy protection: First steps. Spienewsroom (2006)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A voting protocol based on the controlled quantum operation teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(5), 2303–2310 (2016)
Wang, Q.L., Yu, C., Gao, F., Qi, H., Wen, Q.: Self-tallying quantum anonymous voting. Phys. Rev. A 94(2), 022333 (2016)
Harn, L.: Cryptanalysis of the blind signatures based on the discrete logarithm problem. Electr. Lett. 31(14), 1136 (1995)
Lysyanskaya, A., Ramzan, Z.: Group blind digital signatures: A scalable solution to electronic cash. Proceedings of the 2nd Financial Cryptography Conference (1998)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Yu, Y.F., Li, P.F.: A electronic voting scheme achieved by using quantum proxy signature. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(9), 4081–4088 (2016)
Thapliyal, K., Sharma, R.D., Pathak, A.: Protocols for quantum binary voting. Int. J. Quantum Inform. 15(01), 1750007 (2017)
Zhang, J.L., Xie, S.C., Zhang, J.Z.: An elaborate secure quantum voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 3019–3028 (2017)
Zhang, J.L., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A choreographed distributed electronic voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 2676–2686 (2018)
Niu, X.F., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C., Chen, B.Q.: An improved quantum voting scheme[J]. International journal of theoretical physics: An improved quantum voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3200–3206 (2018)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Jiang, X.L., Li, P.F.: A new proxy electronic voting scheme achieved by six-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(2), 1–8 (2017)
Muralidharan, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Perfect teleportation, quantum-state sharing, and superdense coding through a genuinely entangled five-qubit state. Phys. Rev. A 77 (3), 032321 (2008)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(21), 3121 (1992)
Goldenberg, L., Vaidman, L.: Quantum cryptography based on orthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75(7), 1239–1243 (1995)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Physical Review A 65(3) (2002)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Inamori, H., Lutkenhaus, N., Mayers, D.: Unconditional security of practical quantum key distribution. European Phys. J. D. 41(3), 599–627 (2007)
Lo, H.-K.: A simple proof of the unconditional security of quantum key distribution. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 34(35), 6957–6967 (2001)
Wang, Q., Das, S., Wilde, M.M.: Hadamard quantum broadcast channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(10), 248 (2017)
Acknowledgments
We thank to the support of Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of the Theory and Computation of Complex Systems. The work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61802118, Open Foundation of State key Laboratory of Networking and Switching Technology (BUPT) under Grant No. SKLNST-2018-1-07, University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province under Grant No. UNPYSCT-2018015, Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province under Grant No.JJ2019LH0173, Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Foundation under Grant No.LBH-Z17048 and Heilongjiang University Innovation Fund under Grant No.YJSCX2019-205HLJU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, BM., Zhang, KJ., Zhang, X. et al. The Cryptanalysis and Improvement of a Particular Quantum Voting Model. Int J Theor Phys 59, 1109–1120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04392-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-020-04392-6