Abstract
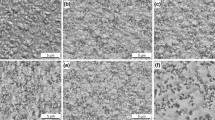
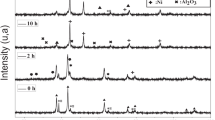
The aim of this work is the production and characterization of composite nickel matrix electrodeposits. Pure nickel and composite nickel matrix deposits containing either micro- or nano-particles of silicon carbide were prepared using a Watts type bath. The electrodeposition was carried out under both direct and pulse current conditions at different frequencies. With the same quantity of powder in the bath, the embedded micro-powder content is about 25–30%w while the nano-powder content is always less than 1%w. The mechanical properties of the nano-composites increases despite the low ceramic content. SEM micrographs of the microstructure and XRD-line profile analysis show that the presence of ceramic powder in both baths changes the crystallisation process leading to enhanced mechanical properties even at ceramic contents less than 1%, as in the nano-composite case. The presence of the ceramic phase and changes in the microstructure both decrease the mass loss during abrasion by up to 70% for micro-composites and 45% for nano-composites.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guglielmi N (1972) J Electrochem Soc 119:1009
Roos JR, Celis JP, Fransaer J, Buelens C (1990) J Metals 42:60
Hovestad R, Janssen LJJ (1995) Rev Appl Electrochem 40:519
Benea L, Bonora PL, Borello R, Martelli A (2002) Wear 249:995
Zimmermann AF, Palumbo G, Aust KT, Erb U (2002) Mater Sci Eng A328:137
Hou KH, Ger MD, Wang LM (2002) Wear 253:994
Garcia I, Fransaer J, Celis JP (2001) Surf Coat Technol 148:171
Low CTJ, Willis RGA, Walsh FC (2006) Surf Coat Technol 201:371
Gyftou P, Stroumbouli M, Pavlatou EA, Asimidis K, Spyrellis N (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:4544
Lekka M, Kouloumbi N, Gajo M, Bonora PL (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:4551
Surender M, Balasubramanian R, Basu B (2004) Surf Coat Technol 187:93
Garcia I, Conde A, Langelaan G, Fransaer J, Celis JP (2003) Corros Sci 45:1173
Medelienè V (2002) Surf Coat Technol 154:104
Malfatti CF, Ferreira JZ, Santos CB, Souza BV, Fallavena EP, Vaillant S, Bonino JP (2005) Corros Sci 47:567
Pavlatou EA, Stroumbouli M, Gyftou P, Spyrellis N (2006) J Appl Electrochem 36:385
Zimmerman AF, Clark DG, Aust KT, Erb U (2002) Mater Lett 52:85
Williamson GK, Hall WH (1953) Acta Metall 1:22
Cullity (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison Wesley Publishing, London
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the microstructures group of the Department of Material Engineering and Industrial Technologies of the University of Trento for the XRD measurements and in particular Prof. Paolo Scardi for useful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanella, C., Lekka, M. & Bonora, P.L. Influence of the particle size on the mechanical and electrochemical behaviour of micro- and nano-nickel matrix composite coatings. J Appl Electrochem 39, 31–38 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-008-9635-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-008-9635-y