Abstract
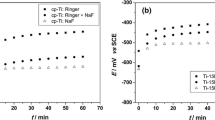
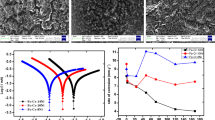
This study concerns an investigation of the corrosion behavior of 316 stainless steel, CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V alloys in simulated body conditions (ringer lactate) at 37 °C by the use of Tafel plots, mixed potential and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Ti6Al4V alloy has the highest corrosion resistance followed by CoCr alloy. Ti6Al4V–CoCrMO was the best couple for galvanic corrosion with the minimum galvanic potential and current values according to mixed potential theory and Tafel method. It was concluded that Ti6Al4V was the most suitable material for implant applications in the human body.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paul JP (1997) J Eng Med 211:119
Kazantzis G (1981) Environ Health Perspect 40:143
Van Noort R (1987) J Mater Sci 22:3801
Clark GC, Williams DF (1982) J Biomed Mater Res 16:125
Williams RL, Brown SA, Merritt K (1988) Biomaterials 9:181
Bandyopadhya R, Cahoon JR (1977) Corrosion 33:204
Gluszek J, Masalki J, Furman P, Nitsch K (1997) Biomaterials 18:789
Hoar TP, Mears DC (1966) Proc R Soc Lond A 294:486
Milošev I, Metikoš-Huković M, Strehblow HH (2000) Biomaterials 21:2103
Reclaru L, Meyer JM (1998) Biomaterials 19:85
Hsu RW, Yang C, Huang C, Chen Y (2004) Mater Chem Phys 86269
Therin M, Meunier A, Christel P (2003) European Cells and Mater 5:21
Gurappa I (2002) Mater Charact 49:73
MacDonald D, Mckubre M (1981) Electrochemical impedance techniques in corrosion science: electrochemical corrosion testing. ASTM Spec Tech Publ 727:110
Mansfeld M, Kendig M, Tsai S (1982) Corrosion 38:478
Popa MV, Demetrescu I, Vasilescu E, Drob P, Lopez AS, Rosca JM, Vasilescua C, Ionita D (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:2113
Grosgogeat B, Boinet M, Dalard F, Lissac M (2004) Biomed Mater Eng 14:323
Rosca JCM, Santana EDH, Castro JR, Lopez AS, Dro P, Vasilescu C (2005) Mater Corros 56:692
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Gazi University Research Fund (Project: 04/2003-14) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Songür, M., Çelikkan, H., Gökmeşe, F. et al. Electrochemical corrosion properties of metal alloys used in orthopaedic implants. J Appl Electrochem 39, 1259–1265 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-9793-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-9793-6