Abstract
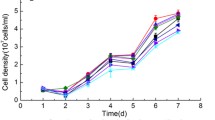
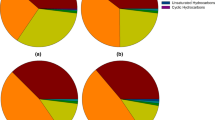
Cultivation in Zehnder medium containing 5.1 mg L−1 zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) boosted the growth of the green algae Desmodesmus subspicatus, Dunaliella salina, Parachlorella kessleri and Raphidocelis subcapitata and the eustigmatophycean algae Nannochloropsis limnetica and Trachydiscus minutus. In the cyanobacterium Arthrospira maxima, growth stimulation occurred at 1.7–5.1 mg L−1 nZVI. In all studied microorganisms, 5.1 mg L−1 nZVI strongly enhanced lipid accumulation, decreased the content of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids with the exception of palmitoleic acid and increased the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids in cells. The nZVI particles may provide a suitable source of iron causing increased cell growth and induce metabolic changes resulting in higher lipid production and changes in fatty acid (FA) composition. Altered lipid synthesis may reflect the oxidative action of nZVI. Further research may contribute to optimizing the economical production of oils from oleaginous microorganisms and help clarify the mechanism of nZVI action.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El Baky HH, El-Baroty GS, Bouaid A, Martinez M, Aracil J (2012) Enhancement of lipid accumulation in Scenedesmus obliquus by optimizing CO2 and Fe3+ levels for biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 119:429–432
Adarme-Vega TC, Thomas-Hall SR, Schenk PM (2014) Towards sustainable sources for omega-3 fatty acids production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 26:14–18
Adeleye AS, Keller AA, Miller RJ, Lenihan HS (2013) Persistence of commercial nanoscaled zero-valent iron (nZVI) and by-products. J Nanopart Res 15:1–18
Andrews NC, Fleming MD, Gunshin H (1999) Iron transport across biologic membranes. Nutr Rev 57:114–123
Bleackley MR, MacGillivray RTA (2011) Transition metal homeostasis: from yeast to human disease. Biometals 24:785–809
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211:112–125
Dembitsky VM, Rezanka T, Bychek IA, Shustov MV (1991) Identification of fatty acids from Cladonia lichens. Phytochemistry 30:4015–4018
Dembitsky VM, Rezanka T, Bychek IA (1992) Fatty acids and phospholipids from lichens of the order Lecanorales. Phytochemistry 31:851–853
Gigova L, Ivanova N, Gacheva G, Andreeva R, Furnadzhieva S (2012) Response of Trachydiscus minutus (Xanthophyceae) to temperature and light. J Phycol 48:85–93
Griffiths MJ, Harrison STL (2009) Lipid productivity as a key characteristic for choosing algal species for biodiesel production. J Appl Phycol 21:493–507
Hong F, Zhou J, Liu C, Yang F, Wu C, Zheng L, Yang P (2005) Effect of nano-TiO2 on photochemical reaction of chloroplasts of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 105:269–279
Huang X, Wei L, Huang Z, Yan J (2014) Effect of high ferric ion concentrations on total lipids and lipid characteristics of Tetraselmis subcordiformis, Nannochloropsis oculata and Pavlova viridis. J Appl Phycol 26:105–114
Johnston BD et al (2010) Bioavailability of nanoscale metal oxides TiO2, CeO2, and ZnO to Fish. Environ Sci Technol 44:1144–1151
Kadar E, Rooks P, Lakey C, White DA (2012) The effect of engineered iron nanoparticles on growth and metabolic status of marine microalgae cultures. Sci Total Environ 439:8–17
Kang NK, Lee B, Choi G-G, Moon M, Park MS, Lim J, Yang J-W (2014) Enhancing lipid productivity of Chlorella vulgaris using oxidative stress by TiO2 nanoparticles. Korean J Chem Eng 31:861–867
Kates M (1986) Techniques of lipidology: isolation, analysis and identification of lipids. In: Work TS, Work E (eds) Laboratory techniques in biochemistry and molecular biology, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 220–223
Krongkan J, Jeeraporn P, Sudaporn T, Chayakorn P, Yuwadee P (2013) Selection of some native microalgal strains for possibility of bio-oil production in Thailand. Chiang Mai J Sci 40:593–602
Li XQ, Elliott DW, Zhang WX (2006) Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 31:111–122
Lukavský J, Furnadjieva S, Cepák V (2003) Toxicity of metals, Al, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb and Zn on microalgae, using microplate bioassay 1: Chlorella kessleri, Scenedesmus quadricauda, Sc. subspicatus and Raphidocelis subcapitata (Selenastrum capricornutum). Arch Hydrobiol Suppl 149:127–141
Mahajan P, Dhoke SK, Khanna AS (2011) Effect of nano-ZnO particle suspension on growth of mung (Vigna radiata) and gram (Cicer arietinum) seedlings using plant agar method. J Nanotechnol 2011:1–7
Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2010) Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 14:217–232
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Nemecek J, Lhotsky O, Cajthaml T (2014) Nanoscale zero-valent iron application for in situ reduction of hexavalent chromium and its effects on indigenous microorganism populations. Sci Total Environ 485:739–747
Pribyl P, Cepak V, Zachleder V (2012) Production of lipids in 10 strains of Chlorella and Parachlorella, and enhanced lipid productivity in Chlorella vulgaris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:549–561
Rezanka T, Lukavsky J, Nedbalova L, Sigler K (2011) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus starvation on the polyunsaturated triacylglycerol composition, including positional isomer distribution, in the alga Trachydiscus minutus. Phytochemistry 72:2342–2351
Ševců A, El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ, Černík M (2011) Oxidative stress induced in microorganisms by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Microbes Environ 26:271–281
Šmilauer P, Lepš J (2014) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO 5. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Staub R (1961) Ernährungsphysiologisch-autökologische Untersuchungen an der planktonischen Blaualge Oscillatoria rubescens DC. Schweiz Z Hydrol 23:82–198
Verma A, Stellacci F (2010) Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle-cell interactions. Small 6:12–21
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by GACR P503/11/0215 and GACR 14-00227S, by Competence Centres TE01020218 and Biorefinery Res. Centre of Competence TE 01020080 grants of the Czech Technology Agency, by the Institutional Internal Project RVO61388971, by ICT IGA project no. A2 FPBT 2014 022, and Centre for Algal Biotechnologies (Algatech) project, reg. no. CZ.1.05/2.1.00/03.0110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 350 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pádrová, K., Lukavský, J., Nedbalová, L. et al. Trace concentrations of iron nanoparticles cause overproduction of biomass and lipids during cultivation of cyanobacteria and microalgae. J Appl Phycol 27, 1443–1451 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0477-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0477-1