Abstract
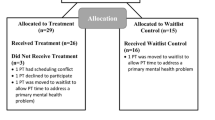
We evaluated the efficacy of a social skills training intervention designed to improve adolescents’ social, emotional and behavioral adjustment, Social Skills Group Intervention-Adolescent (S.S.GRIN-A). Seventy-four adolescents (ages 13–16 years) and their parents were randomly assigned to either the treatment group (N = 40) or a wait-list control group (N = 34). Adolescents in the treatment and control groups were compared on global self-concept, social self-efficacy, internalizing problems, and externalizing problems pre- and post-intervention. Youth in the treatment group demonstrated enhanced global self-concept, increased social self-efficacy, and decreased internalizing problems as compared to youth in the control group. No differences in externalizing behavior were found. We discuss the effectiveness of S.S.GRIN-A as a general program designed for addressing a range of adjustment issues and social skill deficits in adolescents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, P. D. (2003). Missing data techniques for structural equation modeling. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 112, 545–557. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.112.4.545.
Armsden, G. T., & Greenberg, M. T. (1987). The inventory of parent and peer attachment: Individual differences and their relationship to psychological well-being in adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 16, 427–454. doi:10.1007/BF02202939.
Arnett, J. J. (1999). Adolescent storm and stress: Reconsidered. The American Psychologist, 54, 317–326. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.54.5.317.
Asher, S. R., Parker, J. G., & Walker, D. L. (1996). Distinguishing friendship from acceptance: Implications for intervention and assessment. In W. M. Bukowski, A. F. Newcomb & W. W. Hartup (Eds.), The company they keep: Friendship in childhood and adolescence (pp. 366–405). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Beelman, A., Pfingsten, U., & Losel, F. (1994). Effects of training social competence in children: A meta analysis of recent evaluation studies. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 23, 260–271. doi:10.1207/s15374424jccp2303_4.
Berndt, T. J. (1996). Exploring the effects of friendship quality on social development. In W. M. Bukowski, A. F. Newcomb & W. W. Hartup (Eds.), The company they keep: Friendships in childhood and adolescence (pp. 346–365). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Bloom, H. S. (2005). Randomizing groups to evaluate place-based programs. In H. S. Bloom (Ed.), Learning more from social experiments: Evolving analytic approaches (pp. 115–172). New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
Brown, B. B. (1990). Peer groups and peer cultures. In S. S. Feldman & G. R. Elliot (Eds.), At the threshold: The developing adolescent (pp. 171–196). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Bukowski, W. M., & Hoza, B. (1989). Popularity and friendship: Issues in theory, measurement and outcome. In T. J. Berndt & G. W. Ladd (Eds.), Peer relationships in child development (pp. 15–45). New York: Wiley.
Cauce, A. M. (1986). Social networks and social competence: Exploring the effects of early adolescent friendships. American Journal of Community Psychology, 14, 607–628. doi:10.1007/BF00931339.
Cheng, H., & Furnham, A. (2004). Perceived parental rearing style, self-esteem and self-criticism as predictors of happiness. Journal of Happiness Studies, 5, 1–21. doi:10.1023/B:JOHS.0000021704.35267.05.
Coates, D. L. (1985). Relationships between self-concept measures and social network characteristics for black adolescents’ social networks. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 5, 319–338. doi:10.1177/0272431685053006.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Coie, J. D. (1990). Toward a theory of peer rejection. In S. R. Asher & J. D. Coie (Eds.), Peer rejection in childhood (pp. 365–401). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Coie, J. D., Lochman, J. E., Terry, R., & Hyman, C. (1992). Predicting early adolescent disorder from childhood aggression and peer rejection. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60, 783–792. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.60.5.783.
Cole, D. A., & Carpentieri, S. (1990). Social status and the comorbidity of child depression and conduct disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 58, 748–757. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.58.6.748.
Consortium on the School-based Promotion of Social Competence. (1996). The School-based Promotion of Social Competence. In R. J. Haggerty, L. R. Sherrod, N. Garmezy & M. Rutter (Eds.), Stress, risk, and resilience in children and adolescents: Processes, mechanisms, and interventions (pp. 268–316). NY: Cambridge University Press.
Cramer, P., & Tracy, A. (2005). The pathway from child personality to adult adjustment: The road is not straight. Journal of Research in Personality, 39, 369–394. doi:10.1016/j.jrp.2004.07.003.
Crick, N. R., & Dodge, K. A. (1994). A review and reformulation of social information processing in children’s social adjustment. Psychological Bulletin, 115, 74–101. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.115.1.74.
Denney, D. R. (1975). The effects of exemplary and cognitive models and self-rehearsal on youth’s interrogative strategies. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 19, 476–488. doi:10.1016/0022-0965(75)90077-6.
DeRosier, M. E. (2004). Building relationships and combating bullying: Effectiveness of a school-based social skills group intervention. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33, 125–130. doi:10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_18.
DeRosier, M. E. (2007). Social Skills GRoup INtervention (S.S.GRIN): Group interventions and exercises for enhancing children’s communication, cooperation, and confidence (4th ed.). Cary, NC: 3-C Institute for Social Development.
DeRosier, M. E., & Marcus, S. (2005). Building friendships and combating bullying: Effectiveness of S.S.GRIN at 1-year follow-up. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34, 140–150. doi:10.1207/s15374424jccp3401_13.
Dishion, T. J., McCord, J., & Poulin, F. (1999). When interventions harm: Peer groups and problem behavior. The American Psychologist, 54, 755–764. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.54.9.755.
DuBois, D., & Flay, B. (2004). The healthy pursuit of self-esteem: Comment on and alternative to the Crocker and Park (2004) formulation. Psychological Bulletin, 130, 415–420. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.130.3.415.
DuBow, E. F., & Ullman, D. G. (1989). Assessing social support in elementary school youth: The survey of youth’s social support. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18, 52–64.
Eccles, J. S., Midgely, C., Wigfield, A., Buchanan, C. M., Reuman, D., Flanagan, C., et al. (1993). Development during adolescence: The impact of stage-environment fit on young adolescents’ experiences in schools and in families. The American Psychologist, 48, 90–101. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.48.2.90.
Furman, W. (1996). The measurement of friendship perceptions: Conceptual and methodological issues. In W. M. Bukowski, A. F. Newcomb & W. W. Hartup (Eds.), The company they keep: Friendships in childhood and adolescence (pp. 41–65). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Goldstein, A. P., Apter, S. J., & Harootunian, B. (1984). School violence. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Greco, L. A., & Morris, T. L. (2001). Treating childhood shyness and related behavior: Empirically evaluated approaches to promote positive social interactions. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 4, 299–318. doi:10.1023/A:1013543320648.
Gresham, F. M. (1997). Social competence and students with behavior disorders: Where we’ve been, where we are, and where we should go. Education and Treatment of Youth, 20, 233–249.
Guerra, N., Tolan, P., Eargle, A., Mosley, M., & Dunn, K. (1993). YES I CAN social responsibility training manual for use in small group sessions (Year 2). University of Illinois, Metropolitan Area Child Study: Chicago.
Hancock, G. R. (2001). Effect size, power, and sample size determination for structured means modeling and MIMIC approaches to between-groups hypothesis testing of means on a single latent construct. Psychometrika, 66, 373–388. doi:10.1007/BF02294440.
Harrell, A., & DeRosier, M. E. (2007). Social Skills GRoup INtervention-Adolescents (S.S. GRIN-A). Cary, NC: 3-C Institute for Social Development.
Hartup, W. W. (1983). Peer relations. In P. H. Mussen (Series Ed.) & E. M. Hetherington (Vol. Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 4. Socialization, personality and social development (pp. 103–196). New York: Wiley.
Hirsch, B. J., & Rapkin, B. D. (1987). The transition to junior high school: A longitudinal study of self-esteem, psychological symptomatology, school life, and social support. Child Development, 58, 1235–1243. doi:10.2307/1130617.
Huey, W. C., & Rank, R. C. (1984). Effects of counselor and peer led group assertive training on Black adolescent aggression. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 31, 95–98. doi:10.1037/0022-0167.31.1.95.
Hymel, S., Rubin, K. H., Rowden, L., & LeMare, L. (1990). Youth’s peer relationships: Longitudinal prediction of internalizing and externalizing problems from middle to late childhood. Child Development, 61, 2004–2021.
Jackibchuk, R., & Smeriglio, U. L. (1976). The influence of symbolic modeling on the social behavior of preschool youth with low levels of social responsiveness. Child Development, 47, 838–841. doi:10.2307/1128203.
Jöreskog, K. G., & Goldberger, A. S. (1975). Estimation of a model with multiple indicators and multiple causes of a single latent variable. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 70, 631–639. doi:10.2307/2285946.
Kano, Y. (2001). Structural equation modeling for experimental data. In R. Cudeck, S. Du Toit & D. Sörbom (Eds.), Structural equation modeling: Present and future (pp. 381–402). Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International.
Keefe, K., & Berndt, T. (1996). Relations of friendship quality to self-esteem in early adolescence. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 16, 110–129. doi:10.1177/0272431696016001007.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford.
Kupersmidt, J. B., Coie, J. D., & Dodge, K. A. (1990). Predicting disorder from peer social problems. In S. R. Asher & J. D. Coie (Eds.), Peer rejection in childhood (pp. 274–305). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Ladd, G. W., Profilet, S., & Hart, C. (1992). Parents’ management of youth’s peer relations: Facilitating and supervising youth’s activities in the peer culture. In R. D. Parke & G. W. Ladd (Eds.), Family-peer relationships: Modes of linkage (pp. 215–253). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
LaGreca, A. M., & Santogrossi, D. A. (1980). Social skills training with elementary school students: A behavioral group approach. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 48(2), 220–227. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.48.2.220.
Larson, R., & Ham, M. (1993). Stress and “storm and stress” in early adolescence: The relationship of negative events with dysphoric affect. Developmental Psychology, 29, 130–140. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.29.1.130.
Lochman, J. E., Coie, J. D., Underwood, M. K., & Terry, R. (1993). Effectiveness of a social relations intervention program for aggressive and nonaggressive, rejected youth. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61, 1053–1058. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.61.6.1053.
McFall, R. M. (1976). Behavioral training: A skill acquisition approach to clinical problems. Morristown, NJ: General Learning Press.
Mendlowitz, S. L., Manassis, K., Bradley, S., Scapilatto, D., Miezitis, S., & Shaw, B. E. (1999). Cognitive-behavioral group treatments in childhood anxiety disorders: The role of parental involvement. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 38, 1223–1229. doi:10.1097/00004583-199910000-00010.
Murray, S. (2005). Regulating the risks of closeness: A relationship-specific sense of felt security. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14, 74–78. doi:10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00338.x.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (1998–2007). MPlus 4.2 user’s guide. Los Angeles, CA: Author.
Newcomb, M. D., & Brady, J. E. (1982). Mutuality in boys’ friendship relations. Child Development, 53, 392–395. doi:10.2307/1128981.
O’Brien, S. F., & Bierman, K. L. (1988). Conceptions and perceived influence of peer group: Interviews with preadolescents and adolescents. Child Development, 59, 1360–1365. doi:10.2307/1130498.
Oden, S., & Asher, S. R. (1977). Coaching youth in social skills for friendship making. Child Development, 48, 495–506. doi:10.2307/1128645.
Offer, D., & Offer, J. B. (1975). From teenage to young manhood. New York: Basic Books.
Ollendick, T. H., & Schmidt, C. R. (1987). Social learning constructs in the prediction of peer interactions. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 16, 80–87. doi:10.1207/s15374424jccp1601_10.
Parker, J. G., & Asher, S. R. (1993). Friendship and friendship quality in middle childhood: Links with peer group acceptance and feelings of loneliness and social dissatisfaction. Developmental Psychology, 29, 611–621. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.29.4.611.
Parker, J. G., Rubin, K. H., Erath, S. A., Wojslawowicz, J. C., & Buskirk, A. A. (2006). Peer relationships, child development, and adjustment: A developmental psychopathology perspective. In D. Cicchetti & D. J. Cohen (Eds.), Developmental psychopathology: Theory and methods (2nd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 96–161). New York: Wiley.
Piaget, J. (1954). The construction of reality in the child. New York: Basic Books.
Piers, E. V., & Herzberg, D. S. (2002). Piers-Harris youth’s self-concept scale (2nd ed. manual). Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Raykov, T. (2005). Analysis of longitudinal studies with missing data using covariance structure modeling with full-information maximum likelihood. Structural Equation Modeling, 12, 493–505. doi:10.1207/s15328007sem1203_8.
Reed, M. K. (1994). Social skills training to reduce depression in adolescents. Adolescence, 29, 293–302.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2004). Behavior assessment system for youth. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Rubin, K. H., Bukowski, W. M., & Parker, J. G. (2006). Peer interactions, relationships, and groups. In N. Eisenberg (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Social, emotional, and personality development (6th ed., pp. 571–645). New York: Wiley.
Rubin, K. H., Burgess, K. B., & Coplan, R. J. (2002). Social withdrawal and shyness. In P. K. Smith & C. H. Hart (Eds.), Blackwell handbook of childhood social development (pp. 330–352). Boston: Blackwell.
Ryan, R. M., Stiller, J. D., & Lynch, J. H. (1994). Representation of relationship to teachers, parents, and friends as predictors of academic motivation and self-esteem. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 14, 226–249. doi:10.1177/027243169401400207.
Savin-Williams, R. C., & Berndt, T. S. (1990). Friendship and peer relations. In S. S. Feldman & G. R. Elliott (Eds.), At the threshold: The developing adolescent (pp. 277–307). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Sedikides, C., Rudich, E., Gregg, A., Kumashiro, M., & Rusbult, C. (2004). Are normal narcissists psychologically healthy? Self-esteem matters. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87, 400–416. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.87.3.400.
Spence, S. (2003). Social skill training with youth and young people: Theory, evidence practice. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 22, 84–96. doi:10.1111/1475-3588.00051.
Sullivan, H. S. (1953). The interpersonal theory of psychiatry. New York: Norton.
Trzesniewski, K., Donnellan, M., Moffitt, T., Robins, R., Poulton, R., & Caspi, A. (2006). Low self-esteem during adolescence predicts poor health, criminal behavior, and limited economic prospects during adulthood. Developmental Psychology, 42, 381–390. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.42.2.381.
Vossekuil, B., Reddy, M., & Fein, R. (2002). Safe school initiative: Final report on the prevention of targeted violence in schools. US Secret Service Threat Assessment Center, US Dept of Ed, & National Institute of Justice.
Way, N., & Chen, L. (2000). General and close friendships among African American, Latino, and Asian American adolescents from low-income families. Journal of Adolescent Research, 15, 274–301. doi:10.1177/0743558400152005.
Youniss, J. (1983). Social construction of adolescence by adolescents and parents. New Directions for Child Development, 22, 93–109. doi:10.1002/cd.23219832208.
Youniss, J., & Smollar, J. (1985). Adolescent relations with mothers, fathers, and friends. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant number R44MH68075-2 from the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). The authors would like to thank the parents and youth who participated in this research as well as the clinical staff of 3-C Family Services who expertly delivered the intervention.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harrell, A.W., Mercer, S.H. & DeRosier, M.E. Improving the Social-Behavioral Adjustment of Adolescents: The Effectiveness of a Social Skills Group Intervention. J Child Fam Stud 18, 378–387 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-008-9241-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-008-9241-y