Abstract
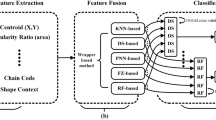
This work introduces a Type-II fuzzy lattice reasoning (FLRtypeII) scheme for learning/generalizing novel 2D shape representations. A 2D shape is represented as an element—induced from populations of three different shape descriptors—in the product lattice (F 3,⪯), where (F,⪯) denotes the lattice of Type-I intervals’ numbers (INs). Learning is carried out by inducing Type-II INs, i.e. intervals in (F,⪯). Our proposed techniques compare well with alternative classification methods from the literature in three benchmark classification problems. Competitive advantages include an accommodation of granular data as well as a visual representation of a class. We discuss extensions to gray/color images, etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amanatiadis, A., Kaburlasos, V.G., Gasteratos, A., Papadakis, S.E.: Evaluation of shape descriptors for shape-based image retrieval. IET Image Process. (2011, in press)
Andreu, G., Crespo, A., Valiente, J.M.: Selecting the toroidal self-organizing feature maps (TSOFM) best organized to object recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 2, pp. 1341–1346 (1997)
Belongie, S., Malik, J., Puzicha, J.: Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(4), 509–522 (2002)
Berretti, S., Del Bimbo, A., Pala, P.: Retrieval by shape similarity with perceptual distance and effective indexing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2(4), 225–239 (2000)
Biasotti, S., Cerri, A., Frosini, P., Giorgi, D., Landi, C.: Multidimensional size functions for shape comparison. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 32(2), 161–179 (2008)
Birkhoff, G.: Lattice Theory. Colloquium Publications, vol. 25. Am. Math. Soc., Providence (1967)
Bloch, I.: Spatial reasoning under imprecision using fuzzy set theory, formal logics and mathematical morphology. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 41(2), 77–95 (2006)
Bloch, I.: Lattices of fuzzy sets and bipolar fuzzy sets and mathematical morphology. Inf. Sci. 181(10), 2002–2015 (2011)
Bloch, I., Maitre, H.: Fuzzy mathematical morphologies: a comparative study. Pattern Recognit. 28(9), 1341–1387 (1995)
Bober, M.: MPEG-7 visual shape descriptors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 11(6), 716–719 (2001)
Braga-Neto, U., Goutsias, J.: A theoretical tour of connectivity in image processing and analysis. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 19(1), 5–31 (2003)
Daliri, M.R., Torre, V.: Shape recognition based on kernel-edit distance. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 114(10), 1097–1103 (2010)
Deng, T.-Q., Heijmans, H.J.A.M.: Grey-scale morphology based on fuzzy logic. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 16(2), 155–171 (2002)
Flusser, J., Suk, T.: Pattern recognition by affine moment invariants. Pattern Recognit. 26(1), 167–174 (1993)
Ganter, B., Wille, R.: Formal Concept Analysis. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Graña, M.: Lattice computing and natural computing—guest editorial. Neurocomputing 72(10–12), 2065–2066 (2009)
Graña, M., Villaverde, I., Maldonado, J.O., Hernandez, C.: Two lattice computing approaches for the unsupervised segmentation of hyperspectral images. Neurocomputing 72(10–12), 2111–2120 (2009)
Graña, M., Savio, A.M., García-Sebastián, M., Fernandez, E.: A lattice computing approach for on-line fMRI analysis. Image Vis. Comput. 28(7), 1155–1161 (2010)
Graña, M., Chyzhyk, D., García-Sebastián, M., Hernández, C.: Lattice independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. Inf. Sci. 181(10), 1910–1928 (2011)
Heijmans, H.J.A.M.: Morphological Image Operators. Academic Press, New York (1994)
Jammeh, E.A., Fleury, M., Wagner, C., Hagras, H., Ghanbari, M.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic congestion control for video streaming across IP networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17(5), 1123–1142 (2009)
Kaburlasos, V.G.: Towards a Unified Modeling and Knowledge-Representation Based on Lattice Theory. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 27. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Kaburlasos, V.G.: Information engineering applications based on lattices—guest editorial. Inf. Sci. 181(10), 1771–1773 (2011)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Kehagias, A.: Novel fuzzy inference system (FIS) analysis and design based on lattice theory. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 15(2), 243–260 (2007)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Pachidis, T.: A lattice-computing ensemble for reasoning based on formal fusion of disparate data types, and an industrial dispensing application. Inf. Fusion (2011, in press)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Papadakis, S.E.: Granular self-organizing map (grSOM) for structure identification. Neural Netw. 19(5), 623–643 (2006)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Papadakis, S.E.: Fuzzy lattice reasoning (FLR) implies a granular enhancement of the fuzzy-ARTMAP classifier. In: Proceedings of JCIS, Salt Lake City, Utah, pp. 1610–1616 (2007)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Papadakis, S.E.: A granular extension of the fuzzy-ARTMAP (FAM) neural classifier based on fuzzy lattice reasoning (FLR). Neurocomputing 72(10–12), 2067–2078 (2009)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Petridis, V.: Fuzzy lattice neurocomputing (FLN) models. Neural Netw. 13(10), 1145–1169 (2000)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Athanasiadis, I.N., Mitkas, P.A.: Fuzzy lattice reasoning (FLR) classifier and its application for ambient ozone estimation. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 45(1), 152–188 (2007)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Moussiades, L., Vakali, A.: Fuzzy lattice reasoning (FLR) type neural computation for weighted graph partitioning. Neurocomputing 72(10–12), 2121–2133 (2009)
Kaburlasos, V.G., Amanatiadis, A., Papadakis, S.E.: 2-D shape representation and recognition by lattice computing techniques. In: Corchado, E., Graña, M., Savio, A.M. (eds.) Proc. Int. Conf. HAIS, San Sebastián, Spain, 2010. LNAI, vol. 6077, pp. 391–398. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Karnik, N.N., Mendel, J.M.: Centroid of a type-2 fuzzy set. Inf. Sci. 132(1–4), 195–220 (2001)
Kauppinen, H., Seppänen, T., Pietikäinen, M.: An experimental comparison of autoregressive and Fourier-based descriptors in 2D shape classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 17(2), 201–207 (1995)
Kim, J.-G., Noble, J.A., Brady, J.M.: Probabilistic models for shapes as continuous curves. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 33(1), 39–65 (2009)
Liao, S.X., Pawlak, M.: On the accuracy of Zernike moments for image analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(12), 1358–1364 (1998)
Ling, H., Jacobs, D.W.: Shape classification using the inner-distance. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(2), 286–299 (2007)
Liu, H., Xiong, S., Fang, Z.: FL-GrCCA: a granular computing classification algorithm based on fuzzy lattices. Comput. Math. Appl. 61(1), 138–147 (2011)
Maragos, P.: Lattice image processing: a unification of morphological and fuzzy algebraic systems. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 22(2–3), 333–353 (2005)
Mélange, T., Nachtegael, M., Sussner, P., Kerre, E.E.: On the decomposition of interval-valued fuzzy morphological operators. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 36(3), 270–290 (2010)
Mendel, J.M.: Type-2 fuzzy sets and systems: an overview. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2(1), 20–29 (2007)
Mendel, J.M., John, R.I.: Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 10(2), 117–127 (2002)
Mendel, J.M., John, R.I., Liu, F.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems made simple. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 14(6), 808–821 (2006)
Nachtegael, M., Sussner, P., Mélange, T., Kerre, E.E.: On the role of complete lattices in mathematical morphology: from tool to uncertainty model. Inf. Sci. 181(10), 1971–1988 (2011)
Papadakis, S.E., Kaburlasos, V.G.: Piecewise-linear approximation of nonlinear models based on probabilistically/possibilistically interpreted intervals’ numbers (INs). Inf. Sci. 180(24), 5060–5076 (2010)
Papadakis, S.E., Tzionas, P., Kaburlasos, V.G., Theocharis, J.B.: A genetic based approach to the Type I structure identification problem. Informatica 16(3), 365–382 (2005)
Pedrycz, W., Skowron, A., Kreinovich, V. (eds.): Handbook of Granular Computing. Wiley, Chichester (2008)
Ronse, C.: Why mathematical morphology needs complete lattices. Signal Process. 21(2), 129–154 (1990)
Sebastian, T.B., Klein, P.N., Kimia, B.B.: Recognition of shapes by editing their shock graphs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(5), 550–571 (2004)
Serra, J.: Image Analysis and Mathematical Morphology. Academic Press, London (1982)
Serra, J.: Image Analysis and Mathematical Morphology. Theoretical Advances, vol. 2. Academic Press, New York (1988)
Sugeno, M., Kang, G.T.: Structure identification of fuzzy model. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 28(1), 15–33 (1988)
Sussner, P.: Generalizing operations of binary autoassociative morphological memories using fuzzy set theory. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 19(2), 81–93 (2003)
Sussner, P., Esmi, E.L.: Morphological perceptrons with competitive learning: lattice-theoretical framework and constructive learning algorithm. Inf. Sci. 181(10), 1929–1950 (2011)
Sussner, P., Valle, M.E.: Classification of fuzzy mathematical morphologies based on concepts of inclusion measure and duality. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 32(2), 139–159 (2008)
Sussner, P., Nachtegael, M., Mélange, T.: L-fuzzy mathematical morphology: an extension of interval-valued and intuitionistic fuzzy mathematical morphology. In: Proceedings of the 28th NAFIPS, Cincinnati, OH, pp. 1–6 (2009)
Tanaka, K., Sano, M., Watanabe, H.: Modeling and control of carbon monoxide concentration using a neuro-fuzzy technique. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 3(3), 271–279 (1995)
Thakoor, N., Gao, J., Jung, S.: Hidden Markov model-based weighted likelihood discriminant for 2-D shape classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(11), 2707–2719 (2007)
Tzafestas, C.S., Maragos, P.: Shape connectivity: multiscale analysis and application to generalized granulometries. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 17(2), 109–129 (2002)
Valle, M.E., Sussner, P.: A general framework for fuzzy morphological associative memories. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 159(7), 747–768 (2008)
Valle, M.E., Sussner, P.: Storage and recall capabilities of fuzzy morphological associative memories with adjunction-based learning. Neural Netw. 24(1), 75–90 (2011)
Wagner, C., Hagras, H.: Toward general type-2 fuzzy logic systems based on zSlices. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 18(4), 637–660 (2010)
Wang, B., Shen, W., Liu, W.-Y., You, X.-G., Bai, X.: Shape classification using tree-unions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 983–986 (2010)
Xu, Y., Ruan, D., Qin, K., Liu, J.: Lattice-Valued Logic. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol. 132. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Yang, M.-S., Lin, D.-C.: On similarity and inclusion measures between type-2 fuzzy sets with an application to clustering. Comput. Math. Appl. 57(6), 896–907 (2009)
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975)
Zadeh, L.A.: From computing with numbers to computing with words—from manipulation of measurements to manipulation of perceptions. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.—I, Fundam. Theory Appl. 45(1), 105–119 (1999)
Zhang, D., Lu, G.: Review of shape representation and description techniques. Pattern Recognit. 37(1), 1–19 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaburlasos, V.G., Papadakis, S.E. & Amanatiadis, A. Binary Image 2D Shape Learning and Recognition Based on Lattice-Computing (LC) Techniques. J Math Imaging Vis 42, 118–133 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-011-0301-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-011-0301-3