Abstract
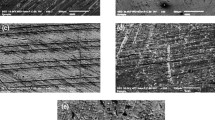
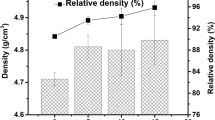
The relationship between alumina inclusion size and mechanical properties of particulate cubic zirconia-alumina composites was studied. The composites of the diverse size and content of alumina inclusions and of the nearly constant size of zirconia grains were used. Physical mixtures of the 8 mol% Y2O3-ZrO2 nano-powder and the γ-Al2O3 or α -Al2O3 micro-powder were cold isostatically pressed and then pressurelessly sintered for 2 h at 1300∘C in air. The γ -Al2O3 and α -Al2O3 powder was composed of the particles of 0.17 and 0.36 μ m in size, respectively. Crystallites of the zirconia powder had the size of 6 nm. Microstructural features of the composites have been characterised quantitatively. Hardness, critical stress intensity factor and bending strength of the composites was measured and correlated with the microstructural features. Depending on the size and content, the alumina inclusions influenced strength of the composites by influencing their fracture toughness and the presence of flaws of critical size. An increase in size of the alumina inclusions was accompanied by the increase of fracture toughness due to the additional contribution of large alumina inclusions to the crack deflection mechanism. It was found that decreasing the alumina inclusion size significantly below the cubic zirconia matrix grain size (more than 3 times) did not lead to the increased values of fracture toughness of the composites. The highest increase in fracture toughness (up to 3.9 MPa⋅ m0.5) has been found when the inclusion size was comparable to the matrix grain size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Q. MINH, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 76 (1993) 563.
E. P. BUTLER and J. DRENNAN, ibid. 65 (1982) 474.
F. J. ESPER, K. H. FRIESE and H. GEIER, in “Science and Technology of Zirconia,” edited by N. Claussen, M. Rühle and A. H. Heuer (American Ceramic Society, Columbus, OH, 1984) p. 528.
S. RAJENDRAN, J. DRENNAN and S. P. S. BADWAL, J. Mat. Sci. Lett. 6 (1987) 1431.
X. GUO, C.-Q. TANG and R.-Z. YUAN, J. Europ. Ceram. Soc. 15 (1995) 25.
M. MIYAYAMA, H. YANAGIDA and A. ASADA, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 64 (1986) 660.
M. MORI, T. ABE, H. ITOH, O. YAMMAMOTO, Y. TAKEDA and T. KAWAHARA, Solid State Ion. 74 (1994) 157.
P. DURAN, L. M. NAVARRO, P. RECIO and J. R. JURADO, Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 32 (1995) 963.
K. OE, K. KIKKAWA, A. KISHIMOTO, Y. NAKAMURA and H. YANAGIDA, Solid State Ion. 91 (1996) 131.
P. BHARGAVA and B. R. PATTERSON, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 80 (1997) 1863.
S. R. CHOI and N. P. BANSAL, Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 23 (2002) 741.
W. PYDA, K. HABERKO and M. M. BUĆKO, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 74 (1991) 2622.
K. NIIHARA, J. Mat. Sci. Lett. 2 (1983) 221.
A. G. EVANS, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 65 (1982) 497.
G. W. SCHERER, ibid. 67 (1984) 709.
R. RAJ and R. BORDIA, Acta Metall. 32 (1984) 1003.
C. H. HSUEH, J. Mater. Sci. 21 (1986) 2067.
C. H. HSUEH, A. G. EVANS, R. M. CANNON and R. J. BROOK, Acta Metall. 34 (1986) 927.
R. K. BORDIA and G. W. SCHERER, ibid. 36 (1988) 2392.
F. F. LANGE, J. Mater. Res. 2 (1987) 59.
S. SUNDARESAN and I. A. AKSAY, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 73 (1990) 54.
O. SUDRE, G. BAO, B. FAN, F. F. LANGE and A. G. EVANS, ibid. 75 (1992) 525.
F. F. LANGE and M. M. HIRLINGER, ibid. 70 (1987) 827.
F. F. LANGE, T. YAMAGUSHI, B. I. DAVIS and P. E. D. MORGAN, ibid. 71 (1988) 446.
B. J. KELLETT and F. F. LANGE, ibid. 72 (1989) 725.
F. F. LANGE and B. J. KELLETT, ibid. 72 (1989) 735.
M. W. WEISER and L. C. DE JONGHE, ibid. 71 (1988) C-125.
A. NAKAHIRA and K. NIIHARA, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 100 (1992) 448.
D. A. PORTER and K. E. ESTERLING, in “Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys,” 2nd edn. (Chapman & Hall, London, 1992) p. 139.
M. KLEITZ, L. DESSEMOND and M. C. STEIL, in Proceedings of SOFC; Materials, Process Engineering and Electrochemistry, Fifth IEA Workshop, edited by P. Biedermann and B. Krahl-Urban, (Julich, 1993) p. 147.
W.E. LEE and W. M. RAINFORTH, in “Ceramic Microstructures, Property Control by Processing” (Chapman & Hall, London, 1994) p. 278.
B. LAWN, in “Fracture of Brittle Solids,” 2nd edn. (Cambridge, UK, 1993).
I. E. REIMANIS, Mater. Sci. Engng. A237 (1997) 159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bućko, M.M., Pyda, W. Effect of inclusion size on mechanical properties of alumina toughened cubic zirconia. J Mater Sci 40, 5191–5198 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-4412-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-4412-3