Abstract
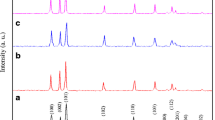
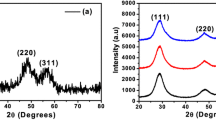
Pure ZnO and cobalt doped ZnO nanocrystals were synthesized using the polymer-pyrolysis route. Samples with a molar ratio of Co(NO3)2:Zn(CH3COO)2 in the range 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7 % were synthesized. The structural, compositional, optical, surface, and magnetic properties of these nanocrystals have been determined. For this purpose characterization techniques including X-ray diffraction (XRD), Energy dispersive X-ray analysis, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), UV–Vis absorption, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer system were used. XRD and FTIR results showed that both Co-doped and undoped ZnO nanocrystals crystallized in a ZnO wurtzite structure. The lattice constants for the Co-doped ZnO samples are very close to that of the pristine ZnO. Also, Co ions are replacing the Zn position in ZnO lattice without much change in the volume of the unit cell. High-quality crystalline sample was confirmed for the Co-doped samples with molar ratio 1 %. The incorporation of Co ions into the Co-doped ZnO lattice in Zn sites was confirmed from UV–Vis results. Optical peaks around 574, 612, and 666 nm were detected, which interpreted to the d–d electronic transitions of the tetrahedrally coordinate of Co2+ ion. Undoped and Co-doped samples show room temperature ferromagnetic (RTFM) behaviors and their magnetic parameters showed Co concentration dependency and thus these results fit the requirements of magnetic applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sato K, Bergqvist L, Kudrnovský J, Dederichs PH, Eriksson O, Turek I, Sanyal B, Bouzerar G, Katayama-Yoshida H, Dinh VA, Fukushima T, Kizaki H, Zeller R (2010) First-principles theory of dilute magnetic semiconductors. Rev Mod Phys 82:1633–1690
Ohno H (2010) A window on the future of spintronics. Nat Mater 9:952–954
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2011) Structural and magnetic study of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by auto combustion method. Int J Nanosci 10:1025–1028
Ogale SB (2010) Dilute doping, defects, and ferromagnetism in metal oxide systems. Adv Mater 22:3125–3155
Ekicibil A, Ozkendir OM, Farha AH, Ufuktepe Y (2015) Study of the electronic properties of Zn0.8–4xHoxOy (0.05 ≤ x≤0.09) by X-ray absorption and photoemission spectroscopy. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 202:56–61
Kıcır N, Ozkendir OM, Farha AF, Kırmızıgül F, Tuken T, Gumus C, Çabuk S, Erbil M, Ufuktepe Y (2015) Physical and electronic properties of electrodeposited ZnO thin films: dependence on thickness. Indian J Phys 89:1013–1024
Ocakoglu K, Mansour ShM, Yildirimcan S, Al Ghamdi AA, El-Tantawy F, Yakuphanoglu F (2015) Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorods. Spectrochim Acta A 148:362–368
Mansour SA, Yakuphanoglu F (2012) Electrical-optical properties of nanofiber ZnO film grown by sol gel method and fabrication of ZnO/p-Si heterojunction. Solid State Sci 14:121–126
Shi S, Yang Y, Xu J, Li L, Zhang X, Hu GH, Dang ZM (2013) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method. J Alloys Compd 576:59–65
Pan F, Song C, Liu XJ, Yang YC, Zeng F (2008) Ferromagnetism and possible application in spintronics of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Mater Sci Eng R 62:1–35
Vijayaprasath G, Murugan R, Ravi TG, Mahalingam YH (2014) Characterization of dilute magnetic semiconducting transition metal doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel spin coating method. Appl Surf Sci 313:870–876
Podila R, Anand B, West JP, Sai SS, He J, Skove M, Philip R, Hwu SJ, Tewari S, Rao AM (2011) Evidence for surface states in pristine and Co-doped ZnO nanostructures: magnetization and nonlinear optical studies. Nanotechnology 22:095703
Akdogan N, Becker HW, Zabel H, Gök S, Nefedov A, Khaibullin R, Westerholt K, Tagirov L (2009) Dose dependence of ferromagnetism in Co-implanted ZnO. J Appl Phys 105:043907
Heald SM, Kaspar T, Droubay T, Shutthanandan V, Chambers S (2009) X-ray absorption fine structure and magnetization characterization of the metallic Co component in Co-doped ZnO thin films. Phys Rev B 79:075202
Lim SM, Hwang SK, Myoung JM (2003) Observation of optical properties related to room-temperature ferromagnetism in co-sputtered Zn1−x Co x O thin films. Solid State Commun 125:231–235
Li YQ, Yong K, Xiao HM, Ma WJ, Zhang GL, Fu SY (2010) Preparation and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles by a polymer pyrolysis method. Mater Lett 64:1735–1737
He R, Hocking RK, Tsuzuki T (2012) Co-doped ZnO nanopowders: location of cobalt and reduction in photocatalytic activity. Mater Chem Phys 132:1035–1040
Li YQ, Wang J, Fu S, Mei S, Zhang JM, Yong K (2010) Facile synthesis of antimony-doped tin oxide nanoparticles by a polymer-pyrolysis method. Mater Res Bull 45:677–681
Kassas M (2010) Non-equilibrium energy transport in nano-layer gold coating onto silica. Curr Appl Phys 10:373–380
Shi T, Xiao Z, Yin Z, Li X, Wang Y, He H, Wang J, Yan W, Wei S (2010) The role of Zn interstitials in cobalt-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors. Appl Phys Lett 96:211905
Ghosh R, Basak D, Fujihara S (2004) Effect of substrate-induced strain on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin films. J Appl Phys 96:2689–2692
Yadav AK, Haque SM, Shukla D, Choudhary RJ, Jha SN, Bhattacharyya D (2015) X-ray absorption spectroscopy of Mn doped ZnO thin films prepared by rf sputtering technique. AIP Adv 5:117138
Mote V, Purushotham Y, Dole B (2012) Williamson–Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particle. J Theor Appl Phys 6:6–14
Kaushik A, Dalela B, Rathore R, Vats VS, Choudhary BL, Alvi PA, Kumar S, Dalela S (2013) Influence of Co doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanocrystals. J Alloys Compd 578:328–335
Maensiri S, Laokul P, Phokha S (2006) A simple synthesis and magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline Zn0.9Co0.1O powders by using Zn and Co acetates and polyvinyl pyrrolidone as precursors. J Magn Magn Mater 305:381–387
Djaja N, Montja D, Saleh R (2013) The effect of Co incorporation into ZnO nanoparticles, advances in materials physics and chemistry. Adv Mater Chem Phys 3:33–41
Senthilkumaar S, Rajendran K, Banerjee S, Chini TK, Sengodan V (2008) Influence of Mn doping on the microstructure and optical property of ZnO. Mater Sci Semicond Process 11:6–12
Li H, Wang J, Liu H, Yang C, Xu H, Li X, Cui H (2004) Sol–gel preparation of transparent zinc oxide films with highly preferential crystal orientation. Vacuum 77:57–62
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2012) Doping effects of Co2+ ions on structural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Microelectron Eng 89:129–132
Maensiri S, Sreesongmuang J, Thomas C, Klinkaewnarong J (2006) Magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline powders of Co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors synthesized by polymerizable precursor method. J Magn Magn Mater 301:422–432
Francis S, Saravanan R, Berchmans LJ (2013) Effect of Co doping on the properties of ZnO bulk samples. J Electron Mater 42:701–710
Murugadoss G (2012) Synthesis and characterization of transition metals doped ZnO nanorods. J Mater Sci Technol 28:587–593. doi:10.1016/S1005-0302(12)60102-9
Song C, Zeng F, Geng KW, Wang XB, Shen YX, Pan F (2007) The magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic insulator films prepared by direct current reactive magnetron co-sputtering. J Magn Magn Mater 309:25–30
Yan W, Jiang Q, Sun Z, Yao T, Hu F, Wei S (2010) Determination of the role of O vacancy in Co:ZnO magnetic film. J Appl Phys 108:013901
Srinet G, Varshney P, Kumar R, Sajal V, Kulriya PK, Knobel M, Sharma SK (2013) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1−x Co x O prepared by the sol–gel route. Ceram Int 39:6077–6085
Shatnawi M, Alsmadi AM, Bsoul I, Salameh B, Alna’washi GA, Al-Dweri F, El Akkad F (2016) Magnetic and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline particles. J. Alloys Compd 655:244–452
Köseoğlu Y (2015) PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Co0.1Zn0.9O DMS nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 373:195–199
Song C, Geng KW, Zeng F, Wang XB, Shen YX, Pan F (2006) Giant magnetic moment in an anomalous ferromagnetic insulator: Co-doped ZnO. Phys Rev B 73:024405
Hong NH, Sakai J, Gervais F (2007) Magnetism due to oxygen vacancies and/or defects in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films. J Magn Magn Mater 316:214–217
Hong NH, Barla A, Sakai J, Huon NQ (2007) Can undoped semiconducting oxides be ferromagnetic? Phys Status Sol C 316:4461–4466
Majumder S, Paramanik D, Gupta A, Varma S (2006) Observation of magnetic-domains in undoped ZnO grains at room temperature. Appl Surf Sci 256:513–516
Xu Q, Schmidt H, Hochmuth H, Meinecke C, Lorenz M, Zhou S, Setzer A, Grundmann M (2008) Room temperature ferromagnetism in ZnO films due to defects. Appl Phys Lett 92:082508
Liu XJ, Song C, Yang PY, Zeng F, Pan F (2008) Substrate orientation-induced distinct ferromagnetic moment in Co:ZnO films. Appl Surf Sci 254:3167–3174
Coey JMD, Venkatesan M, Fitzgerald CB (2005) Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat Mater 4:173–179
Fitzgerald CB, Venkatesan M, Lunney JG, Dorneles LS, Coey JMD (2005) Cobalt-doped ZnO—a room temperature dilute magnetic semiconductor. Appl Surf Sci 247:493–496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farha, A.H., Mansour, S.A. & Kotkata, M.F. Structural, optical, and magnetic study of dilute magnetic semiconducting Co-doped ZnO nanocrystals synthesized using polymer-pyrolysis route. J Mater Sci 51, 9855–9864 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0218-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0218-8