Abstract
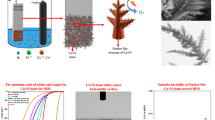
In this work, CuO nanoneedles have been in situ grown on Cu foam through simple thermal oxidation in the air. The morphologies and microstructures of as-prepared sample were characterized by using X-ray diffraction, Raman spectrum, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopes. It was found that the one-dimensional CuO nanoneedles with single crystalline were uniform distributed upon the layer of Cu foam’s skeleton. Directly using the as-prepared sample as the anode material for lithium-ion battery, the electrochemical performances of CuO nanoneedles on Cu foam were investigated by galvanostatic discharge–charge tests, cyclic voltammetry, as well as impedance spectroscopy measurement. The in situ growth electrode without binder realized an initial capacity as high as 940 and 446 mAh g−1 still retained even after 100 cycles of charging and discharging. The superior lithium storage performance may be attributed to the unique hierarchical architectured of nanoneedles on skeleton of porous foam, which offers excellent electro-conductivity for the intimate contact between CuO active material and Cu foam current collector, and provides a large surface to volume ratio that favors lithium-storage. The results propose that the as-prepared CuO nanoneedles on Cu foam would be a potential anode material for lithium-ion battery applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Ji, Z. Lin, M. Alcoutlabi, X. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 2682 (2011)
L. Ren, Y. Liu, X. Qi et al., J. Mater. Chem. 22, 21513 (2012)
X. Xu, W. Liu, Y. Kim, J. Cho, Nano Today 9, 604 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2014.09.005
P. Poizot, S. Laruelle, S. Grugeon, L. Dupont, J. Tarascon, Nature 407, 496 (2000)
A.S. Arico, P. Bruce, B. Scrosati, J.-M. Tarascon, W. Van Schalkwijk, Nat. Mater. 4, 366 (2005)
M. Reddy, G. Subba Rao, B. Chowdari, Chem. Rev. 113, 5364 (2013)
H. Li, Z. Wang, L. Chen, X. Huang, Adv. Mater. 21, 4593 (2009)
S.-F. Zheng, J.-S. Hu, L.-S. Zhong, W.-G. Song, L.-J. Wan, Y.-G. Guo, Chem. Mater. 20, 3617 (2008)
X. Chen, N. Zhang, K. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. 22, 13637 (2012)
S. Gao, S. Yang, J. Shu, S. Zhang, Z. Li, K. Jiang, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 19324 (2008)
X. Gao, J. Bao, G. Pan et al., J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 5547 (2004)
R. Sahay, P. Suresh Kumar, V. Aravindan et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 18087 (2012)
C. Wang, Q. Li, F. Wang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 1243 (2014)
Y. Zhu, N. Sun, W. Lin, Y. Ma, C. Lai, Q. Wang, RSC Adv. 5, 68061 (2015)
L. Shi, C. Fan, C. Sun et al., RSC Adv. 5, 28611 (2015)
D.H. Nam, R.H. Kim, D.W. Han, H.S. Kwon, Electrochim. Acta 66, 126 (2012)
Y. Liu, L. Liao, J. Li, C. Pan, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 5050 (2007)
T. Yu, X. Zhao, Z. Shen, Y. Wu, W. Su, J. Cryst. Growth 268, 590 (2004)
Q. Zhang, J. Wang, D. Xu, Z. Wang, X. Li, K. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 3865 (2014)
K. Chen, D. Xue, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 11168 (2014)
S. Laruelle, S. Grugeon, P. Poizot, M. Dolle, L. Dupont, J. Tarascon, J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, A627 (2002)
J. Morales, L. Sánchez, F. Martin, J.R. Ramos-Barrado, M. Sánchez, Electrochim. Acta 49, 4589 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11474244, 11504312), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 15C1322), National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB921103), and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT13093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Tang, H., Wang, Y. et al. Thermally oxidation synthesis of CuO nanoneedles on Cu foam and its enhanced lithium storage performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 2353–2357 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5803-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5803-8