Abstract
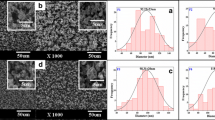
Cellulose acetate (CA) fibers loaded with the ester prodrugs of naproxen, including methyl ester, ethyl ester and isopropyl ester, were prepared through electrospinning using acetone/N,N-dimethylacetamide(DMAc)/ethanol (4:1:1, v/v/v) as solvent. The chemical and morphological characterizations of the medicated fibers were investigated by means of SEM, DSC, XRD and FTIR, as well as the studies of the drug release properties. The results indicated that the morphology and diameter of the fibers were influenced by the concentration of spinning solution, applied voltage, electrospun solvent and the surfactants. The average diameters of the fibers ranged between 100 and 500 nm for three prodrugs. There was good compatibility between CA and three prodrugs in the blended fibers, respectively. In vitro release indicated that constant drug release from the fiber was observed over 6 days. The prodrugs were successfully encapsulated into the fibers, and this system was stable in terms of effectiveness in release.









Similar content being viewed by others

References
Aungst A. Permeability and metabolism as barriers to transmucosal delivery of peptides and proteins. In: Hsieh DS, editor. Drug permeation enhancement: theory and applications. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1994. p. 323–43.
Suh H, Jun HW, Dzimianski MT, Lu GW. Pharmacokinetic and local tissue disposition studies of naproxen following topical and enhanced topical systemic administration in dogs and rats. Biopharm Drug Disp. 1997;18:623–33.
Mikulak SA, Vangsness CT, Nimni ME. Transdermal delivery and accumulation of indomethacin in subcutaneous tissues in rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1998;50:153–8.
Bando H, Yamashita F, Takakura Y, Hashida M. Skin penetration enhancement of acyclovir by prodrug-enhancer combination. Biol Pharm Bull. 1994;17:1141–3.
Bando H, Yamashita F, Takagi T, Takakura Y, Hashida M. Theoretical design of prodrug-enhancer combination for transdermal delivery based on skin diffusion model. Pharm Res. 1996;13:427–32.
Reneker DH, Yarin AL, Fong H, Koombhongse S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J Appl Phys. 2000;87:4531–47.
Min BM, Lee G, Kim SH, Nam YS, Lee TS, Park WH. Electrospinning of silk fibroin nanofibers and its effect on the adhesion and spreading of normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials. 2004;25:1289–97.
Noh HK, Lee SW, Oh JE, Kim KH, Chung CP, Choi SC, Park WH, Min BM. Electrospinning of chitin nanofibers: degradation behavior and cellular response to normal human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Biomaterials. 2006;27:3934–44.
Yoshimoto H, Shin YM, Terai H, Vacanti JP. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24:2077–82.
Sombatmankhong K, Sanchavanakit N, Pavasant P, Supaphol P. Bone scaffolds from electrospun fiber mats of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and their blend. Polymer. 2007;48:1419–27.
Suwantong O, Waleetorncheepsawat S, Sanchavanakit N, Pavasant P, Cheepsunthorn P, Bunaprasert T, Supaphol P. In vitro biocompatibility of electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fiber mats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2007;40:217–23.
Kenawy ER, Bowlin GL, Mansfield K, Layman J, Simpson DG, Sanders EH, Wnek GE. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J Control Release. 2002;81:57–64.
Zeng J, Xu XY, Chen XS, Liang QZ, Bian XC, Yang LX, Jing XB. Biodegradable electrospun fibers for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2003;92:227–31.
Taepaiboon P, Rungsardthong U, Supaphol P. Drug-loaded electrospun mats of poly(vinyl alcohol) fibres and their release characteristics of four model drugs. Nanotechnology. 2006;17:2317–29.
Taepaiboon P, Rungsardthong U, Supaphol P. Vitamin-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate nanofiber mats as transdermal and dermal therapeutic agents of vitamin A acid and vitamin E. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;67:387–97.
Tungprapa S, Jangchud I, Supaphol P. Release characteristics of four model drugs from drug-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats. Polymer. 2007;48:5030–41.
Li J, He A, Han CC, Fang D, Hsiao BS, Chu B. Electrospinning of hyaluronic acid(HA) and HA/gelatin blends. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2006;27:114–20.
Bhattarai N, Edmondsona D, Veiseha O, Matsenb FA, Zhang M. Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6176–84.
Bhattarai N, Li Z, Edmondson D, Zhang M. Alginate-based nanofibrous scaffolds: structural, mechanical and biological properties. Adv Mater. 2006;18:1463–7.
Li J, He A, Zheng J, Han CC. Gelatin and gelatin-hyaluronic acid nanofibrous membranes produced by electrospinning of their aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:2243–7.
Nge TT, Sugiyama J. Surface functional group dependent apatite formation on bacterial cellulose microfibrils network in a simulated body fluid. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;81A:124–34.
Nishio Y. Material functionalization of cellulose and related polysaccharides via diverse microcompositions. Adv Polym Sci. 2006;205:97–151.
Suwantong O, Opanasopit P, Ruktanonchai U, Supaphol P. Electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats containing curcumin and release characteristic of the herbal substance. Polymer. 2007;48:7546–57.
Singh P, Roberts MS. Skin permeability and local tissue concentrations of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs after topical application. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;268:144–51.
Mario G, Michela M, Caterina B, Francesca G, Carlo B. Frovatriptan vs. transdermal oestrogens or naproxen sodium for the prophylaxis of menstrual migraine. J Headache Pain. 2007;8:283–8.
Thorsteinsson T, Masson M, Loftsson T, Haraldsson GG, Stefansson E. Diacyl glyceryl ester prodrugs for slow release in the skin: synthesis and in vitro degradation and absorption studies for naproxen derivatives. Pharmazie. 1999;54:831–6.
Bonina FP, Puglia C, Barbuzzi T, de Caprariis P, Palagiano F, Rimoli MG, Saija A. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of polyoxyethylene esters as dermal prodrugs of ketoprofen, naproxen and diclofenac. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2001;14:123–34.
Kim BY, Doh HJ, Le TN, Cho WJ, Yong CS, Choi HG, Kim JS, Lee CH, Kim DD. Ketorolac amide prodrugs for transdermal delivery: stability and in vitro rat skin permeation studies. Int J Pharm. 2005;293:193–202.
Henk SA, Breytenbach JC, Hadgraft J, du Plessis J. Synthesis and transdermal penetration of NSAID glycoside esters. Int J Pharm. 2005;301:71–9.
Morena JM, Sinisterra JV. Immobilization of lipase from Candida cylindracea in inorganic supports. J Mol Catal. 1994;93:357–69.
Lee KH, Kim HY, La YM, Lee DR, Sung NH. Influence of a mixing solvent with tetrahydrofuran and N, N-dimethylformamide on electrospun poly(vinyl chloride) nonwoven mats. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys. 2002;40:2259–68.
Zong XH, Kim KS, Fang DF, Ran SF, Hsiao BS, Chu BJ. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer. 2002;43:4403–12.
Yao L, Haas TW, Guiseppi-Elie A, Bowlin GL, Simpson DG, Wnek GE. Electrospinning and stabilization of fully hydrolyzed poly(vinyl alcohol) fibers. Chem Mater. 2003;15:1860–4.
Lin T, Wang HX, Wang HM, Wang XG. The charge effect of cationic surfactants on the elimination of fibre beads in the electrospinning of polystyrene. Nanotechnology. 2004;15:1375–81.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by UK–CHINA Joint Laboratory for Therapeutic Textiles; Biomedical Textile Materials ‘‘111 Project’’ from Ministry of Education of P. R. China (No. B07024); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20080440564); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Special Grade No. 200902195).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Xm., Branford-White, C.J., Zhu, Lm. et al. Ester prodrug-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats as transdermal drug delivery systems. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 21, 2403–2411 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4100-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4100-y