Abstract
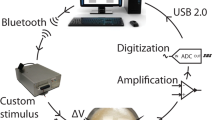
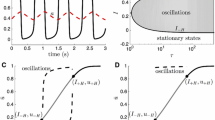
We study the dynamics of the transition between the low- and high-firing states of the cortical slow oscillation by using intracellular recordings of the membrane potential from cortical neurons of rats. We investigate the evidence for a bistability in assemblies of cortical neurons playing a major role in the maintenance of this oscillation. We show that the trajectory of a typical transition takes an approximately exponential form, equivalent to the response of a resistor–capacitor circuit to a step-change in input. The time constant for the transition is negatively correlated with the membrane potential of the low-firing state, and values are broadly equivalent to neural time constants measured elsewhere. Overall, the results do not strongly support the hypothesis of a bistability in cortical neurons; rather, they suggest the cortical manifestation of the oscillation is a result of a step-change in input to the cortical neurons. Since there is evidence from previous work that a phase transition exists, we speculate that the step-change may be a result of a bistability within other brain areas, such as the thalamus, or a bistability among only a small subset of cortical neurons, or as a result of more complicated brain dynamics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steriade, M., Núnez, A., Amzica, F.: A novel slow (<1 Hz) oscillation of neocortical neurons in vivo: depolarizing and hyperpolarizing components. J. Neurosci. 13, 3252–3265 (1993)
Marshall, L., Helgadóttir, H., Mölle, M., Born, J.: Boosting slow oscillations during sleep potentiates memory. Nature 444, 610–613 (2006)
Tononi, G., Cirelli, C.: Sleep function and synaptic homeostatis. Sleep Med. Rev. 10, 49–62 (2006)
Destexhe, A.: Self-sustained asynchronous irregular states and up-down states in thalamic, cortical and thalamocortical networks of nonlinear integrate-and-fire neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. (2009). doi:10.1007/s10827-009-0164-4
Compte, A., Sanchez-Vives, M.V., McCormick, D.A., Wang, X.J.: Cellular and network mechanisms of slow oscillatory activity (<1 Hz) and wave propagations in a cortical network model. J. Neurophysiol. 89, 2707–2725 (2003)
Hill, S., Tononi, G.: Modeling sleep and wakefulness in the thalamocortical system. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 1671–1698 (2005)
Steriade, M., Núnez, A., Amzica, F.: Intracellular analysis of relations between the slow (<1 Hz) neocortical oscillation and other sleep rhythms of the electroencephalogram. J. Neurosci. 13, 3266–3283 (1993)
Timofeev, I., Grenier, F., Bazhenov, M., Sejnowski, T.J., Steriade, M.: Origin of slow cortical oscillations in deafferated cortical slabs. Cerebral Cortex 10, 1185–1199 (2000)
Blethyn, K.L., Hughes, S.W., Tóth, T.I., Cope, D.W., Crunelli, V.: Neuronal basis of the slow (<1 Hz) oscillation in neurons of the nucleus reticularis thalami in vitro. J. Neurosci. 26, 2474–2486 (2006)
Fuentealba, P., Timofeev, I., Bazhenov, M., Sejnowski, T., Steriade, M.: Membrane bistability in thalamic reticular neurons during spindle oscillations. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 294–304 (2005)
Wilson, M.T., Steyn-Ross, D.A., Sleigh, J.W., Steyn-Ross, M.L., Wilcocks, L.C., Gillies, I.P.: The k-complex and slow oscillation in terms of a mean-field cortical model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 21, 243–257 (2006)
Massimini, M., Huber, R., Ferrarelli, F., Hill, S., Tononi, G.: The sleep slow oscillation as a traveling wave. J. Neurosci. 24, 6862–6870 (2004)
Bazhenov, M., Timofeev, I., Steriade, M., Sejnowski, T.J.: Model of thalamocortical slow-wave sleep oscillations and transitions to activated states. J. Neurosci. 22, 8691–8704 (2002)
Sanchez-Vives, M.V., McCormick, D.A.: Cellular and network mechanisms of rhythmic recurrent activity in neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1027–1034 (2000)
Amzica, F., Steriade, M.: The functional significance of the k-complexes. Sleep Med. Rev. 6, 139–149 (2002)
Molaee-Ardekani, B., Senhadji, L., Shamsollahi, M.B., Vosoughi-Vahdat, B., Wodey, E.: Brain activity modeling in general anesthesia: enhancing local mean-field models using a slow adaptive firing rate. Phys. Rev. E 76, 041911 (2007)
Robinson, P.A., Wu, H., Kim, J.W.: Neural rate equations for bursting dynamics derived from conductance-based equations. J. Theor. Biol. 250, 663–672 (2008)
Wilson, M.T., Barry, M., Reynolds, J.N.J., Hutchison, E.J.W., Steyn-Ross, D.: Characteristics of temporal fluctuations in the hyperpolarized state of the cortical slow oscillation. Phys. Rev. E 77, 061908 (2008)
Steyn-Ross, D.A., Steyn-Ross, M.L., Sleigh, J.W., Wilson, M.T., Gillies, I.P., Wright, J.J.: The sleep cycle modelled as a cortical phase transition. J. Biophys. 31, 547–569 (2005)
Steyn-Ross, D.A., Steyn-Ross, M.L., Wilson, M.T., Sleigh, J.W.: White-noise susceptibility and critical slowing in neurons near spiking threshold. Phys. Rev. E 74, 051920 (2006)
Cossart, R., Aronov, D., Yuste, R.: Attractor dynamics of network up states in the neocortex. Nature 423, 283–288 (2003)
Wilson, M.T., Steyn-Ross, M.L., Steyn-Ross, D.A., Sleigh, J.W.: Predictions and simulations of cortical dynamics during natural sleep using a continuum approach. Phys. Rev. E 72, 051,910 1–14 (2005)
Strogatz, S.H.: Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos. Westview, Cambridge (2000)
Chagnac-Amitai, Y., Luhmann, H.J., Prince, D.A.: Burst generating and regular spiking layer 5 pyramidal neurons of rat neocortex have different morphology features. J. Comp. Neurol. 296, 598–613 (1990)
Steriade, M.: Corticothalamic resonance, states of vigilance and mentation. Neuroscience 101, 243–276 (2000)
Brecht, M., Krauss, A., Muhammed, S., Sinai-Esfahani, L., Bellanca, S., Margrie, T.W.: Organization of rat vibrissa motor cortex and adjacent areas according to cytoarchitectonics, microstimulation, and intracellular stimulation of identified cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 479, 360–373 (2004)
Games, K.D., Winer, J.A.: Layer V in rat auditory cortex: projections to the inferior colliculus and contralateral cortex. Hear. Res. 34, 1–25 (1988)
Reynolds, J.N.J., Hyland, B.I., Wickens, J.R.: Modulation of an afterhyperpolarization by the substantia nigra induces pauses in the tonic firing of striatal cholinergic interneurons. J. Neurosci. 24, 9870–9877 (2004)
Kerr, J.N.D., Greenberg, D., Helmchen, F.: Imaging input and output of neocortical networks in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102(39), 14063–14068 (2005)
Bojak, I., Liley, D.T.J.: Modeling the effects of anaesthesia on the electroencephalogram. Phys. Rev. E 71, 41,902 (2005)
Steyn-Ross, M.L., Steyn-Ross, D.A., Wilson, M.T., Sleigh, J.W.: Modeling brain activation patterns for the default and cognitive states. NeuroImage 45, 289–311 (2009)
Hutt, A., Frank, T.D.: Critical fluctuations and 1/f α-activity of neural fields involving transmission delays. Acta Phys. Pol., A 108, 1021–1040 (2005)
Destexhe, A., Paré, D.: Impact of network activity on the integrative properties of neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 1531–1547 (1999)
Destexhe, A., Rudolph, M., Paré, D.: The high-conductance state of neocortical neurons in vivo. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 739–751 (2003)
Clement, E.A., Richard, A., Thwaites, M., Ailon, J., Peters, S., Dickson, C.T.: Cyclic and sleep-like spontaneous alternations of brain state under urethane anaesthesia. PLoS ONE 3, e2004 (2008)
Sceniak, M.P., MacIver, M.B.: Cellular actions of urethance on rat visual cortical neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 95, 3865–3874 (2006)
Steriade, M., Timofeev, I., Grenier, F.: Natural waking and sleep states: A view from inside neocortical neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 1969–1985 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Peter Robinson of the University of Sydney for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, M.T., Barry, M., Reynolds, J.N.J. et al. An analysis of the transitions between down and up states of the cortical slow oscillation under urethane anaesthesia. J Biol Phys 36, 245–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-009-9180-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-009-9180-x