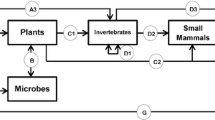
Abstract
Heavy metals are an important class of pollutants with both lethal and sublethal effects on organisms. The latter are receiving increased attention, as these may have harmful ecological outcomes. For example, recent explorations of heavy metals in freshwater habitats reveal that they can modify chemical communication between individuals, resulting in “info-disruption” that can impact ecological relationships within and between species. Info-disruption can affect animal behavior and social structure, which in turn can modify both intraspecies and interspecies interactions. In terrestrial habitats, info-disruption by metals is not well studied, but recent demonstrations of chemical signaling between plants via both roots and volatile organic molecules provide potential opportunities for info-disruption. Metals in terrestrial habitats also can form elemental plant defenses, in which they can defend a plant against natural enemies. For example, hyperaccumulation of metals by terrestrial plants has been shown to provide defensive benefits, although in almost all known cases the metals are not anthropogenic pollutants but are naturally present in soils inhabited by these plants. Info-disruption among microbes is another arena in which metal pollutants may have ecological effects, as recent discoveries regarding quorum sensing in bacteria provide an avenue for metals to affect interactions among bacteria or between bacteria and other organisms. Metal pollutants also may influence immune responses of organisms, and thus affect pathogen/host relationships. Immunomodulation (modification of immune system function) has been tied to some metal pollutants, although specific metals may boost or reduce immune system function depending on dose. Finally, the study of metal pollutants is complicated by their frequent occurrence as mixtures, either with other metals or with organic pollutants. Most studies of metal pollutants focus on single metals and therefore oversimplify complex field conditions. Study of pollutant impacts on chemical ecology also are difficult due to the necessity of studying effects at varying ecological scales: “dynamic scaling” of chemical ecology studies is rarely done completely. It is clear that much remains to be learned about how heavy metal pollution impacts organisms, and that exciting new research frontiers are available for experimental exploration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, E. B., Coleman, R. G., Keeler-Wolf, T., and Harrison, S. P. 2007. Serpentine Geoecology of Western North America: Geology, Soils, and Vegetation, p. 512. Oxford University Press, New York.
Aminov, R. I., and Mackie, R. I. 2007. Evolution and ecology of antibiotic resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 271:147–161.
Baker, A. J. M., Mcgrath, S. P., Reeves, R. D., and Smith, J. A. C. 2000. Metal hyperaccumulator plants: a review of the ecology and physiology of a biological resource for phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils, pp. 85–107, in N. Terry and G. S. Bañuelos (eds.). Phytoremediation of Contaminated Soil and Water. CRC, Boca Raton.
Baker-Austin, C., Wright, M. S., Stepanauskas, R., and Mcarthur, J. V. 2006. Co-selection of antibiotic and metal resistance. Trends Microbiol. 14:176–182.
Baldwin, D. H., Sandahl, J. F., Labenia, J. S., and Scholz, N. L. 2003. Sublethal effects of copper on coho salmon: impacts on nonoverlapping receptor pathways in the peripheral olfactory nervous system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 22:2266–2274.
Baquero, F., Martínez, J.-L., and Cantón, R. 2008. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 19:260–265.
Berg, J., Tom-Petersen, A., and Nybroe, O. 2005. Copper amendment of agricultural soil selects for bacterial antibiotic resistance in the field. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 40:146–151.
Beyers, D. W., and Farmer, M. S. 2001. Effects of copper on olfaction of Colorado pikeminnow. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20:907–912.
Bishayi, B., and Sengupta, M. 2003. Intracellular survival of Staphylococcus aureus due to alteration of cellular activity in arsenic and lead intoxicated mature Swiss albino mice. Toxicology 184:31–39.
Blechinger, S. R., Kusch, R. C., Haugo, K., Matz, C., Chivers, D. P., and Krone, P. H. 2007. Brief embryonic cadmium exposure induces a stress response and cell death in the developing olfactory system followed by long-term olfactory deficits in juvenile zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 224:72–80.
Boyd, R. S. 2002. Does elevated body Ni concentration protect insects against pathogens? A test using Melanotrichus boydi (Heteroptera: Miridae). Am. Mid. Nat. 147:225–236.
Boyd, R. S. 2004. Ecology of metal hyperaccumulation. New Phytol. 162:563–567.
Boyd, R. S. 2007. The defense hypothesis of elemental hyperaccumulation: status, challenges and new directions. Plant Soil 293:153–176.
Boyd, R. S. 2009. High-nickel insects and nickel hyperaccumulator plants: A review. Insect Sci. 16:19–31.
Boyd, R. S., and Martens, S. N. 1992. The raison d’etre for metal hyperaccumulation by plants, pp. 270–289, in A. J. M. Baker, J. Proctor, and R. D. Reeves (eds.). The Vegetation of Ultramafic (Serpentine) Soils: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Serpentine Ecology. Intercept, Andover.
Boyd, R. S., and Martens, S. N. 1998. The significance of metal hyperaccumulation for biotic interactions. Chemoecology 8:1–7.
Boyd, R. S., and Wall, M. A. 2001. Responses of generalist predators fed high-Ni Melanotrichus boydi (Heteroptera: Miridae): elemental defense against the third trophic level. Am. Midl. Nat. 146:186–198.
Boyd, R. S., Kruckeberg, A. R., and Rajakaruna, N. 2009. Biology of ultramafic rocks and soils: research goals for the future. Northeast. Nat. 16:422–440.
Burger, J. 2008. Assessment and management of risk to wildlife from cadmium. Sci. Total Environ. 389:37–45.
Buskey, E. J., and Swift, E. 1983. Behavioral responses of the coastal copepod Acartia hudsonica (Pinhey) to simulated dinoflagellate bioluminescence. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 72:43–58.
Cabassi, E. 2007. The immune system and exposure to xenobiotics in animals. Vet. Res. Comm. 31:115–120.
Capon, R. J., Elsbury, K., Butler, M. S., Lu, C. C., Hooper, J. N. A., Rostas, J. A. P., O’Brien, K. J., Mudge, L.-M., and Sim, A. T. R. 1993. Extraordinary levels of cadmium and zinc in a marine sponge, Tedania charcoti Topsent: inorganic defense agents. Experientia 49:263–264.
Carreau, N. D., and Pyle, G. G. 2005. Effect of copper exposure during embryonic development on chemosensory function of juvenile fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 61:1–6.
Challis, G. L. 2005. A widely distributed bacterial pathway for siderophore biosynthesis independent of nonribosomal peptide synthetases. ChemBioChem 6:601–611.
Clotfelter, E. D., Bell, A. M., and Levering, K. R. 2004. The role of animal behaviour in the study of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Anim. Behav. 68:665–676.
Cronin, T. W. 2005. The visual ecology of predator-prey interactions, pp. 105–138, in P. Barbosa, and I. Castellaris (eds.). Ecology of Predator-prey Interactions. Oxford University Press, New York.
Dang, H., Ren, J., Song, L., Sun, S., and An, L. 2008. Dominant chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in coastal marine waters of Jiaozhou Bay, China. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24:209–217.
de Kroon, H. 2007. How do roots interact? Science 318:1562–1563.
Dearing, M. D., Foley, W. J., and Mclean, S. 2005. The influence of plant secondary metabolites on the nutritional ecology of herbivorous terrestrial vertebrates. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 36:169–189.
Deheyn, D. D., and Latz, M. I. 2009. Internal and secreted bioluminescence of the marine polychaete Odontosyllis phosphorea (Syllidae). Invertebr. Biol. 128:31–45.
Deheyn, D., Jangoux, M., and Warnau, M. 2000. Alteration of bioluminescence in Amphipholis squamata (Ophiuroidea: Echinodermata) by heavy metals contamination: a field study. Sci. Total Environ. 247:41–49.
Dietert, R. R., and Piepenbrink, M. S. 2006. Lead and immune function. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 36:359–385.
Diggle, S. P., Griffin, A. S., Campbell, G. S., and West, S. A. 2007. Cooperation and conflict in quorum-sensing bacterial populations. Nature 450:411–415.
Dudley, S. A., and File, A. L. 2007. Kin recognition in an annual plant. Biol. Lett. 3:435–438.
Duruibe, J. O., Ogwoegbu, M. O. C., and Egwurugwu, J. N. 2007. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2:112–118.
Falik, O., Reides, P., Gersani, M., and Novoplansky, A. 2003. Self/non-self discrimination in roots. J. Ecol. 91:525–531.
Fleeger, J. W., Carman, K. R., and Nisbet, R. M. 2003. Indirect effects of contaminants in aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 317:207–233.
Fournier, M., Cyr, D., Blakley, B., Boermans, H., and Brousseau, P. 2000. Phagocytosis as a biomarker of immunotoxicity in wildlife species exposed to environmental xenobiotics. Am. Zool. 40:412–420.
González, J. E., and Keshavan, N. D. 2006. Messing with bacterial quorum sensing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70:859–875.
Goodyear, K. L., and Mcneill, S. 1999. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by aquatic macro-invertebrates of different feeding guilds: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 229:1–19.
Gray, J. S. 2002. Biomagnification in marine systems: the perspective of an ecologist. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 45:46–52.
Greger, M. 2004. Metal availability, uptake, transport and accumulation in plants, pp. 1–27, in M. N. V. Prasad (ed.). Heavy Metal Stress in Plants: From Biomolecules to Ecosystems. Springer, Berlin.
Gruntman, M., and Novoplansky, A. 2004. Physiologically mediated self/non-self discrimination in roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:3863–3867.
Haines, B. J. 2002. Zincophilic root foraging in Thlaspi caerulescens. New Phytol. 155:363–372.
Han, F. X., Banin, A., Su, Y., Monts, D. L., Plodinec, M. J., Kingery, W. L., and Triplett, G. E. 2002. Industrial age anthropogenic inputs of heavy metals into the pedosphere. Naturwissenschaften 89:497–504.
Hansen, J. A., Marr, J. C. A., Lipton, J., Cacela, D., and Bergman, H. L. 1999a. Differences in neurobehavioral responses of Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to copper and cobalt: behavioral avoidance. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18:1972–1978.
Hansen, J. A., Rose, J. D., Jenkins, R. A., Gerow, K. G., and Bergman, H. L. 1999b. Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to copper: neurophysiological and histological effects on the olfactory system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18:1979–1991.
Hay, M. E. 1996. Marine chemical ecology: What’s known and what’s next? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 200:103–134.
Hess, L., and de Kroon, H. 2007. Effects of rooting volume and nutrient availability as an alternative explanation for root self/non-self discrimination. J. Ecol. 95:241–251.
Hilgers, M. T., and Ludwig, M. L. 2001. Crystal structure of the quorum-sensing protein LuxS reveals a catalytic metal site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98:11169–11174.
Hodge, A. 2009. Root decisions. Plant Cell Environ. 32:628–640.
Hollows, C. F., Johnston, E. L., and Marshall, D. J. 2007. Copper reduces fertilization success and exacerbates Allee effects in the field. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 333:51–60.
Honda, R. T., Fernandes-de-Castilho, M., and Val, A. L. 2008. Cadmium-induced disruption of environmental exploration and chemical communication in matrinxã, Brycon amazonicus. Aquat. Toxicol. 89:204–206.
Ilbäck, N.-G., Frisk, P., and Friman, G. 2008. Effects of xenobiotics and nutrients on host resistance studied in experimental human infections adapted to rodents. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 58:179–188.
Janssens, T. K. S., Roelofs, D., and van Straalen, N. M. 2009. Molecular mechanisms of heavy metal tolerance and evolution in invertebrates. Insect Sci. 16:3–18.
Jensen, P. D., Johnson, L. R., and Trumble, J. T. 2006. Individual and joint actions of selenate and methylmercury on the development and survival of insect detritivore Megaselia scalaris (Diptera: Phoridae). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 50:523–530.
Jhee, E. M., Boyd, R. S., and Eubanks, M. D. 2006. Effectiveness of metal-metal and metal-organic compound combinations against Plutella xylostella: implications for plant elemental defense. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:239–259.
Jones, B. W., and Nishiguchi, M. K. 2004. Counterillumination in the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes Berry (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). Mar. Biol. 144:1151–1155.
Jöst, C., and Zauke, G.-P. 2008. Trace metal concentrations in Antarctic sea spiders (Pycnogonida: Pantopoda). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 56:1396–1399.
Karban, R., and Shiojiri, K. 2009. Self-recognition affects plant communication and defense. Ecol. Lett. 12:502–506.
Karban, R., Huntzinger, M., and Mccall, A. C. 2004. The specificity of eavesdropping on sagebrush by other plants. Ecology 85:1846–1852.
Kats, L. B., and Dill, L. M. 1998. The scent of death: chemosensory assessment of predation risk by prey animals. Ecoscience 5:361–394.
Kessler, A., Halitschke, R., and Baldwin, I. T. 2004. Silencing the jasmonate cascade: induced plant defenses and insect populations. Science 305: 665–668.
Klaschka, U. 2008. The infochemical effect—a new chapter in ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 15:452–462.
Klemens, J. A. 2008. Kin recognition in plants? Biol. Lett. 4:67–68.
Koricheva, J., Larsson, S., and Haukioja, E. 1998. Insect performance on experimentally stressed woody plants: A meta-analysis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 43:195–216.
Kusch, R. C., Krone, P. H., and Chivers, D. P. 2008. Chronic exposure to low concentrations of waterborne cadmium during embryonic and larval development results in the long-term hindrance of antipredator behavior in zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27:705–710.
Lass, S., and Spaak, P. 2003. Chemically induced anti-predator defences in plankton: a review. Hydrobiologia 491:221–239.
Lawrence, D. A., and Mccabe, M. J. Jr. 2002. Immunomodulation by metals. Int. Immunopharm. 2:293–302.
Lefcort, H., Aguon, M. Q., Bond, K. A., Chapman, K. R., Chaquette, R., Clark, J., Kornachuk, P., Lang, B. Z., and Martin, J. C. 2002. Indirect effects of heavy metals on parasites may cause shifts in snail species composition. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 43:34–41.
Lefcort, H., Freedman, Z., House, S., and Pendleton, M. 2008. Hormetic effects of heavy metals in aquatic snails: is a little bit of pollution good? EcoHealth 5:10–17.
Levitan, D. R., and Mcgovern, T. M. 2005. The Allee effect in the sea, pp. 47–57, in E. A. Norse, and L. B. Crowder (eds.). Marine Conservation Biology: The Science of Maintaining the Sea’s Biodiversity. Island, Washington.
Liu, H.-Y., Lin, Z.-S., and Liu, H.-Y. 2008. Response of oriental white storks Ciconia boyciana to the accumulative impact of anthropogenic habitat destruction and possible Allee effect. Bird Conserv. Int. 18:292–300.
Liu, F., Tang, Y., Du, R., Yang, H., Wu, Q., and Rongliang, Q. 2009. Root foraging for zinc and cadmium requirement in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. Plant Soil. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-0060-8.
Lürling, M. 2006. Effects of a surfactant (FFD-6) on Scenedesmus morphology and growth under different nutrient conditions. Chemosphere 62:1351–1358.
Lürling, M., and Scheffer, M. 2007. Info-disruption: pollution and the transfer of chemical information between organisms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 22:374–379.
Mackenzie, B. R., Mosegaard, H., and Rosenberg, A. A. 2008. Impending collapse of bluefin tuna in the northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean. Conserv. Lett. 2:26–35.
Mahall, B. E., and Callaway, R. M. 1992. Root communication mechanisms and intracommunity distributions of two Mojave Desert shrubs. Ecology 73:2145–2151.
Mahall, B. E., and Callaway, R. M. 1996. Effects of regional origin and genotype on intraspecific root communication in the desert shrub Ambrosia dumosa (Asteraceae). Am. J. Bot. 83:93–98.
Manefield, M., Rasmussen, T. B., Henzter, M., Andersen, J. B., Steinberg, P., Kjelleberg, S., and Givskov, M. 2002. Halogenated furanones inhibit quorum sensing through accelerated LuxR turnover. Microbiology 148:1119–1127.
Martens, S. N., and Boyd, R. S. 1994. The ecological significance of nickel hyperaccumulation: a plant chemical defense. Oecologia 98:379–384.
Mcnickle, G. G., Cassady St. Clair, C., and Cahill, J. F. Jr. 2009. Focusing the metaphor: plant root foraging behaviour. Trends Ecol. Evol. 24:419–426.
Mcpherson, T. D., Mirza, R. S., and Pyle, G. G. 2004. Responses of wild fishes to alarm chemicals in pristine and metal-contaminated lakes. Can. J. Zool. 82:694–700.
Michels, E., Semsari, S., Bin, C., and de Meester, L. 2000. Effect of sublethal doses of cadmium on the phototactic behavior of Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 47:261–265.
Milla, R., Forero, D. M., Escudero, A., and Iriondo, J. M. 2009. Growing with siblings: a common ground for cooperation or for fiercer competition among plants? Proc. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B 276:2531–2540.
Mirza, R. S., and Pyle, G. G. 2009. Waterborne metals impair inducible defences in Daphnia pulex: morphology, life-history traits and encounters with predators. Freshwat. Biol. 54:1016–1027.
Mirza, R. S., Green, W. W., Connor, S., WeekS, A. C. W., Wood, C. M., and Pyle, G. G. 2009. Do you smell what I smell? Olfactory impairment in wild yellow perch from metal-contaminated waters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 72:677–683.
Mithöfer, A., Schulze, B., and Boland, W. 2004. Biotic and heavy metal stress response in plants: evidence for common signals. FEBS Lett. 566: 1–5.
Ni, N., Li, M., Wang, J., and Wang, B. 2009. Inhibitors and antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing. Med. Res. Rev. 29:65–124.
Odate, S., and Pawlik, J. R. 2007. The role of vanadium in the chemical defense of the solitary tunicate, Phallusia nigra. J. Chem. Ecol. 33:643–654.
Oken, E., Kleinman, K. P., Berland, W. E., Simon, S. R., Rich-Edwards, J. W., and Gillman, M. W. 2003. Decline in fish consumption among pregnant women after a national mercury advisory. Obstet. Gynecol. 102:346–351.
Oweson, C., and Hernroth, B. 2009. A comparative study on the influence of manganese on the bactericidal response of marine invertebrates. Fish & Shellfish Immunol. 27:500–507.
Parejko, K. 1991. Predation by chaoborids on typical and spined Daphnia pulex. Freshwat. Biol. 25:211–217.
Paul, V. J., and Ritson-Williams, R. 2008. Marine chemical ecology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 25:662–695.
Pawlik, J. R. 1993. Marine invertebrate chemical defenses. Chem. Rev. 93:1911–1922.
Piotrowska-Seget, Z., Cycon, M., and Kozdrój, J. 2005. Metal-tolerant bacteria occurring in heavily polluted soil and mine spoil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 28:237–246.
Poschenrieder, C., Tolrà, R., and Barceló, J. 2006. Can metals defend plants against biotic stress? Trends Plant Sci. 11:288–295.
Pyle, G. G., and Mirza, R. S. 2007. Copper-impaired chemosensory function and behavior in aquatic animals. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 13:492–505.
Rasmussen, T. B., and Givskov, M. 2006. Quorum sensing inhibitors: a bargain of effects. Microbiology 152:895–904.
Sánchez, M. L. (ed.) 2008. Causes and Effects of Heavy Metal Pollution, p. 392. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge.
Sanchez-Dardon, J., Voccia, I., Hontela, A., Chilmonczyk, S., Dunier, M., Boermans, H., Blakley, B., and Fournier, M. 1999. Immunomodulation by heavy metals tested individually or in mixtures in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18:1492–1497.
Sandahl, J. F., Miyasaka, G., Koide, N., and Ueda, H. 2006. Olfactory inhibition and recovery in chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) following copper exposure. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 63:1840–1847.
Sarkar, S., and Chakraborty, R. 2008. Quorum sensing in metal tolerance of Acinetobacter junii BB1A is associated with biofilm production. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 282:160–165.
Scheirs, J., Vandevyvere, I., Wollaert, K., Blust, R., and de Bruyn, L. 2006. Plant-mediated effects of heavy metal pollution on host choice in a grass miner. Environ. Pollut. 143:138–145.
Schertzer, J. W., Boulette, M. L., and Whiteley, M. 2009. More than a signal: non-signaling properties of quorum sensing molecules. Trends Microbiol. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2009.02.001.
Schowalter, T. 2006. Insect Ecology: An Ecosystem Approach, p. 576. Academic, San Diego.
Schwartz C., Morel, J. L., Saumier, S., Whiting, S. N., and Baker, A. J. M. 1999. Root development of the Zinc-hyperaccumulator plant Thlaspi caerulescens as affected by metal origin, content and localization in soil. Plant Soil 208:103–115.
Scott, G. R., and Sloman, K. A. 2004. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behaviour and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 68:369–392.
Sloman, K. A. 2007. Effects of trace metals on salmonid fish: the role of social hierarchies. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 104:326–345.
Sloman, K. A., Baker, D. W., Wood, C. M., and Mcdonald, G. 2002. Social interactions affect physiological consequences of sublethal copper exposure in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 21:1255–1263.
Sloman, K. A., Scott, G. R., Diao, Z., Rouleau, C., Wood, C. M., and Mcdonald, D. G. 2003. Cadmium affects the social behaviour of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 65:171–185.
Sloman, K. A., Scott, G. R., Mcdonald, D. G., and Wood, C. M. 2004. Diminished social status affects ionoregulation at the gills and kidney in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 61:618–626.
Smith, R. J. F. 1992. Alarm signals in fishes. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisher. 2:33–63.
Smith, G. M., and Weiss, J. S. 1997. Predator-prey relationships in mummichogs (Fundulus heteroclitus (L.)): effects of living in a polluted environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 209:75–87.
Sorvari, J., Rantala, L. M., Rantala, M. J., Hakkarainen, H., and Eeva, T. 2007. Heavy metal pollution disturbs immune response in wild ant populations. Environ. Pollut. 145:324–328.
Stepanauskas, R., Glenn, T. C., Jagoe, C. H., Tuckfield, R. C., Lindell, A. H., and Mcarthur, J. V. 2005. Elevated microbial tolerance to metals and antibiotics in metal-contaminated industrial environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39:3671–3678.
Stepanauskas, R., Glenn, T. C., Jagoe, C. H., Tuckfield, R. C., Lindell, A. H., King, C. J., and Mcarthur, J. V. 2006. Coselection for microbial resistance to metals and antibiotics in freshwater microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 8:1510–1514.
Stephens, P. A., Sutherland, W. J., and Freckleton, R. P. 1999. What is the Allee effect? Oikos 87:185–190.
Stoecker, D. 1980. Chemical defenses of ascidians against predators. Ecology 61:1327–1334.
Teplitski, M., Chen, H., Rajamani, S., Gao, M., Merighi, M., Sayre, R. T., Robinson, J. B., Rolfe, B. G., and Bauer, W. D. 2004. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii secretes compounds that mimic bacterial signals and interfere with quorum sensing regulation in bacteria. Plant Physiol. 134:137–146.
Trewavas, A. 2009. What is plant behaviour? Plant Cell Environ. 32:606–616.
Turovskiy, Y., Kashtanov, D., Paskhover, B., and Chikindas, M. 2007. Quorum sensing: fact, fiction, and everything in between. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 62:191–234.
van Ooik, T., Pausio, S., and Rantala, M. J. 2008. Direct effects of heavy metal pollution on the immune function of a geometrid moth, Epirrita autumnata. Chemosphere 71:1840–1844.
Vickerman, D. B., and Trumble, J. T. 2003. Biotransfer of selenium: effects on an insect predator, Podisus maculiventris. Ecotoxicology 12:497–504.
Vijayavel, K., Gopalakrishnan, S., Thiagarajan, R., and Thilagam, H. 2009. Immunotoxic effects of nickel in the mud crab Scylla serrata. Fish & Shellfish Immunol. 26:133–139.
Vuori, K. M. 1994. Rapid behavioural and morphological responses of hydropsychid larvae (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae) to sublethal cadmium exposure. Environ. Pollut. 84:291–299.
Waters, C. M., and Bassler, B. L. 2005. Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21:319–346.
West, S. A., Diggle, S. P., Buckling, A., Gardner, A., and Griffin, A. S. 2007. The social lives of microbes. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 38:53–77.
Williams, P., Winzer, K., Chan, W. C., and Cámara, M. 2007. Look who’s talking: communication and quorum sensing in the bacterial world. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond, Ser. B 362:1119–1134.
Wilson, A. J. 1996. The Living Rock: The Story of Metals Since Earliest Time and Their Impact on Civilization, p. 272. Whitehurst & Clark, Flemington.
YANG, R. S. H. 1994. Toxicology of Chemical Mixtures: Case Studies, Mechanisms, and Novel Approaches, p. 720. Academic, New York.
Zhang, Q.-G., Buckling, A., Ellis, R. J., and Godfray, H. C. J. 2009. Coevolution of cooperators and cheats in a microbial system. Evolution. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2009.00708.x.
Zimmer, R. K., and Zimmer, C. A. 2008. Dynamic scaling in chemical ecology. J. Chem. Ecol. 34:822–836.
Acknowledgments
I thank Hugh Lefcort and two anonymous reviewers for helpful suggestions regarding an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyd, R.S. Heavy Metal Pollutants and Chemical Ecology: Exploring New Frontiers. J Chem Ecol 36, 46–58 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9730-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-009-9730-5