Abstract
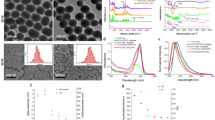
The use of fluorescent nanomaterials has gained great importance in the field of medical imaging. Many traditional imaging technologies have been reported utilizing dyes in the past. These methods face drawbacks due to non-specific accumulation and photobleaching of dyes. We studied the uptake and internalization of two different sized (30 nm and 100 nm) FITC labeled silica nanoparticles in Human umbilical vein endothelial cell line. These nanomaterials show high biocompatability and are highly photostable inside live cells for increased period of time in comparison to the dye alone. To our knowledge, we report for the first time the use of 30 nm fluorescent silica nanoparticles as efficient endothelial tags along with the well studied 100 nm particles. We also have emphasized the good photostability of these materials in live cells.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santra S, Liesenfeld B, Bertolino C, Dutta D, Cao Z, Tan W, Moudgil BM, Mericle RA (2006) Fluorescence lifetime measurements to determine the core–shell nanostructure of FITC-doped silica nanoparticles: an optical approach to evaluate nanoparticle photostability. J Lumin 117(1):75–82
Larson DR, Zipfel WR, Williams RM, Clark SW, Bruchez MP, Wise FW, Webb WW (2003) Water-soluble quantum dots for multiphoton fluorescence imaging in vivo. Science 300(5624):1434–1436
Babes L, Denizot B, Tanguy G, Jeune JJL, Jallet P (1999) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles used as MRI contrast agents: a parametric study. J Colloid Interf Sci 212(2):474–482
Rosenholm JM, Meinander A, Peuhu E, Niemi R, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Linden M (2009) Targeting of porous hybrid silica nanoparticles to cancer cells. ACS Nano 3(1):197–206
Barreto JA, O’Malley W, Kubeil M, Graham B, Stephan H, Spiccia L (2011) Nanomaterials: applications in cancer imaging and therapy. Adv Mater 23(12):H18–H40
Wu H, Huo Q, Varnum S, Wang J, Liu G, Zimin N, Liu J, Lin Y (2008) Dye-doped silica nanoparticle labels/protein microarray for detection of protein biomarkers. Analyst 133(11):1550–1555
Bailey RE, Smith AM, Shuming N (2004) Quantum dots in biology and medicine. Phys E 25(1):1–12
Li KG, Chen JT, Bai SS, Wen X, Song SY, Yu Q, Li J, Wang YQ (2009) Intracellular oxidative stress and cadmium ions release induce cytotoxicity of unmodified cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Toxicol Vitr 23(6):1007–1013
Lin Y-S, Tsai C-P, Huang H-Y, Kuo C-T, Hung Y, Huang D-M, Chen Y-C, Mou C-Y (2005) Well ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles as cell markers. Chem Mater 17(18):4570–4573
Santra S, Yang H, Dutta D, Stanley JT, Holloway PH, Tan W, Moudgil BM, Mericle RA (2004) TAT conjugated, FITC doped silica nanoparticles for bioimaging applications. Chem Commun (24):2810–2811
Mal NK, Fujiwara M, Tanaka Y (2003) Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous silica. Nature 421(6921):350–353
He X, Duan J, Wang K, Tan W (2004) A novel fluorescent label based on organic dye-doped silica nanoparticles for HepG liver cancer cell recognition. J Nanosci Nanotech 4(6):585–589
Slowing II, Vivero-Escoto JL, C-W Wu, Lin VS-Y (2008) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 60(11):1278–1288
Liong M, Lu J, Kovochich M, Xia T, Ruehm SG, Nel AE, Tamanoi F, Zink JI (2008) Multifunctional inorganic nanoparticles for imaging, targeting, and drug delivery. ACS Nano 2(5):889–896
Nair R, Poulose AC, Nagaoka Y, Yoshida Y, Maekawa T, Kumar DS (2011) Uptake of FITC labeled silica nanoparticles and quantum dots by rice seedlings: effects on seed germination and their potential as biolabels for plants. J Fluoresc. doi:10.1007/s10895-011-0904-5
Lai CY, Trewyn BG, Jeftinija DM, Jeftinija K, Xu S, Jeftinija S, Lin VS-Y (2003) A mesoporous silica nanosphere-based carrier system with chemically removable CdS nanoparticle caps for stimuli-responsive controlled release of neurotransmitters and drug molecules. J Am Chem Soc 125(15):4451–4459
Lin Y-S, Hung Y, Su JK, Lee R, Chang C, Lin M-L, Mou C-Y (2004) Gadolinium(III)-incorporated nanosized mesoporous silica as potential magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J Phys Chem B 108(40):15608–15611
Trewyn BG, Nieweg JA, Zhao Y, Lin VY-S (2008) Biocompatible mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different morphologies for animal cell membrane penetration. Chem Eng J 137(1):23–29
Yang J, Lee J, Kang J, Lee K, Suh JS, Yoon HG, Huh YM, Haam S (2008) Hollow silica nanocontainers as drug delivery vehicles. Langmuir 24(7):3417–3421
Chen JF, Ding HM, Wang JX, Shao L (2004) Preparation and characterization of porous hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Biomaterials 25(4):723–727
Vallhov H, Gabrielsson S, Strømme M, Scheynius A, Garcia-Bennett AE (2007) Mesoporous silica particles induce size dependent effects on human dendritic cells. Nano Lett 7(12):3576–3582
Lu J, Liong M, Zink JI, Tamanoi F (2008) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 3(8):1341–1346
Rosenholm JM, Peuhu E, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C, Linden M (2009) Targeted intracellular delivery of hydrophobic agents using mesoporous hybrid silica nanoparticles as carrier systems. Nano Lett 9(9):3308–3311
Suzuki K, Kenichi Ikari K, Imai H (2004) Synthesis of silica nanoparticles having a well-ordered mesostructure using a double surfactant system. J Am Chem Soc 126(2):462–463
Acknowledgement
Srivani Veeranarayanan, Aby Cheruvathoor Poulose, Sheikh Mohamed and Athulya Aravind thank Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan for providing financial support, the Monbukagakusho fellowship. Authors thank Prof. Fukushima for Photoluminescence measurement and Dr. Iwai for guiding in Flow cytometry analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veeranarayanan, S., Cheruvathoor Poulose, A., Mohamed, S. et al. FITC Labeled Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Cell Tags: Uptake and Photostability Study in Endothelial Cells. J Fluoresc 22, 537–548 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0991-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0991-3