Abstract
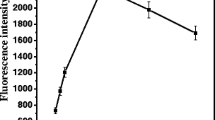
We describe here the construction of a sensitive and selective optical sensor system for the detection of human α-thrombin. The surface functionalized luminescent [Ru(dpsphen)3]4− (dpsphen-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline disulfonate) ion doped silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) with a size ~70 nm have been prepared. The DABCYL (2-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)diazenyl-benzoic acid) quencher labeled thrombin binding aptamer is conjugated to the surface of SiNPs using BS3 (bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate) as a cross-linker, resulting in the conformational change of aptamer to form G-quadruplex structure upon the addition of thrombin. The binding event is translated into a change in the luminescence intensity of Ru(II) complex via FRET mechanism, due to the close proximity of DABCYL quencher with SiNPs. The selective detection of thrombin using the SiNPs-aptamer system up to 4 nM is confirmed by comparing its sensitivity towards other proteins. This work demonstrates the application of simple aptamer-SiNPs conjugate as a highly sensitive system for the detection of thrombin and also it is highly sensitive towards thrombin in the presence of other proteins and complex medium such as BSA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249:505–510
Wang Y, Li J, Wang H, Jin J, Liu J, Wang K, Tan W, Yang R (2010) Silver ions-mediated conformational switch: facile design of structure-controllable nucleic acid probes. Anal Chem 82:6607–6612
Zhen SJ, Chen LQ, Xiao SJ, Li YF, Hu PP, Zhan L, Peng L, Song EQ, Huang CZ (2010) Carbon nanotubes as a low background signal platform for a molecular aptamer beacon on the basis of long-range resonance energy transfer. Anal Chem 82:8432–8437
Zhang X, Li Y, Su H, Zhang S (2010) Highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ using mismatched DNA and a molecular light switch complex in aqueous solution. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1338–1343
Choi MS, Yoon M, Baeg J-O, Kim J (2009) Label-free dual assay of DNA sequences and potassium ions using an aptamer probe and a molecular light switch complex. Chem Commun 7419–7421
Heyduk E, Heyduk T (2005) Nucleic acid-based fluorescence sensors for detecting proteins. Anal Chem 77:1147–1156
Drabovich AP, Okhonin V, Berezovski M, Krylov SN (2007) Smart aptamers facilitate multi-probe affinity analysis of proteins with ultra-wide dynamic range of measured concentrations. J Am Chem Soc 129:7260–7261
He J-L, Wu Z-S, Zhang S-B, Shen G-L, Yu R-Q (2009) Novel fluorescence enhancement IgE assay using a DNA aptamer. Analyst 134:1003–1007
Chen X, Estevez M-C, Zhu Z, Huang Y-F, Chen Y, Wang L, Tan W (2009) Using aptamer-conjugated fluorescence resonance energy transfer nanoparticles for multiplexed cancer cell monitoring. Anal Chem 81:7009–7014
Freeman R, Sharon E, Tel-Vered R, Willner I (2009) Supramolecular cocaine-aptamer complexes activate biocatalytic cascades. J Am Chem Soc 131:5028–5029
Kang H, O’Donoghue MB, Liu H, Tan W (2010) A liposome-based nanostructure for aptamer directed delivery. Chem Commun 46:249–251
Zheng D, Seferos DS, Giljohann DA, Patel PC, Mirkin CA (2009) Aptamer nano-flares for molecular detection in living cells. Nano Lett 9:3258–3261
Shieh Y-A, Yang S-J, Wei M-F, Shieh M-J (2010) Aptamer-Based Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery for Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Nano 4:1433–1442
Kim D, Jeong YY, Jon S (2010) A drug-loaded aptamer-gold nanoparticle bioconjugate for combined ct imaging and therapy of prostate cancer. ACS Nano 4:3689–3696
Zhang S, Xia J, Li X (2008) Electrochemical biosensor for detection of adenosine based on structure-switching aptamer and amplification with reporter probe DNA modified Au-nanoparticles. Anal Chem 80:8382–8388
Xu W, Lu Y (2010) Label-free fluorescent aptamer sensor based on regulation of malachite green fluorescence. Anal Chem 82:574–578
Yao W, Wang L, Wang H, Zhang X, Li L (2009) An aptamer-based electrochemiluminescent biosensor for ATP detection. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3269–3274
Wang J, Zhou HS (2008) Aptamer-based Au nanoparticles-enhanced surface plasmon resonance detection of small molecules. Anal Chem 80:7174–7178
Chhabra R, Sharma J, Ke Y, Liu Y, Rinker S, Lindsay S, Yan H (2007) Spatially addressable multiprotein nanoarrays templated by aptamer-tagged DNA nanoarchitectures. J Am Chem Soc 129:10304–10305
Yao C, Qi Y, Zhao Y, Xiang Y, Chen Q, Fu W (2009) Aptamer-based piezoelectric quartz crystal microbalance biosensor array for the quantification of IgE. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2499–2503
Attia MS, Othman AM, Aboaly MM, Abdel-Mottaleb MSA (2010) Novel spectrofluorimetric method for measuring the activity of the enzyme α-l-fucosidase using the nano composite optical sensor samarium(III)-doxycycline complex doped in sol–gel matrix. Anal Chem 82:6230–6236
Shenhar R, Rotello VM (2003) Nanoparticles: scaffolds and building blocks. Acc Chem Res 36:549–561
Mulder WJM, Strijkers GJ, Van Tilborg GAF, Cormode DP, Fayad ZA, Nicolay K (2009) Nanoparticulate assemblies of amphiphiles and diagnostically active materials for multimodality imaging. Acc Chem Res 42:904–914
Senarath-Yapa MD, Phimphivong S, Coym JW, Wirth MJ, Aspinwall CA, Scott Saavedra S (2007) Preparation and characterization of Poly(lipid)-coated, fluorophore-doped silica nanoparticles for biolabeling and cellular imaging. Langmuir 23:12624–12633
Liu D, He X, Wang K, He C, Shi H, Jian L (2010) Biocompatible silica nanoparticles-insulin conjugates for mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic differentiation. Bioconjugate Chem 21:1673–1684
Burns AA, Vider J, Ow H, Herz E, Penate-Medina O, Baumgart M, Larson SM, Wiesner U, Bradbury M (2009) Fluorescent silica nanoparticles with efficient urinary excretion for nanomedicine. Nano Lett 9:442–448
Moulari B, Pertuit D, Pellequer Y, Lamprecht A (2008) The targeting of surface modified silica nanoparticles to inflamed tissue in experimental colitis. Biomaterials 29:4554–4560
Qhobosheane M, Santra S, Zhang P, Tan W (2001) Biochemically functionalized silica nanoparticles. Analyst 126:1274–1278
Wu YF, Chen CL, Liu SQ (2009) Enzyme-functionalized silica nanoparticles as sensitive labels in biosensing. Anal Chem 81:1600–1607
Wang H, Yang R, Yang L, Tan W (2009) Nucleic acid conjugated nanomaterials for enhanced molecular recognition. ACS Nano 3:2451–2460
Arduini M, Mancin F, Tecilla P, Tonellato U (2007) Self-organized fluorescent nanosensors for ratiometric pb2+ detection. Langmuir 23:8632–8636
Wang S, Wang H, Jiao J, Chen K-J, Owens GE, Kamei K-I, Sun J, Sherman DJ, Behrenbruch CP, Wu H, Tseng H-R (2009) Three-dimensional nanostructured substrates toward efficient capture of circulating tumor cells. Angew Chem 121:9132–9135
Wang L, Yang C, Tan W (2005) Dual-luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for multiplexed signaling. Nano Lett 5:37–43
Wang L, Zhao W, O’Donoghue MB, Tan W (2007) Fluorescent nanoparticles for multiplexed bacteria monitoring. Bioconjugate Chem 18:297–301
Wu H, Huo Q, Varnum S, Wang J, Liu G, Nie Z, Liu J, Lin Y (2008) Dye-doped silica nanoparticle labels/protein microarray for detection of protein biomarkers. Analyst 133:1550–1555
Yan J, Estevez MC, Smith JE, Wang K, He X, Wang L, Tan W (2007) Dye-doped nanoparticles for bioanalysis. Nano Today 2:44–50
Herr JK, Smith JE, Medley CD, Shangguan D, Tan W (2006) Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for selective collection and detection of cancer cells. Anal Chem 78:2918–2924
Wang Y, Liu B (2009) Conjugated polyelectrolyte-sensitized fluorescent detection of thrombin in blood serum using aptamer-immobilized silica nanoparticles as the platform. Langmuir 25:12787–12793
Hedges SJ, Dehoney SB, Hooper JS, Amanzadeh J, Busti AJ (2007) Evidence-based treatment recommendations for uremic bleeding. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 3:138–153
Nishino A, Suzuki M, Ohtani H, Motohashi O, Umezawa K, Nagura H, Yoshimoto TJ (1993) Thrombin may contribute to the pathophysiology of central nervous system injury. Neurotrauma 10:167–179
Serruys PW, Vranckx P, Allikmets K (2006) Clinical development of bivalirudin (Angiox®): rationale for thrombin-specific anticoagulation in percutaneous coronary intervention and acute coronary syndromes. Int J Clin Pract 60:344–350
Arai T, Miklossy J, Klegeris A, Guo JP, McGeer PLJ (2006) Thrombin and prothrombin are expressed by neurons and glial cells and accumulate in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease brain. Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:19–25
Vaughan PJ, Pike CJ, Cotman CW, Cunningham DD (1995) Thrombin receptor activation protects neurons and astrocytes from cell death produced by environmental insults. J Neurosci 15:5389–5401
Striggow F, Riek M, Breder J, Henrich-Noack P, Reymann KG, Reiser G (2000) The protease thrombin is an endogenous mediator of hippocampal neuroprotection against ischemia at low concentrations but causes degeneration at high concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2264–2269
Bock LC, Griffin LC, Latham JA, Vermaas EH, Toole JJ (1992) Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 355:564–566
Vairamani M, Gross ML (2003) G-quadruplex formation of thrombin-binding aptamer detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Chem Soc 125:42–43
Zanarini S, Ciana LD, Marcaccio M, Marzocchi E, Paolucci F, Prodi L (2008) Electrochemistry and electrochemiluminescence of [Ru(II)-tris(bathophenanthroline-disulfonate)]4− in aprotic conditions and aqueous buffers. J Phys Chem B 112:10188–10193
Santra S, Zhang P, Wang K, Tapec R, Tan W (2001) Conjugation of biomolecules with luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for photostable biomarkers. Anal Chem 73:4988–4993
Freeman R, Li Y, Tel-Vered R, Sharon E, Elbaz J, Willner I (2009) Self-assembly of supramolecular aptamer structures for optical or electrochemical sensing. Analyst 134:653–656
Jares-Erijman EA, Jovin TM (2003) FRET imaging. Nat Biotechnol 21:1387–1395
Wang L, Yang C, Tan W (2005) Dual-luminophore-doped silica nanoparticles for multiplexed signaling. Nano Latt 5:37–43
Zhang D, Wu Z, Xu J, Liang J, Li J, Yang W (2010) Tuning the emission properties of Ru(phen) 2+3 doped silica nanoparticles by changing the addition time of the dye during the stober process. Langmuir 26:6657–6662
Amoroso AJ, Coogan MP, Dunne JE, Fernandez-Moreira V, Hess JB, Hayes AJ, Lloyd D, Millet C, Pope SJA, Williams C (2007) Rhenium fac tricarbonyl bisimine complexes: biologically useful fluorochromes for cell imaging applications. Chem Commun 3066–3068
Wang Y, Liu B (2007) Silica nanoparticle assisted DNA assays for optical signal amplification of conjugated polymer based fluorescent sensors. Chem Commun 3553–3555
Chang H, Tang L, Wang Y, Jiang J, Li J (2010) Graphene fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor for the thrombin detection. Anal Chem 82:2341–2346
Grynyov RS, Sorokin AV, Guralchuk GY, Yefimova SL, Borovoy IA, Malyukin YV (2008) Squaraine dye as an exciton trap for cyanine j-aggregates in a solution. J Phys Chem C 112:20458–20462
Lakowizc JR (2006) Principles in fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Wu C, Peng H, Jiang Y, McNeill J (2006) Energy transfer mediated fluorescence from blended conjugated polymer nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 110:14148–14154
Wu C, Szymanski C, McNeill J (2006) Preparation and encapsulation of highly fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles. Langmuir 22:2956–2960
Zhang S, Yan Y, Bi S (2009) Design of molecular beacons as signaling probes for adenosine triphosphate detection in cancer cells based on chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer. Anal Chem 81:8695–8701
Huanga DW, Niua CG, Qina PZ, Ruana M, Zenga GM (2001) Time-resolved fluorescence aptamer-based sandwich assay for thrombin detection. Talanta 83:185–189
Hamaguchi N, Ellington A, Stanton M (2001) Aptamer beacons for the direct detection of proteins. Anal Biochem 294:126–131
Edwards KA, Baeumner AJ (2010) Aptamer sandwich assays: label-free and fluorescence investigations of heterogeneous binding events. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:2635–2644
Forster T, Sinanoglu O (eds) (1996) Modern quantum chemistry, Vol. 3. Academic, New York, p 93
Vu TKH, Wheaton VI, Hune DT, Charo I, Couehlin SR (1991) Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature 353:674–677
Corral-Rodrguez MA, Macedo-Ribeiro S, Pereira PJB, Fuentes-Prior P (2010) Leech-derived thrombin inhibitors: from structures to mechanisms to clinical applications. J Med Chem 53:3847–3861
Padmanabhan K, Tulinsky A (1996) An ambiguous structure of a DNA 15-mer thrombin complex. Acta Crystallogr D52:272–282
Jin Y, Bai J, Li H (2010) Label-free protein recognition using aptamer-based fluorescence assay. Analyst 135:1731–1735
Rinker S, Ke Y, Liu Y, Chhabra R, Yan H (2008) Self-assembled DNA nanostructures for distance-dependent multivalent ligand-protein binding. Nat Nanotechnol 3:418–422
Rosenholm JM, Sahlgren C, Linden M (2010) Towards multifunctional, targeted drug delivery systems using mesoporous silica nanoparticles - opportunities & challenges. Nanoscale 2:1870–1883
Latterini L, Amelia M (2009) Sensing proteins with luminescent silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 25:4767–4773
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India. We thank Prof. S. Krishnasamy and P. Manojkumar, School of Biotechnology, Madurai Kamaraj University for valuable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
The detailed experimental scheme, SEM, EDX data and label free scheme with luminescence spectral studies in the presence of thrombin. (DOCX 1979 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, E., Mareeswaran, P.M. & Rajagopal, S. Highly Sensitive Optical Biosensor for Thrombin Based on Structure Switching Aptamer-Luminescent Silica Nanoparticles. J Fluoresc 23, 137–146 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-012-1127-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-012-1127-0