Abstract
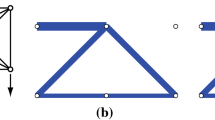
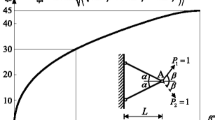
This article considers the non-linear mixed 0–1 optimization problems that appear in topology optimization of load carrying structures. The main objective is to present a Generalized Benders’ Decomposition (GBD) method for solving single and multiple load minimum compliance (maximum stiffness) problems with discrete design variables to global optimality. We present the theoretical aspects of the method, including a proof of finite convergence and conditions for obtaining global optimal solutions. The method is also linked to, and compared with, an Outer-Approximation approach and a mixed 0–1 semi definite programming formulation of the considered problem. Several ways to accelerate the method are suggested and an implementation is described. Finally, a set of truss topology optimization problems are numerically solved to global optimality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtziger W., Kŏcvara M.: Structural topology optimization with eigenvalues. SIAM J. Optim. 18(4), 1129–1164 (2007)
Achtziger W., Stolpe M.: Global optimization of truss topology with discrete bar areas—Part I: Theory of relaxed problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 40(2), 247–280 (2007)
Achtziger W., Stolpe M.: Truss topology optimization with discrete design variables—Guaranteed global optimality and benchmark examples. Struct. Multidiscipl. Optim. 34(1), 1–20 (2007)
Anjos M., Vannelli A.: Computing globally optimal solutions for single-row layout problems using semidefinite programming and cutting planes. INFORMS J. Comput. 20(4), 611–617 (2008)
Ben-Tal A., Nemirovski A.: Robust truss topology design via semidefinite programming. SIAM J. Optim. 7(4), 991–1016 (1997)
Benders J.: Partitioning procedures for solving mixed-variables programming problems. Numerische Mathematik 4(1), 238–252 (1962)
Bendsøe M., Sigmund O.: Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Bollapragada S., Ghattas O., Hooker J.: Optimal design of truss structures by logic-based branch and cut. Oper. Res. 49(1), 42–51 (2001)
Brenner S., Scott L.: The mathematical theory of finite element methods. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Canto S.: Application of Benders’ decomposition to power plant preventive maintenance scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 184, 759–777 (2008)
Codato G., Fischetti M.: Combinatorial Benders’ cuts for mixed-integer linear programming. Oper. Res. 54(4), 756–766 (2006)
Costa A.: A survey on Benders decomposition applied to fixed-charge network analysis problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 32, 1429–1450 (2005)
Craven B., Mond B.: Linear programming with matrix variables. Linear Algebra Appl. 38, 73–80 (1981)
Datta B.: Numerical Linear Algebra and Applications. Brooks/Cole Publishing, Wisconsin (1995)
Deufhard P., Hohmann A.: Numerical Analysis in Modern Scientific Computing. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Duran M., Grossmann I.: An outer-approximation algorithm for a class of mixed-integer nonlinear programs. Math. Program. 36(3), 307–339 (1986)
Geoffrion A.: Elements of large-scale mathematical programming: Part I: Concepts. Inst. Manag. Sci. 16(11), 652–675 (1970)
Geoffrion A.: Elements of large-scale mathematical programming: Part II: Synthesis of Algorithms and Bibliography. Inst. Manag. Sci. 16(11), 676–691 (1970)
Geoffrion A.: Duality in non linear programming: a simplified applications-oriented development. SIAM Rev. 13(1), 1–37 (1971)
Geoffrion A.: Generalized Benders decomposition. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 10(4), 237–260 (1972)
Hiriart-Urruty J., Lemaréchal C.: Convex Analysis and Minimization Algorithms II. Springer, Berlin (1996)
ILOG Inc.: IBM ILOG CPLEX 9.1 Users Manual for CPLEX (2007)
Kojima, M., Kojima, S., Hara, S.: Linear algebra for semidefinite programming. Tech. rep., Department of Mathematical and Computing Sciences, Tokyo Institute of Technology. Research Report B-290 (1994)
Lazimy R.: Extension of the generalized Benders decomposition. Commun. Appl. Numer. Methods 6, 195–203 (1986)
Leyffer S., Fletcher R.: Solving mixed-integer nonlinear programs by outer-approximation. Math. Program. 66(3), 327–349 (1994)
Magnanti T., Magnanti T., Magnanti T.: Accelerating Benders decomposition: Algorithmic enhancement and model selection criteria. Oper Res. 29(3), 464–484 (1981)
The MathWorks, Inc.: Matlab user manual version 7.1 (2005)
Muñoz, E.: Global optimization for discrete topology design problems by generalized Benders’ decomposition. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mathematics, Technical University of Denmark (2010)
Rasmussen M., Stolpe M.: Global optimization of discrete truss topology design problems using a parallel cut-and-branch method. Comput. Struct. 86(13-14), 1527–1538 (2008)
Rei W., Cordeau J., Gendreau M., Soriano P.: Accelerating Benders decomposition by local branching. INFORMS J. Comput. 21(2), 333–346 (2009)
Sahinidis N., Grossman I.: Convergence properties of generalized Benders decomposition. Comput. Chem. Eng. 15, 481–491 (1991)
Svanberg K.: Method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 24(2), 359–373 (1987)
Svanberg K.: On the convexity and concavity of compliances. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 7(1–2), 42–46 (1994)
Svanberg K.: A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations.. SIAM J. Optim. 12(2), 555–573 (2002)
Vandenberghe L., Boyd S.: Semidefinite programming. SIAM Rev. 38(1), 49–95 (1996)
Zhu Y., Kuno T.: Global optimization of non-convex MILP by a hybrid branch-and-bound and revised general Benders decomposition approach. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 42(3), 528–539 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz, E., Stolpe, M. Generalized Benders’ Decomposition for topology optimization problems. J Glob Optim 51, 149–183 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-010-9627-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-010-9627-4
Keywords
- Structural topology optimization
- Global optimization
- Generalized Benders’ Decomposition
- Outer-approximation