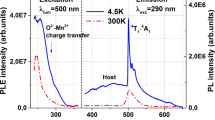
Optical characterizations for ZnO doped with killer impurities (Co or Fe or Ni) having doping concentrations 0.05–1.00% by weight have been carried out at 77 K. Optical properties such as excited state lifetime, trap-depth and decay constant values have been measured using the pulse excitation method. The effect of killer dopants, concentration of killer ions as well as the effect of temperature on various optical parameters values has been observed. Multi-exponential decay curves have been observed. Lifetime values are found to be in the micro- and nano-second time domain and a reverse trend is obtained with increase in concentration of killer impurities. With decreases in temperature from 300 to 77 K, lifetime shortening takes place. The effect of killer impurities is more prominent at higher concentrations. A mixed trend in decay constant values is observed with the increase proportional to the concentration of killer impurities. The values of the decay constant show a mixed effect with change in impurity concentrations. The value of the decay constant 0.76, corresponding to ZnO: Ni (0.7%) is the highest among all the doped ZnO phosphors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wegh R.T., Donker H., Van Loef E.V.D., Oskam K.D., Meijerink A. (2000). J. Lumin. 87: 1017
Salley G.M., Wenger O.S., Kramer K.W., Gudel H.U. (2002). Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 6: 487
Ronda C.R. (1997). J. Lumin. 72: 49
Bagnall D.M., Chen Y.F., Zhu Z., Yao T., Koyama S., Sen M.Y., Goto T. (1997). Appl. Phys. Lett. 70: 2230
Reynolds D.C., Look D.C., Jogai B. (1996). Solid State Commun. 99:873
Ohta H., Kawamura K., Orita M., Hirano M., Sarukura N., Hosono H. (2000). Appl. Phys. Lett. 77: 475
Ronfard-Haret J.C. (2003). J. Lumin. 104: 103
Ueda K., Tabat H., Kawai T. (2001). Appl. Phys. Lett. 79: 988
Sato K., Yoshida H.K. (2002). Semicond. Sci. Technol. 17: 376
Boemare C., Monteiro T., Guilherme J.G., Alves E. (2001). Physica B 308: 985
Moncorge R., Bettinelli M., Guyot Y., Capobianco J.A., Girard S. (1999). J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 11: 6831
Walker G., Kamaluddin B., Glynn T.J., Sherlock R. (1994). J. Lumin. 60: 123
White W.B., Matsumura M., Linnehan D.G., Furukawa T., Chandrasekhar B.K. (1986). Am. Mineral. 71: 1415
Pressel K., Thonke K., Dornen A., Pensl G. (1991). Phys. Rev. B 43: 2239
Troccoli M., Scamarico G., Fraboni B., Priolo F., Gasparotto A. (2000). Semicond. Sci. Technol. 16: L1
Bhatti H.S., Sharma R., Verma N.K., Vadera S.R., Manzoor K. (2006). J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39: 1754
Bhatti H.S., Gupta A., Verma N.K., Kumar S. (2006). J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 17: 281
Reynolds D.C., Look D.C., Jogai B., Hoelscher J.E., Sherriff R.E., Harris M.T., Callahan M.J. (2000). J. Appl. Phys. 88: 2152
Teke A., Ozgur U., Dogan S., Gu X., Morkoç H., Nemeth B., Nause J., Everitt H.O. (2004). Phys. Rev. B 70: 195207
Koida T., Chichibu S.F., Uedono A., Tsukazaki A., Kawasaki M., Sota T., Segawa Y., Koinuma H. (2003). Appl. Phys. Lett. 82: 532
Kobayashi A., Sankey O.F., Dow J.D. (1983). Phys. Rev. B 28: 946
Jung S.W., Park W.I., Cheong H.D., Yi G.C., Jang H.M., Hong S., Joo T. (2002). Appl. Phys. Lett. 80: 1924
Sapra S., Shanthi N., Sarma D.D. (2002). Phys. Rev. B, 66: 205202
Chen W., Sammynaiken R., Huamg Y., Malam J.O., Wallenberg R., Bovin J.O., Zwiller V., Kotov N.A. (2001). J. Appl. Phys 89: 1120
Bhatti H.S., Sharma R., Verma N.K. (2006). Physica B 382:38
Bhatti H.S., Sharma R., Verma N.K. (2006). J. Mod. Optics 53: 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Verma, N.K. & Bhatti, H.S. Effect of Killer Impurities on Optical Properties of ZnO at Low Temperature. J Low Temp Phys 147, 49–57 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-006-9297-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-006-9297-2