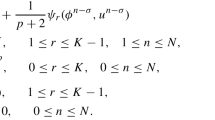Abstract
We perform in this paper the numerical analysis of some penalty stabilized solvers for the unsteady Navier–Stokes equations. We consider low-order and high-order methods. The low-order method is a pure penalty method, while the high-order one is a projection-stabilized method. We perform their numerical analysis (stability and convergence) for solutions that only need to bear the natural regularity. In this analysis, the stability is based upon specific inf-sup conditions. No local orthogonality properties are needed for the projection-interpolation operator. The convergence is based upon the representation of the stabilizing terms by means of bubble finite element spaces. We include some numerical tests for realistic flows that confirm the theoretical expectations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgrall, R., Mezine, M.: Construction of second-order accurate monotone and stable residual distribution schemes for steady problems. J. Comput. Phys. 195, 474–507 (2004)
Abgrall, R., Roe, P.L.: High order fluctuation schemes on triangular meshes. J. Sci. Comput. 19, 3–36 (2003)
Blasco, J., Codina, R.: Stabilized finite element method for the transient Navier–Stokes equations based on a pressure gradient projection. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 182, 277–300 (2000)
Braack, M., Burman, E.: Local projection stabilization for the Oseen problem and its interpretation as a variational multiscale method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43, 2544–2566 (2000)
Braack, M., Burman, E., John, V., Lube, G.: Stabilized finite element methods for the generalized Oseen problem. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196, 853–866 (2007)
Brezis, H.: Analyse Fonctionnelle. Théorie Appl (Dunod, 2005)
Brezzi, F., Pitkäranta, J.: On the stabilization of finite element approximations of the Stokes problem. In: Hackbush, W. (ed.) Efficient Solutions of Elliptic Systems. Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics, pp. 11–19. Vieweg, Braunchsweig/Wiesbaden (1984)
Burman, E.: Interior penalty variational multiscale method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations: monitoring artificial dissipation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196, 4045–4058 (2007)
Burman, E., Fernández, M.: Continuous interior penalty finite element method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations: space discretization and convergence. Numer. Math. 107, 39–77 (2007)
Burman, E., Fernández, M., Hansbo, P.: Continuous interior penalty finite element method for Oseen equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 1248–1274 (2006)
Chacón Rebollo, T.: A term by term stabilzation algorithm for finite element solution of incompressible flow problems. Numer. Math. 79, 283–319 (1998)
Chacón Rebollo, T.: An analysis technique for stabilized finite element solution of incompressible flows. M2AN Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 35, 57–89 (2001)
Chacón Rebollo, T., Girault, V., Gómez Mármol, M., Sánchez Muñoz, I.: A high order term-by-term stabilization solver for incompressible flow problems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 33, 974–1007 (2013)
Chacón Rebollo, T., Gómez Mármol, M., Narbona Reina, G.: Numerical analysis of the PSI solution of advection–diffusion problems through a Petrov–Galerkin formulation. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 17, 1905–1936 (2004)
Christie, I., Griffiths, D.F., Mitchell, A.R., Zienkiewicz, O.C.: Finite element methods for second order differential equations with significant first derivatives. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 10, 1389–1396 (1976)
Ciarlet, P.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problem. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Codina, R.: Stabilization of incompressibility and convection through orthogonal sub-scales in finite element methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 1597–1599 (2000)
Cools, R.: An encyclopedia of curbature formulas. J. Complex. 19, 445–453 (2003)
Deconinck, H., Struijs, R., Roe, P.L.: Compact advection schemes on unstructured grids. Comput. Fluid Dynamics. VKI Lecture Series, vol. 1993–04 (1993)
Franca, L.P., Frey, S.L.: Stabilized finite elements II: the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 99, 209–233 (1992)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Inoue, O., Sakuragi, A.: Vortex shedding from a circular cylinder of finite length at low Reynolds numbers. Phys. Fluids 20, 033601 (2008)
John, V., Knobloch, P.: On spurious oscillations at layers diminishing (SOLD) methods for convection–diffusion equations: part I—a review. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 96, 2197–2215 (2007)
Knobloch, P.: A generalization of the local projection stabilization for convection–diffusion–reaction equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 48, 659–680 (2010)
Lions, J.L.: Quelques méthodes de résolution des problèmes aux limites non linéaires (Dunod, 2002)
Matthies, G., Skrypacz, P., Tobiska, L.: A unified convergence analysis for local projection stabilisations applied to the Oseen problem. M2AN Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 41, 713–742 (2007)
Oswald, P.: On a BPX preconditioner for \(P_1\) elements. Computing 51, 125–133 (1993)
Roe, P.L.: Fluctuations and signals—a framework for numerical evolution problems. In: Morton, K.W., Baines, M.J. (eds.) Numerical Methods for Fluid Dynamics, pp. 219–257. Academic Press, London (1982)
Roos, H.G., Stynes, M., Tobiska, L.: Robust Numerical Methods for Singularly Perturbed Differential Equations. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 24, 2nd ed. Springer, New York-Heidelberg (2008)
Simon, J.: Compact sets in \(L^p(0, T;B)\). Ann. Mat. Pur. Appl. (IV) 146, 65–96 (1987)
Snyder, D.O., Degrez, G.: Large-eddy simulation with complex 2-D geometries using a parallel finite-element/spectral algorithm. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 41, 1119–1135 (2003)
Struijs, R.: A multidimensional upwind discretization method for the Euler equations on unstructured grids. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Delft (1994)
Struijs, R., Deconinck, H., Roe, P.L.: Fluctuation splitting schemes for the 2D Euler equations. Comput. Fluid Dyn. VKI Lecture Series, vol. 1991–01 (1991)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. AMS (2000)
Wen, C.Y., Lin, C.Y.: Two-dimensional vortex shedding of a circular cylinder. Phys. Fluids 13, 557–560 (2001)
Acknowledgments
The work of all three authors has been partially supported by Proyectos de Excelencia de la Junta de Andalucia—FEDER funds P07-FQM-02538 and P12-FQM-454. The work of M. Restelli has been partially supported by Regione Lombardia and CILEA Consortium through a “LISA” 2012 project as well as by the CINECA Consortium award N. HP10C9F0EL, 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chacón Rebollo, T., Gómez Mármol, M. & Restelli, M. Numerical Analysis of Penalty Stabilized Finite Element Discretizations of Evolution Navier–Stokes Equations. J Sci Comput 63, 885–912 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9918-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9918-x