Abstract
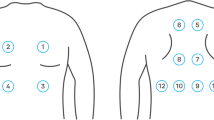
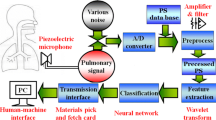
Recognition of lung sounds is an important goal in pulmonary medicine. In this work, we present a study for neural networks–genetic algorithm approach intended to aid in lung sound classification. Lung sound was captured from the chest wall of The subjects with different pulmonary diseases and also from the healthy subjects. Sound intervals with duration of 15–20 s were sampled from subjects. From each interval, full breath cycles were selected. Of each selected breath cycle, a 256-point Fourier Power Spectrum Density (PSD) was calculated. Total of 129 data values calculated by the spectral analysis are selected by genetic algorithm and applied to neural network. Multilayer perceptron (MLP) neural network employing backpropagation training algorithm was used to predict the presence or absence of adventitious sounds (wheeze and crackle). We used genetic algorithms to search for optimal structure and training parameters of neural network for a better predicting of lung sounds. This application resulted in designing of optimum network structure and, hence reducing the processing load and time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sovijarvi, A. R. A., Vanderschoot, J., and Earis, J. E., Standardization of computerised respiratory sound analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 10:77, 585, 2000.
Pasterkamp, H., Kraman, S. S., and Wodicka, G. R., Respiratory sounds: Advances beyond the stethoscope. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 156:974–987, 1997.
Anderson, K., Aitken, S., Carter, R., MacLeod, J. E., and Moran, F., Variation of breath sound and airway caliber induced by histamine challenge. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 141:1147–1150, 1990.
Gavriely, N., Palti, Y., Alroy, G., and Grotberg, J. B., Measurement and theory of wheezing breath sounds. J. Appl. Physiol. 57:481–492, 1984.
Malmberg, L. P., Pesu, L., and Sovijärvi, A. R. A., Significant differences in flow standardised breath sound spectra in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stable asthma, and healthy lungs. Thorax 50:1285–1291, 1995.
Pasterkamp, H., Consunji-Araneta, R., Oh, Y., and Holbrow, J., Chest surface mapping of lung sounds during methacholine challenge. Pediatric. Pulmonol. 2;21–30, 1997.
Schreur, H. J., Diamant, Z., Vanderschoot, J., Zwinderman, A. H., Dijkman, J. H., and Sterk, P. J., Lung sounds during allergeninduced asthmatic responses in patients with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 153:1474–1480, 1996.
Baughman, R. P., Shipley, R. T., Loudon, R. G., and Lower, E., Crackles in interstitial lung disease: Comparison of sarcoidosis and fibrosing alveolitis. Chest 100:96–101, 1991.
Dalmasso, F., Guarene, M., Spagnolo, R., Benedetto, G., and Righini, G., A computer system for timing and acoustical analysis of crackles: A study in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Bull. Eur. Physio-Pathol. Respir. 20:139–144, 1984.
al Jarad, N., Strickland, B., Borhamley, G., Lock, S., Logan-Sinclair, R., and Rudd, R. M., Diagnosis of asbestosis by a time expanded wave form analysis, auscultation and high resolution computed tomography: A comparative study. Thorax 48;347–353, 1993.
Murphy, R. L., Gaensler, E. A., Holford, S. K., Del Bono, E. A., and Epler, G., Crackles in the early detection of asbestosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 129:375–379, 1984.
Piirilä, P., Sovijärvi, A. R. A., Kaisla, T., Rajala, H. M., and Katila, T., Crackles in patients with fibrosing alveolitis, bronchiectasis, COPD and heart failure. Chest 99:1076–1083, 1991.
Sovijärvi, A. R. A., Malmberg, L. P., Paajanen, E., Piirilä, P., Kallio, K., and Katila, K., Averaged and time-gated spectral analysis of respiratory sounds. Repeatability of spectral parameters in healthy men and in patient with fibrosing alveolitis. Chest 109:1283–1290, 1996.
Sovijärvi, A. R. A., Piirilä, P., and Luukkonen, R., Separation of pulmonary disorders with two-dimensional discriminant analysis of crackles. Clin. Physiol. 16:172–181, 1996.
Forgacs, P., Lung Sounds, Macmillan, New York, 1978.
Sovijärvi, A. R. A., Malmberg, L. P., Charbonneau, G., Vanderschoot, J., Dalmasso, F., Sacco, C., Rossi, M., and Earis, J. E., Characteristics of breath sounds and adventitious respiratory sounds. Eur. Respir. Rev. 10:77,591–596, 2000.
Sovijarvi, A. R. A., Vandershoot, J., and Earis J. E., (eds.), Computerized Sound Analysis (CORSA): Recommended Standards for Terms and Techniques-ERS Task Force Report, European Respiratory Review, Vol. 10, ERS Journals Ltd, UK, 2000, Review No. 77.
Crick, F., The recent excitement about neural networks. Nature 337:129–132, 1989.
Tu, J., Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 49:1225–1231, 1996.
Pesu, L., Helistö, P., Ademovic, E., Pesquet, J. C., Saarinen, A., Sovijärvi, A. R. A., Classification of respiratory sounds based on wavelet packet decomposition and learning vector quantization. Technol. Health Care 6:65–74, 1998.
Oud, M., Lung function interpolation by means of neural-network-supported analysis of respiration sounds. Med. Eng. Phys. 25:309–316, 2003.
Rietveld, S., Oud, M., and Dooijes, E. H., Classification of asthmatic breath sounds: Preliminary results of the classifying capacity of human examiners versus artificial neural networks. Comput. Biomed. Res. 32:440–448, 1992.
Wilks, P. A. D., and English, M. J., A system for rapid identification of respiratory abnormalities using a neural network. Med. Eng. Phys. 17:551–555, 1995.
Malmberg, L., Kallio, K., Haltsonen, S., Katila, T., Sovijarvi, A., Classification of lung sounds in patients with asthma, emphysema, fibrosing alveolitis and healthy lungs by using self-organizing maps. Clin. Physiol. 16:115–129, 1996.
Waitman, L. R., Clarkson, K. P., Barwise, J. A., and King, P. H., Representation and classification of breath sounds recorded in an intensive care setting using neural networks. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 16:95–105, 2005.
Yao, X., Evolving artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 87:1423–1447, 1999.
Castillo, P. A., Merelo, J. J., Prieto, A., Rivas, V., and Romero, G., G-prop: Global optimization of multilayer perceptrons using Gas. Neurocompution 35:149–163, 2000.
Bath, P. A., Pendleton, N., Morgan, K., Clague, J. E., Horan, M. A., and Lucas, S. B., New approach to risk determination: Development of risk profile for new falls among community-dwelling older people by use of a genetic algorithm neural network (GANN). J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 55:M17–M21, 2000.
Narayanan, M. N., and Lucas, S. B., A genetic algorithm to improve a neural network to predict a patient’s response to warfarin. Methods Inf. Med. 32:55–58, 1993.
Potter, S. R., Miller, M. C., and Mangold, L. A., Genetically engineered neural networks for predicting prostate cancer progression after radical prostatectomy., Urology. 54:791–795, 1999.
Dybowski, R., Weller, P., Chang, R., and Gant, V., Prediction of outcome in critically ill patients using artificial neural network synthesised by genetic algorithm. Lancet 347:1146–1150, 1997.
Heckerling, P. S., Gerber, B. S., Tape, T. G., and Wigton, R. S., Use of genetic algorithm for neural network to predict community-acquired pneumonia. Artif. Intell. Med. 30:71–84, 2004.
Güler, I., and Übeyli, E. D., Detection of ophthalmic artery stenosis by least-mean squares backpropagation neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 33:333–343, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Güler, İ., Polat, H. & Ergün, U. Combining Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm for Prediction of Lung Sounds. J Med Syst 29, 217–231 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-005-5182-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-005-5182-9