Abstract
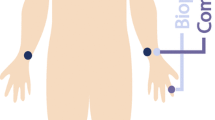
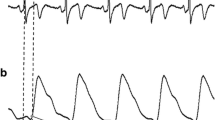
Pulse wave velocity (PWV) is a useful method to assess arterial stiffness and predict mortality of atherosclerosis-related diseases. The progression of atherosclerosis is not homogeneous. There must be difference of PWV between sites by site. Therefore we designed a multi-channel instrument to measure PWV at different sites of the body simultaneously. We measured PWV at six different regions simultaneously. Thirty four healthy adults received the measurement. We found that PWVs were higher in the large vessels, by measuring from the heart to toes and heart to fingers as compared with the measurement from the heart to the earlobes (4.76 ± 0.46 m/s; 4.67 ± 0.41 m/s; 1.10 ± 0.16 m/s). The PWV of the left and right sides were the same. Although there were statistically significances, the correlation of PWV between foot and hand is better than those between ear and foot and between ear and hand. Herein we presented a novel and reliable measurement of PWV. The changes of PWV in different regions may be used in predicting disease processes such as stroke, coronary artery diseases and renal diseases, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laurent, S., Boutouyrie, P., Asmar, R., Gautier, I., Laloux, B., Guize, L., Ducimetiere, P., and Benetos, A., Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 37:1236–1241, 2001.
London, G. M., and Cohn, J. N., Prognostic application of arterial stiffness: task forces. Am. J. Hypertens. 15:754–758, 2002.
Wang, X., Keith, J. C., Jr., Struthers, A. D., and Feuerstein, G. Z., Assessment of arterial stiffness, a translational medicine biomarker system for evaluation of vascular risk. Cardiovasc. Ther. 26(3):214–223, 2008.
Mackenzie, I. S., Wilkinson, I. B., and Cockcroft, J. R., Assessment of arterial stiffness in clinical practice. QJM. 95:67–74, 2002.
Oliver, J. J., and Webb, D. J., Noninvasive assessment of arterial stiffness and risk of atherosclerotic events. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:554–566, 2003.
Blacher, J., Asmar, R., Djane, S., London, G. M., and Safar, M. E., Aortic pulse wave velocity as a marker of cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 33:1111–1117, 1999.
Wilkinson, I. B., Webb, D. J., and Cockcroft, J. R., Aortic pulse-wave velocity. Lancet. 354:1996–1997, 1999.
Millasseau, S. C., Guigui, F. G., Kelly, R. P., Prasad, K., Cockcroft, J. R., Ritter, J. M., and Chowienczyk, P. J., Noninvasive assessment of the digital volume pulse. Comparison with the peripheral pressure pulse. Hypertension. 36:952–956, 2000.
Tsai, W. C., Chen, J. Y., Wang, M. C., Wu, H. T., Chi, C. K., Chen, Y. K., Chen, J. H., and Lin, L. J., Association of risk factors with increased pulse wave velocity detected by a novel method using dual-channel photoplethysmography. Am. J. Hypertens. 18:1118–1122, 2005.
McLeod, A. L., Uren, N. G., Wilkinson, I. B., Webb, D. J., Maxwell, S. R., Northridge, D. B., and Newby, D. E., Non-invasive measures of pulse wave velocity correlate with coronary arterial plaque load in humans. J. Hypertens. 22:363–368, 2004.
Tillin, T., Chambers, J., Malik, I., Coady, E., Byrd, S., Mayet, J., Wright, A. R., Kooner, J., Shore, A., Thom, S., Chaturvedi, N., and Hughes, A., Measurement of pulse wave velocity: site matters. J. Hypertens. 25:383–389, 2007.
Yu, W. C., Chuang, S. Y., Lin, Y. P., and Chen, C. H., Brachial-ankle vs carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity as a determinant of cardiovascular structure and function. J. Hum. Hypertens. 22:24–31, 2008.
Ulijaszek, S. J., and Kerr, D. A., Anthropometric measurement error and the assessment of nutritional status. Br. J. Nutr. 82:165–177, 1999.
Mattace-Raso, F. U., van der Cammen, T. J., Hofman, A., van Popele, N. M., Bos, M. L., Schalekamp, M. A., Asmar, R., Reneman, R. S., Hoeks, A. P., Breteler, M. M., and Witteman, J. C., Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation. 113:657–663, 2006.
Willum-Hansen, T., Staessen, J. A., Torp-Pedersen, C., Rasmussen, S., Thijs, L., Ibsen, H., and Jeppesen, J., Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation. 113:664–670, 2006.
Foo, J. Y. A., Bilateral transit time assessment of upper and lower limbs as a surrogate ankle brachial index marker. Angiology. 59:283–289, 2008.
Foo, J. Y. A., Wilson, S. J., Williams, G. R., Harris, M. A., and Cooper, D. M., Pulse transit time changes observed with different limb positions. Physiol. Meas. 26:1093–1102, 2005.
Gladdish, S., Manawadu, D., Banya, W., Cameron, J., Bulpitt, C. J., and Rajkumar, C., Repeatability of non-invasive measurement of intracerebral pulse wave velocity using transcranial Doppler. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 108:433–439, 2005.
Jiang, B., Liu, B., McNeill, K. L., and Chowienczyk, P. J., Measurement of pulse wave velocity using pulse wave Doppler ultrasound: Comparison with arterial tonometry. Ultrasound. Med. Biol. 34:509–512, 2008.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the National Science Council under Grant NSC 97-2221- E-259-019, Taiwan, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Subjects | Age(yrs) | PWV(Normalized) | PWV(Ear) | PWV(Hand-Foot) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mean | SD | CV | Mean | SD | CV | Mean(m/s) | SD | CV | ||
1 | 25 | 0.9681 | 0.0567 | 0.0586 | 1.2375 | 0.0354 | 0.0286 | 4.7225 | 0.1767 | 0.0374 |
2 | 27 | 0.8863 | 0.0800 | 0.0902 | 1.0884 | 0.0719 | 0.0661 | 4.4125 | 0.1289 | 0.0292 |
3 | 25 | 1.1088 | 0.0533 | 0.0481 | 1.4964 | 0.0934 | 0.0624 | 5.2875 | 0.2207 | 0.0417 |
4 | 49 | 1.0138 | 0.0338 | 0.0333 | 1.4025 | 0.0036 | 0.0026 | 4.775 | 0.158 | 0.0331 |
5 | 24 | 0.9593 | 0.0703 | 0.0733 | 1.4403 | 0.0217 | 0.0151 | 4.325 | 0.1008 | 0.0233 |
6 | 28 | 0.9972 | 0.0311 | 0.0312 | 1.4027 | 0.0392 | 0.0279 | 4.66 | 0.1885 | 0.0405 |
7 | 23 | 0.9533 | 0.0440 | 0.0461 | 1.2709 | 0.1002 | 0.0789 | 4.575 | 0.1714 | 0.0375 |
8 | 22 | 0.9181 | 0.0734 | 0.0799 | 1.1767 | 0.1439 | 0.1223 | 4.485 | 0.1328 | 0.0296 |
9 | 24 | 0.9728 | 0.0284 | 0.0292 | 1.3519 | 0.0680 | 0.0503 | 4.5725 | 0.045 | 0.0098 |
10 | 27 | 1.0055 | 0.0545 | 0.0542 | 1.3397 | 0.0208 | 0.0155 | 4.825 | 0.2859 | 0.0593 |
11 | 26 | 1.0607 | 0.0278 | 0.0262 | 1.4720 | 0.0665 | 0.0451 | 4.99 | 0.1424 | 0.0285 |
12 | 26 | 1.0816 | 0.0620 | 0.0573 | 1.5347 | 0.0314 | 0.0205 | 5.0275 | 0.2869 | 0.0571 |
13 | 27 | 1.0279 | 0.0403 | 0.0392 | 1.4651 | 0.0670 | 0.0457 | 4.77 | 0.1512 | 0.0317 |
14 | 55 | 1.0609 | 0.0565 | 0.0533 | 1.3772 | 0.0322 | 0.0234 | 5.155 | 0.2243 | 0.0435 |
15 | 65 | 1.2448 | 0.0388 | 0.0311 | 1.6729 | 0.0029 | 0.0017 | 5.95 | 0.2347 | 0.0394 |
16 | 62 | 1.0828 | 0.0450 | 0.0416 | 1.5093 | 0.0222 | 0.0147 | 5.08 | 0.207 | 0.0408 |
17 | 70 | 1.1310 | 0.0736 | 0.0651 | 1.6604 | 0.0030 | 0.0018 | 5.1675 | 0.3397 | 0.0657 |
18 | 68 | 1.0374 | 0.0480 | 0.0463 | 1.4911 | 0.1111 | 0.0745 | 4.7925 | 0.0718 | 0.015 |
19 | 65 | 0.8209 | 0.0603 | 0.0735 | 1.2136 | 0.0515 | 0.0424 | 3.7325 | 0.1717 | 0.046 |
20 | 51 | 0.8479 | 0.0715 | 0.0843 | 1.0570 | 0.0806 | 0.0762 | 4.195 | 0.1828 | 0.0436 |
21 | 49 | 0.8951 | 0.0275 | 0.0307 | 1.2267 | 0.0732 | 0.0596 | 4.2375 | 0.0964 | 0.0227 |
22 | 58 | 0.9388 | 0.1612 | 0.1717 | 1.0125 | 0.0177 | 0.0175 | 4.915 | 0.2344 | 0.0477 |
23 | 69 | 1.0404 | 0.0257 | 0.0247 | 1.4526 | 0.0493 | 0.0340 | 4.88 | 0.1364 | 0.0279 |
24 | 58 | 0.9581 | 0.0403 | 0.0421 | 1.2578 | 0.0244 | 0.0194 | 4.63 | 0.1197 | 0.0259 |
25 | 53 | 1.0041 | 0.0132 | 0.0131 | 1.4025 | 0.0036 | 0.0026 | 4.7075 | 0.0222 | 0.0047 |
26 | 61 | 1.0243 | 0.0315 | 0.0307 | 1.4147 | 0.0853 | 0.0603 | 4.83 | 0.1039 | 0.0215 |
27 | 57 | 0.9925 | 0.0170 | 0.0171 | 1.3901 | 0.0390 | 0.0281 | 4.6475 | 0.0556 | 0.012 |
28 | 66 | 0.9552 | 0.0664 | 0.0695 | 1.2769 | 0.0380 | 0.0298 | 4.58 | 0.4186 | 0.0914 |
29 | 44 | 0.9052 | 0.0398 | 0.0440 | 1.3016 | 0.0685 | 0.0526 | 4.18 | 0.0392 | 0.0094 |
30 | 56 | 0.9030 | 0.0420 | 0.0465 | 1.1761 | 0.0016 | 0.0013 | 4.38 | 0.1329 | 0.0303 |
31 | 55 | 0.9409 | 0.0128 | 0.0136 | 1.3018 | 0.0151 | 0.0116 | 4.4325 | 0.0763 | 0.0172 |
32 | 53 | 1.2170 | 0.1749 | 0.1437 | 1.9809 | 0.0624 | 0.0315 | 5.225 | 0.1967 | 0.0377 |
33 | 76 | 1.1422 | 0.1231 | 0.1078 | 1.7863 | 0.0337 | 0.0189 | 5.0275 | 0.1541 | 0.0307 |
34 | 60 | 0.9042 | 0.0302 | 0.0333 | 1.2263 | 0.0336 | 0.0274 | 4.3025 | 0.168 | 0.039 |
Mean | 1.0000 | 0.0546 | 0.0544 | 1.3784 | 0.0474 | 0.0356 | 4.7199 | 0.164 | 0.0344 | |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, AB., Hsu, PC., Chen, ZL. et al. Measuring Pulse Wave Velocity Using ECG and Photoplethysmography. J Med Syst 35, 771–777 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9469-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-010-9469-0