Abstract
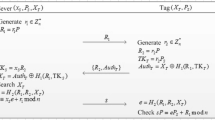
Recently, Chen et al. have proposed a novel tamper resistant prescription RFID access control system, published in the Journal of Medical Systems. In this paper we consider the security of the proposed protocol and identify some existing weaknesses. The main attack is a reader impersonation attack which allows an active adversary to impersonate a legitimate doctor, e.g. the patient’s doctor, to access the patient’s tag and change the patient prescription. The presented attack is quite efficient. To impersonate a doctor, the adversary should eavesdrop one session between the doctor and the patient’s tag and then she can impersonate the doctor with the success probability of ‘1’. In addition, we present efficient reader-tag to back-end database impersonation, de-synchronization and traceability attacks against the protocol. Finally, we propose an improved version of protocol which is more efficient compared to the original protocol while provides the desired security against the presented attacks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdanov, A., Knudsen, L. R., Leander, G., Paar, C., Poschmann, A., Robshaw, M. J. B., Seurin, Y., and Vikkelsoe, C., PRESENT: An Ultra-Lightweight Block Cipher. In: CHES, pp. 450–466, 2007.
Boyer, S. T., WANURSES, New Tamper Resistant Prescription Pad Law, Nursing Practice Blog. http://www.wsnaweb.org/nursing-practice-update/index.php/2009/09/new-tamper-resistant-prescription-pad-law/, 2009.
Chen, Y.-Y., Huang, D.-C., Tsai, M.-L., and Jan, J.-K., A design of tamper resistant prescription RFID access control system. J. Med. Syst. 35:1–7, 2011. doi:10.1007/s10916-011-958-2.
Chien, H.-Y., Yang, C.-C., Wu, T.-C., and Lee, C.-F., Two RFID-based solutions to enhance inpatient medication safety. J. Med. Syst. 35:369–375, 2011.
Phan R. C.-W., Cryptanalysis of a new ultralightweight RFID Authentication protocol—SASI. IEEE Trans. Dep. Sec. Comp. 6(4):316–320, 2009.
Feldhofer, M., and Rechberger, C., A case against currently used hash functions in RFID protocols. In: OTM 2006, volume 4277 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 372–381. Springer, 2006.
Fisher, J. A., and Monahan, T., Tracking the social dimensions of RFID systems in hospitals. Int. J. Med. Inform. 77(3):176–183, 2008.
Wamba, S. F., RFID-enabled healthcare applications, issues and benefits: An archival analysis (1997–2011). J. Med. Syst. 1–6, 2012. doi:10.1007/s10916-011-9807-x.
Huang, H.-H., and Ku, C.-Y., An RFID grouping proof protocol for medication safety of inpatient. J. Med. Syst. 33:467–474, 2009.
Ivetic, D., and Dragan, D., Medical image on the go! J. Med. Syst. 35:499–516, 2011.
Min, D., and Yih, Y., Fuzzy logic-based approach to detecting a passive RFID tag in an outpatient clinic. J. Med. Syst. 35:423–432, 2011.
Ngai, E. W., Poon, J. K., Suk, F. F., and Ng, C. C., Design of an RFID-based healthcare management system using an information system design theory. Inf. Syst. Front. 11(4):405–417, 2009.
Østbye, T., Lobach, D. F., Cheesborough, D., Lee, A. M. M., Krause, K. M., Hasselblad, V., and Bright, D., Evaluation of an infrared/radio frequency equipment-tracking system in a tertiary care hospital. J. Med. Syst. 27:367–380, 2003.
Peris-Lopeza, P., Orfila, A., Mitrokotsa, A., and van der Lubbe, J. C., A comprehensive RFID solution to enhance inpatient medication safety. Int. J. Med. Inform. 80(1):13–24, 2011.
Safkhani, M., Bagheri, N., Sanadhya, S. K., Naderi, M., and Behnam, H., On the security of mutual authentication protocols for RFID systems: The case of Wei et al.’s protocol. In: Garcia-Alfaro, J. et al. (Eds.), volume 7122 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 90–103. Springer, 2011.
Stahl, J., Holt, J., and Gagliano, N., Understanding performance and behavior of tightly coupled outpatient systems using RFID: Initial experience. J. Med. Syst. 35:291–297, 2011.
Sun, P., Wang, B., and Wu, F., A new method to guard inpatient medication safety by the implementation of RFID. J. Med. Syst. 32:327–332, 2008.
Ting, S., Kwok, S., Tsang, A., and Lee, W., Critical elements and lessons learnt from the implementation of an RFID-enabled healthcare management system in a medical organization. J. Med. Syst. 35:657–669, 2011.
Wang, S.-W., Chen, W.-H., Ong, C.-S., Liu, L., and Chuang, Y.-W., RFID applications in hospitals: A case study on a demonstration RFID project in a Taiwan hospital. In: Proceedings of The 39th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 2006.
Wickboldt, A.-K., and Piramuthu, S., Patient safety through RFID: Vulnerabilities in recently proposed grouping protocols. J. Med. Syst. 36(2):431–435, 2012.
Tamper Resistant Prescription Drug Pad Program. Newfoundland labrador, Department of Health and Community Services. http://www.health.gov.nl.ca/health/prescription/hcp_tamperresistantdrugpad.html, 2006.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their suggestions to improve the content and presentation of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have noconflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safkhani, M., Bagheri, N. & Naderi, M. On the Designing of a Tamper Resistant Prescription RFID Access Control System. J Med Syst 36, 3995–4004 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9872-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9872-9