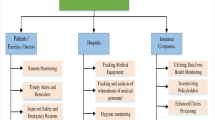
Abstract
Radio frequency identification (RFID) applications have the potential to increase the reliability of healthcare environments. However, there are obvious security and privacy concerns with regard to storing personal and medical data in RFID tags, and the lack of secure authentication systems in healthcare environments remains as a challenge the further use of this technology, one that touches on issues of confidentiality, unforgeability, location privacy, and scalability. This study proposes a novel mutual authentication protocol that considers all of these issues and solves the tradeoff between location privacy and scalability in healthcare environments. A formal proof and analysis is demonstrated to prove the effectiveness of the proposed scheme, and that high reliability has and can be easily deployed and managed. This study also provides a scenario example that applied proposed protocol in the newborn care and management. The result shows that the proposed scheme solves the related tradeoff problem, and is capable of providing both location privacy and scalability. To apply the authentication scheme proposed in this work would be able to increase confidence in future implementations of RFID systems in healthcare environments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, S. W., Chen, W. H., Ong, C. S., Liu, L., and Chuang, Y. W., RFID application in hospitals: a case study on a demonstration RFID project in a Taiwan hospital. In: Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. IEEE, pp. 184a–194a, 2006.
Hwang, M. S., Wei, C. H., and Lee, C. Y., Privacy and security requirements for RFID applications. J. Comput. 20(3):55–60, 2009.
Najera, P., Lopez, J., and Roman, R., Real-time location and inpatient care systems based on passive RFID. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 34(3):980–989, 2011.
Singapore Fights SARS with RFID (2003) Available: http://www.rfidjournal.com/article/view/446
Collins, J., Hospital gets ultra-wideband RFID. RFID J, 2004.
Jeong, B., Cheng, C., Prabhu, V., and Yu, B., An RFID application model for surgery patient identification. IEEE, pp. 1–3, 2008.
Glabman, M., Room for tracking. RFID technology finds the way. Mater. Manag. Health Care 13(5):26, 2004.
Brewin, B., RFID gets FDA push. Fed. Comput. Week. 2004.
Thompson, C. A., Radio frequency tags for identifying legitimate drug products discussed by tech industry. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 61(14):1430–1432, 2004.
Katz, J. E., and Rice, R. E., Public views of mobile medical devices and services: A US national survey of consumer sentiments towards RFID healthcare technology. Int. J. Med. Inform. 78(2):104–114, 2009.
Hung, Y. K., The study of adopting RFID technology in medical institute with the perspectives of cost benefit. International Medical Informatics Symposium in Taiwan, Taiwan, 2007.
Leu, J. G., The benefit analysis of RFID use in the health management center—The experience in Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital. National Taiwan University, 2010.
Yu, C., Chen, C., Liao, P., and Lee, Y., RFID-based operation room and medicare system for patient safety enhancement—a case study of keelung branch. J. Inf. Manag. 15:97–122, 2008.
Barrows, R. C., Jr., and Clayton, P. D., Privacy, confidentiality, and electronic medical records. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 3(2):139–148, 1996.
Loomis, G. A., Ries, J. S., Saywell, R. M., and Thakker, N. R., If electronic medical records are so great, why aren’t family physicians using them? J. Fam. Pract. 51(7):636–641, 2002.
Chatmon, C., van Le, T., and Burmester, M., Secure anonymous RFID authentication protocols. Florida State University, Department of Computer Science, Tech Rep, pp. 1–10, 2006.
Chien, H. Y., Secure access control schemes for RFID systems with anonymity. FMUIT′06, Japan, IEEE, pp. 96–96, 2006.
Luo, Z., Chan, T., and Li, J. S., A lightweight RFID protocol to protect against traceability and cloning attacks. IEEE International Conference on Security and Privacy for Emerging Areas in Communications Networks (ICEBE′05), IEEE, pp. 59–66, 2005.
Duc, D. N., Lee, H., and Kim, K., Enhancing security of EPCglobal Gen-2 RFID against traceability and cloning. Symposium on Cryptography and Information Security, 2006.
Henrici, D., and Muller, P., Hash-based enhancement of location privacy for radio-frequency identification devices using varying identifiers. PerSec′04. IEEE, pp. 149–153, 2004.
Karthikeyan, S., and Nesterenko, M. RFID security without extensive cryptography. SASN, 2005. ACM, pp. 63–67, 2005.
Lee, S., Asano, T., and Kim, K., RFID Mutual Authentication Scheme based on Synchronized Secret Information. Symposium on Cryptography and Information Security, Hiroshima, p. 98, 2006.
Lee, Y. K., and Verbauwhede, I., Secure and low-cost RFID authentication protocols. In: Adaptive Wireless Networks (AWiN). Florida State University, Department of Computer Science, Tallahassee, Florida, USA, pp. 1–5, 2005.
Luo, Z., Chan, T., and Li, J. S., A lightweight mutual authentication protocol for RFID networks. IEEE, pp. 620–625, 2005.
Lee, S., Hwang, Y., Lee, D., and Lim, J., Efficient authentication for low-cost RFID systems. Computational Science and Its Applications (ICCSA):619–627, 2005.
Molnar, D., and Wagner, D., Privacy and security in library RFID: Issues, practices, and architectures. ACM, pp. 210–219, 2004.
Ohkubo, M., Suzuki, K., and Kinoshita, S., Cryptographic approach to “privacy-friendly” tags. MIT, Cambridge, 2003.
Weis, S., Sarma, S., Rivest, R., and Engels, D., Security and privacy aspects of low-cost radio frequency identification systems. Security in pervasive computing. pp. 50–59, 2004.
Overbey, J., Traves, W., and Wojdylo, J., On the keyspace of the Hill cipher. Cryptologia 29(1):59–72, 2005.
Shoup, V. Sequences of games: a tool for taming complexity in security proofs. cryptology eprint archive, report 2004/332, 2004.
Dimitriou, T., A lightweight RFID protocol to protect against traceability and cloning attacks. First International Conference on Security and Privacy for Emerging Areas in Communications Networks (Secure Comm 2005), IEEE, pp. 59–66, 2005.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partially by National Science Council, Taiwan under Grants NSC 101-2218-E-346-001.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ZY., Chen, L. & Wu, JC. A Reliable RFID Mutual Authentication Scheme for Healthcare Environments. J Med Syst 37, 9917 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9917-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9917-0