Abstract
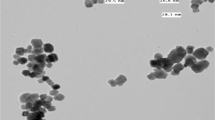
The best approach to induce oxo-biodegradation in polyethylene is the use of special additives known as pro-oxidants. Pro-oxidants accelerate abiotic oxidation and subsequent polymer chain cleavage rendering the product apparently more susceptible to biodegradation. In this work, the abiotic oxidation is studied to understand how the addition of nanoclay affects the oxidation rate and the degradation mechanism of oxo-biodegradable polyethylene. In order to achieve this, the following materials were used in this study: (1) polyethylene (PE), (2) oxo-biodegradable polyethylene (OPE), (3) polyethylene nanocomposite (PENac), and (4) oxo-biodegradable polyethylene nanocomposite (OPENac). Wide-Angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) studies reveal that grafting in the preparation of composites helps to achieve mixed intercalated/exfoliated morphology in PENac and OPENac. Abiotic oxidation was carried out in an oven for a period of 14 days at 70 °C with air supply. The effect of abiotic oxidation was evaluated by measuring the changes in tensile strength, elongation at break, carbonyl index and molecular weight. Results show that OPE and OPENac are more susceptible to oxidation than PENac. The molecular weight distribution data obtained from GPC reveal that the addition of nanoclay does not alter the oxidation mechanism in OPE significantly.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briassoulis D, Aristopoulou A, Bonora M, Verlodt I (2004) Biosyst Eng 88:131–143
Albertsson AC, Andersson SO, Karlsson S (1987) Polym Degrad Stab 18:73–87
Jakubowicz I (2002) Polym Degrad Stab 80:39–43
Albertsson AC, Barenstedt C, Karlsson S (1993) Acta Polym 45:97–103
Khabbaz F, Albertsson AC, Karlsson S (1999) Polym Degrad Stab 63:127–138
Weiland M, Daro A, David C (1995) Polym Degrad Stab 48:275–289
Solaro R, Corti A, Chiellini E (1998) J Envi Poly Deg 6:203–208
Bonhommea S, Cuerb A, Delortb AM, Lemairea J, Sancelmeb M, Scott G (2003) Polym Degrad Stab 81:441–452
Albertsson AC, Karlsson S (1995) Acta Polym 46:114–123
Kawai F, Shibata M, Yokoyama S, Maeda S, Tada K, Hayashi S (1999) Macromol Symp 144:73–84
Sebaa M, Servens C, Pouyet J (1993) J Appl Polym Sci 47:1897–1903
Eyenga II, Focke WW, Prinsloo LC, Tolmay AT (2002) Macromol Symp 178:139–152
ASTM standard D-6954-04 (2004) In: Annual book of ASTM standards. ASTM, Philadelphia, PA
Koutny M, Sancelme M, Dabin C, Pichon N, Delort AM, Lemaire J (2006) Polym Degrad Stab 91:1495–1503
Hakkarainen M, Albertsson AC, Karlsson S (1997) J Appl Polym Sci 66:959–967
Krishna Sastry P, Satyanarayana D, Mohan Rao DV (1998) J Appl Polym Sci 70:2251–2257
Alexandre M, Dubois P (2000) Mater Sci Eng 28:1–63
Stotzky (1966) Can J Microbiol 12:1235–1246
Gopakumar TG, Lee JA, Kontopoulou M, Parent JS (2002) Polymer 43:5483–5491
Qureshi FS, Amin MB, Maadhah AG, Hamid SH (1990) J Poly Eng 9:67–84
Serverini F, Gallo R, Landro LD, Pegoraro M Brambilla L, Tommasini M (2001) Polymer 42:3609–3625
Grassie N, Scott G (1985) Polymer degradation and stabilisation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Seal KL (1994) In: Griffin GJL (ed) Chemistry and Technology of Biodegradable Polymers, pp 116–134
Erlandsson B, Karlsson S, Albertsson AC (1997) Polym Degrad Stab 55:231–245
Bharadwaj RK (2001) Macromolecules 34:9189–9192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, M.M., Gupta, R.K., Gupta, R.K. et al. Abiotic Oxidation Studies of Oxo-biodegradable Polyethylene. J Polym Environ 16, 27–34 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-008-0081-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-008-0081-z