Abstract
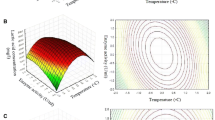
The chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) to its monomer is crucial to reduce both the consumption of renewable resources for the monomer synthesis and the environmental impact related to its production and disposal. In particular, the production of lactic acid from PLA wastes, rather than from virgin raw materials, it is also possible to achieve considerable primary energy savings. The focus of this work is to analyse deeply the PLA hydrolytic decomposition by means of a kinetic model based on two reactions mechanism. To this end, new experimental data have been gathered in order to investigate a wider temperature range (from 140 to 180 °C) and to extend the water/PLA ratio up to 50 % of PLA by weight. The reported results clearly highlight that more than 95 % of PLA is hydrolyzed to water-soluble lactic acid within 120 min, when it is hydrolyzed within 160–180 °C. Furthermore, the kinetic constant is highly influenced by reaction temperature. The proposed “two reactions” kinetic mechanism complies satisfactorily with the experimental data under analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukushima K (2012) Chapter 7 in polylactic acid: synthesis, properties and applications. In: Piemonte V (ed). Nova Science, New York, ISBN: 978-1-62100-248-9
Bastioli C (2005) Starch-based technology. In: Bastioli C (ed) Handbook of biodegradable polymers. Rapra Technology, Italy, pp 257–286
Hakkarainen M (2002) Aliphatic polyesters: abiotic and biotic degradation and degradation products. Adv Polym Sci 157:113
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2011) Bioplastics and petroleum-based plastics: strengths and weaknesses. Energy Sources Part A Energy Recover Environ Effect 33:1949–1959
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2012) Bioplastics and GHGs saving: the land use change (LUC) emissions issue. Energy Sources Part A Energy Recover Environ Effect 34(21):1995–2003
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2011) Land use change emissions: how green are the bioplastics? Environ Prog Sustain Energy 30(4):685–691
Piemonte V (2011) Bioplastic wastes: the best final disposition for energy saving. J Polym Environ 19:988–994
Gironi F, Piemonte V (2011) Life cycle assessment of PET and PLA bottles for drinking water. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 30(3):459–468
Kopinke FD, Remmler M, Mackenzie K, Milder M, Wachsen O (1996) Thermal decomposition of biodegradable polyesters-11. Poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 143:329–342
Noda M, Okuyama H (1999) Thermal catalytic depolymerization of poly(l-lactic acid) oligomer into ll-lactide: effects of Al, Ti, Zn and Zr compounds as catalysts. Chem Pharm Bull 47:467–471
Tsuji H, Daimon H, Fujie K (2003) A new strategy for recycling and preparation of poly(l-lacticacid): hydrolysis in the melt. Biomacromolecules 4:835–840
Matsumura M (2008) Enzymatic depolymerization process of polylactic acid and producing process of polylactic acid using depolymerization products. United States Patent 7396667
Brake LD, Subramanian NS (1993) US Patent 5,229,5281993
Coszach P, Bogaert JC, Willocq J Chemical recycling Of PLA by hydrolysis. WO patent 2010/118954 A1
Coszach P, Bogaert JC, Willocq J Chemical recycling of PLA by alcoholysis. WO patent 2010/118955 A1
Piemonte V, Gironi F (2012) Lactic acid production by hydrolysis of poly(l-lactic acid) in the solid state in aqueous solutions: an experimental and kinetic study. J Polym Environ. doi:10.1007/s10924-012-0468-8
Pitt C, Chasalow F, Hibionada Y, Klimas D, Schindler A (1981) Crucial differences in the hydrolytic degradation between industrial polylactide and laboratory-scale poly(l-lactide). J Appl PolymSci 26:3779–3787
Pitt C, Shah S (1996) Manipulation of the rate of hydrolysis of polymer-drug conjugates: the secondary structure of the polymer. J Controlled Release 39:221–229
Cha Y, Pitt C (1989) The acceleration of degradation-controlled drug delivery from polyester microspheres. J Controlled Release 8:259–265
Li S, Garreau H, Vert M (1990) Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive aliphatic poly-(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. J Mater Sci Mater Med 1:123–130
Li S, Garreau H, Vert M, Li SM, Garreau H, Vert M (1990) Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive poly(a-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. Part 2. Degradation of lactide–glycolide copolymers: PLA37.5GA25 and PLA75GA25. J Mater Sci MaterMed 1:131–139
Li S, Garreau H, Vert M (1990) Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive poly(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. J Mater Sci Mater Med 1:198–206
Li S, McCarthy S (1999) Further investigations on the hydrolytic degradation of poly (dl-lactide). Biomaterials 20:35–44
Gopferich A (1996) Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials 17:103–114
Vert M, Li S, Garreau H (1991) More about the degradation of LA/GA-derived matrices in aqueous media. J Controlled Release 16:15–26
Therin M, Christel P, Li S, Garreau H, Vert M (1992) In vivo degradation of massive poly(alpha-hydroxy acids): validation of in vitro findings. Biomaterials 13:594–600
Grizzi I, Garreau H, Li S, Vert M (1995) Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly (dl-lactic acid) size dependence. Biomaterials 16:305–311
Gopferich A (1997) Polymer bulk erosion. Macromolecules 30:2598–2604
Lyu S, Schley J, Loy B, Lind D, Hobot C, Sparer R, Untereker D (2007) Kinetics and time-temperature equivalence of polymer degradation. Biomacromolecules 8:2301–2310
Viera A (2012) Chapter 8 in polylactic acid: synthesis, properties and applications. In: Piemonte V (ed). Nova Science, New York. ISBN: 978-1-62100-248-9
Proikakis CS, Mamouzelos NJ, Tarantili PA, Andreopulos AG (2006) Swelling and hydrolytic degradation of poly(d,l-lactic acid) in aqueous solutions. Polym Degrad Stab 91:614–619
Burkesroda F, Schedl L, Gopferich A (2002) Why degradable polymers undergo surface or bulk erosion. Biomaterials 23:4221–4231
Tsuji H, Saeki T, Tsukegi T, Daimon H, Fujie K (2008) Comparative study on hydrolytic degradation and monomer recovery of poly(l-lactic acid) in the solid and in the melt. Polym Degrad Stab 93:1956–1963
Cha Y, Pitt CG (1990) The biodegradability of polyester blends. Biomaterials 11:108–112
Yagihashi M, Funazukuri T (2010) Ind Eng Chem Res 49(3):1247–1251
Carrasco F, Pages P, Gamez-Perez J (2010) Polym Degrad Stab 95(12):2508–2514
Henton DE, Gruber P, Lunt J, Randall J (2005) Polylactic acid tecnology. In: Mohanty K, Misra M, Drzal LT (eds) Natural fibers. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Gironi F, Piemonte V (2011) Temperature and solvent effects on polyphenols extraction process from chestnut tree wood. Chem Eng Res Des 89(7):857–862
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Sara Sabatini for his useful contribution and for the many days spent in the laboratory to collect experimental data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piemonte, V., Gironi, F. Kinetics of Hydrolytic Degradation of PLA. J Polym Environ 21, 313–318 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0547-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0547-x