Abstract
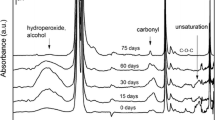
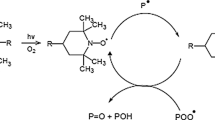
Oxidatively degradable polyethylene is finding widespread use, particularly in applications such as single use packaging and agriculture. However, the key question which still remains unanswered is the ultimate fate and biodegradability of these polymers. During a short-time frame only the oxidized low molecular weight fraction will be amenable to significant biodegradation. The short-time frame biodegradation potential of different LDPE-transition metal formulations was, thus, explored through a simple chemical extraction of oxidized fraction. In addition the effectiveness of different transitions metals was evaluated by comparing the extractable fractions. Blown LDPE films modified with different transition metal based pro-oxidants were thermo-oxidized at 60 °C over extended periods. The structural changes occurring in the polymer were monitored and the oxidized degradation products formed as a result of the aging process were estimated by extractions with water and acetone. The extractable fraction first increased to approximately 22 % as a result of thermo-oxidative aging and then leveled off. The extractable fraction was approximately two times higher after acetone extraction compared to extraction with water and as expected, it was higher for the samples containing pro-oxidants. Based on our results in combination with existing literature we propose that acetone extractable fraction gives an estimation of the maximum short-term biodegradation potential of the material, while water extractable fraction indicates the part that is easily accessible to microorganisms and rapidly assimilated. The final level of biodegradation under real environmental conditions will of course be highly dependent on the specific environment, material history and degradation time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy PK, Hakkarainen M, Varma IK, Albertsson A-C (2011) Environ Sci Technol 45:4217
ASTM-D6954 (2004) Standard guide for exposing and testing plastics that degrade in the environment by a combination of oxidation and biodegradation
ASTM-D6400 (2004) Standard specification for compostable plastics
EN13432:2000 (2000) Packaging. Requirements for packaging recoverable through composting and biodegradation. Test scheme and evaluation criteria for the final acceptance of packaging
ISO-17088 (2008) Specifications for compostable plastics
Thomas N, Clarke J, McLauchlin A, Patrick S (2010) EV0422: assessing the environmental impacts of oxo-degradable plastics across their life cycle; Report for the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
Hakkarainen M, Albertsson A-C (2004) Adv Polym Sci 169:177
Scott G, Wiles DM (2006) Polym Degrad Stab 91:1581
Ojeda TFM, Dalmolin E, Forte MMC, Jacques RJS, Bento FM, Camargo FAO (2009) Polym Degrad Stab 94:965
Yabannavar AV, Bartha R (1994) Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3608
Fontanella S, Bonhomme S, Koutny M, Husarova L, Brusson JM, Courdavault JP, Pitteri S, Samuel G, Pichon G, Lemaire J, Delort A-M (2010) Polym Degrad Stab 95:1011
Chiellini E, Corti A, Swift G (2003) Polym Degrad Stab 81:341
Jakubowicz I (2003) Polym Degrad Stab 80:39
Roy PK, Titus S, Surekha P, Tulsi E, Deshmukh C, Rajagopal C (2008) Polym Degrad Stab 93:1917
Reddy MM, Deighton M, Gupta RK, Bhattacharya SN, Parthasarathy R (2009) J Appl Polym Sci 111:1426
Albertsson A-C (1977) Studies on the mineralisation of 14C labelled polyethylenes in aerobic biodegradation and aqueous aging Stockholm. Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden
Potts JE (1978) Aspects of degradation and stabilization of polymers. Elsevier, New York
Potts JE, Clendinning RA, Ackart WB, Niegischi WD (1972) Polym Prepr 13:629
Haines JR, Alexander M (1974) Appl Microbiol 28:1084
Setti L, Pifferi PG, Lanzarini G (1995) J Chem Technol Biotechnol 64:41
Boethling RS (1984) Environ Toxicol Chem 3:5
Amin PM, Nigam JN, Lonsane BK, Baruah B, Singh HD (1973) Folia Biol 18:49
Baker KH, Herson DS (1994) Bioremediation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Albertsson A-C (1978) J Appl Polym Sci 22:3419
Albertsson A-C, Karlsson S (1990) Prog Polym Sci 15:177
Koutny M, Lemaire J, Delort AM (2006) Chemosphere 64:1243
Koutny M, Sancelme M, Dabin C, Pichon N, Delort AM, Lemaire J (2006) Polym Degrad Stab 91:1495
Chiellini E, Corti A, D’Antone S (2007) Polym Degrad Stab 92:1378
Narayan R (2010) BioPlastics Mag 5:38
Feuilloley P, Cesar G, Benguigui L, Grohens Y, Pillin I, Bewa H et al (2005) J Polym Environ 13:349
Mohee R, Unmar GD, Mudhoo A, Khadoo P (2008) Waste Manage 28:1624
Roy PK, Surekha P, Raman R, Rajagopal C (2009) Polym Degrad Stab 94:1033
ASTM-D3895 (2007) Standard test method for oxidative-induction time of polyolefins by differential scanning calorimetry
Sebaa M, Servens C, Pouyet J (1992) J Appl Polym Sci 45:1049
Burman L, Albertsson A-C, Hakkarainen M, Adv M (2008) Polym Sci 211:1
Karlsson S, Hakkarainen M, Albertsson A-C (1997) Macromolecules 30:7721
Hakkarainen M, Albertsson A-C, Karlsson S (1997) J Environ Polym Degrad 5:67
Hakkarainen M, Albertsson A-C, Karlsson S (1996) J Chromatogr A 741:251
Albertsson A-C, Barenstedt C, Karlsson S (1994) Acta Polym 45:97
Khabbaz F, Albertsson A-C, Karlsson S (1998) Polym Degrad Stab 61:329
Khabbaz F, Albertsson A-C, Karlsson S (1999) Polym Degrad Stab 63:127
Acknowledgments
P.K. Roy is pleased to acknowledge Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, New Delhi, for providing financial support through BOYSCAST program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, P.K., Hakkarainen, M. & Albertsson, AC. Exploring the Biodegradation Potential of Polyethylene Through a Simple Chemical Test Method. J Polym Environ 22, 69–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-013-0629-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-013-0629-4