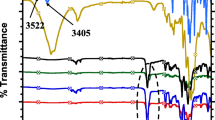
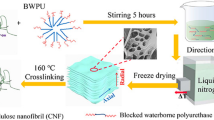
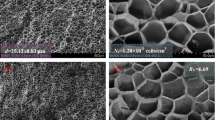
Abstract
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) have been used as reinforcement in polymer nanocomposites to improve their mechanical and thermal properties. In this study, we synthesized CNC-reinforced polyurethane foams (CNC-PUF), which are the most important component of liquefied natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas insulation systems, using various CNC loadings. The temperature-dependent mechanical and thermal characteristics of the CNC-PUF samples were investigated. In addition, the microstructural and X-ray diffraction investigations of the composite samples were performed. It was observed that the thermal and mechanical characteristics of the CNC-PUF sample with 0.6 wt% cellulose nanocrystals were superior to those of neat PUF under room and cryogenic temperatures. These properties showed a significant dependence on CNC loading, temperature, and foam density.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hiroshi T, Hirotomo O, Toshinori I, Satoshi M (2013) Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Tech Rev 50:12
Michale S (2011) Szycher’s handbook of polyurethanes. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, p 37
Irfan MH (1998) Chemistry and technology of thermosetting polymers in construction applications. Springer, Berlin, p 123
Estravís S, Tirado-Mediavilla J, Santiago-Calvo M, Ruiz-Herrero JL, Villafañe F, Rodríguez-Pérez M (2016) Eur Polym J 80:1
Taheri S, Sadeghi GMM (2015) Appl Clay Sci 114:430
Liu TX, Huang S (2017) Properties and applications of polymer nanocomposites. Springer, Berlin, p 37
Glicksman LR (1994) Low density cellular plastics. Springer, Dordrecht, p 104
Singh SN (2002) Blowing agents for polyurethane foams. Rapra Technology, Shrewsbury, p 1
Saha MC, Kabir ME, Jeelani S (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 479:213
Blanco A, Monte MC, Campano C, Balea A, Merayo N, Negro C (2018) Handbook of nanomaterials for industrial applications. Elsevier Inc, Amsterdam, p 74
Nasir M, Hashim R, Sulaiman O, Asim M (2017) Cellulose-reinforced nanofibre composites production, properties and applications. Elsevier Ltd, Amsterdam, p 261
Zhu H, Li Y, Fang Z, Xu J, Cao F, Wan J, Preston C, Yang B, Hu L (2014) ACS Nano 8:3606
Uetani K, Hatori K (2017) Sci Technol Adv Mater 8:877
Septevani AA, Evans DAC, Annamalai PK, Martin DJ (2017) Ind Crops Prod 107:114
Li Y, Ren HF, Ragauskas AJ (2010) Nano-Micro Lett 2:89
Lee JH, Park SH, Kim SH (2017) Macromol Res 22:424
Linul E, Marsavina L, Voiconi T, Sadowski T (2013) J Phys Conf Ser 451:1
Park SB, Choi SW, Kim JH, Bang CS, Lee JM (2016) Compos Part B Eng 93:317
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) Text Res J 29:786
Lu P, Hsieh YL (2012) Carbohydr Polym 87:564
Vanderfleet OM, Osorio DA, Cranston ED (2018) Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 376:1
Marett J, Aning A, Foster EJ (2017) Ind Crops Prod 109:869
Lee C, Dazen K, Kafle K, Moore A, David KJ, Park S, Kim SH (2016) Cellulose chemistry and properties: fibers, nanocelluloses and advanced materials. Springer, Berlin, p 115
Thygesen A, Oddershede J, Lilholt H, Thomsen AB, Ståhl K (2005) Cellulose 12:563
Schuetz MA, Glicksman LR (1984) J Cell Plast 20:114
Yuri K, Tsuguyuki S, Akira I (2014) Angew Chem Int Ed 53:10394
Schilling SL (2006) HFC 245fa blown polyurethane foams with lower thermal conductivity. Bayer Material Science, Pittsburgh, p 234
Thomas H (2016) Cellulose chemistry and properties: fibers, nanocelluloses and advanced materials. Springer, Berlin, p 1
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (1997) Cellular solids structure and properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 175
Mane JV, Chandra S, Sharma S, Ali H, Chavan VM, Manjunath BS, Patel RJ (2017) Procedia Eng 173:726
Park SB, Lee CS, Choi SW, Kim JH, Bang CS, Lee JM (2016) Compos Struct 136:258
Fabrice SM, Laurent C, Calaillé JY, Emanuelle C (2006) Compos Sci Technol 66:2700
Dorris SE, Kumarakrishnan S (1970) J Appl Polym Sci 14:1913
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the R&D Platform Establishment of Eco-Friendly Hydrogen Propulsion Ship Program (No. 20006644) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea). This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (No. 2018R1A2B6007403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, V.H., Kim, JD., Kim, JH. et al. Influence of Cellulose Nanocrystal on the Cryogenic Mechanical Behavior and Thermal Conductivity of Polyurethane Composite. J Polym Environ 28, 1169–1179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01673-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01673-3