Abstract
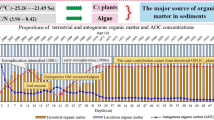
Environmental change in Lake Taihu and its catchment since the early to middle part of the twentieth century has left a clear geochemical record in the lake sediments. The human activities in the lake and its catchment responsible for the change include agriculture, fishery, urbanisation, sewage and industrial waster disposal. Sediment cores were collected from Meilian Bay of northern Lake Taihu to investigate the record of anthropogenic impacts on the lake’s ecosystem and to assess its natural, pre-eutrophication baseline state. Two marked stratigraphic sediment units were identified on the basis of total phosphorus concentration (TP), pigments, total organic carbon (TOC)/total nitrogen (TN), δ13C and δ15N corresponding to stages in the lake history dominated by phytoplankton, and by aquatic macrophytes. Results show that as TP loading increased from the early 1950s the lake produced sediments with increasing amounts of organic matter derived from phytoplankton. In the early 1950s, the first evidence for eutrophication at the Meilian Bay site is recorded by an increase in C/N values and in sediment accumulation rate, but there is little change in phosphorus concentrations, pigments, δ13C and δ15N at this time. After 1990 a more rapid increase in trophic status took place indicated by increased levels of phosphorus, pigments, δ15N and by decreased δ13C and TOC/TN values in the lake sediments. The first increase in trophic status of the early 1950s results mainly from agricultural development in the catchment. In contrast, the acceleration from ca. 1990 originates from the recent development of fisheries and the urbanisation and industrialisation of the catchment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battarbee RW, Anderson NJ, Jeppesen E, Leavitt PR (2005) Combining palaeolimnological and limnological approaches in assessing lake ecosystem response to nutrient reduction. Freshw Biol 50:1772–1780
Bernasconi SM, Barbieri A, Simona M (1997) Carbon and nitrogen isotope variations in sedimenting organic matter in Lake Lugano. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1755–1765
Brenner M, Whitmore TJ, Curtis JH, Hodell DA, Schelske CL (1999) Stable isotope (δ13C, δ15N) signatures of sedimented organic matter as indicators of historical lake trophic state. J Paleolimnol 22:205–221
Chang WYB, Liu JL (1996) The origin and evolution of Taihu Lake: An 11 000-year journey. Acta Palae Sinica 35:129–135 (in Chinese)
Chen Y, Fan C, Teubner K, Dokulil M (2003) Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: an 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 506:273–279
Dickman MD, Pu PM, Zheng CS (2001) Some consequences of hypereutrophication and wind-induced mixing for the limnology of Lake Tai in eastern China. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 27:3669–3673
Feuillade M, Dominik J, Druart JC, Loizeau JL (1995) Trophic status evolution of Lake Nantua as revealed by biological records in sediment. Arch Hydrobiol 132:337–362
Goericke R, Montoya J, Fry B (1994) Physiology and isotopic fractionation in algae and cyanobacteria. In: Lajtha K, Michener R (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Blackwell, London, pp 187–221
Hertsberg S, Liaaen-Jensen S, Siegelman HW (1971) The carotenoids of blue-green alga. Phytochemistry 10:3121–3127
Hu B (2003) Analysis on effect of water pollution in Lake Taihu basin on water quality of Lake Taihu. Shanghai Environ Sci 22:1017–1021
Kaushal S, Binford MW (1999) Relationship between C:N ratios of lake sediments, organic matter sources, and historical deforestation of Lake Pleasant, Massachusetts, USA. J Paleolimnol 22:439–442
Kelley CA, Coffin RB, Cifuentes LA (1998) Stable isotope evidence for alternative bacterial carbon sources in the Gulf of Mexico. Limnol Oceanogr 43:1962–1969
McKenzie JA (1985) Carbon isotopes and productivity in the lacustrine and marine environment. In: Stumm W (ed) Chemical processes in Lakes. Wiley, New York, pp 99–118
Meyers PA (2003) Applications of organic geochemistry to paleolimnological reconstructions: a summary of examples from the Laurentian Great Lakes. Org Geochem 34:261–289
Meyers PA, Teranes JL (2001) Sediment organic matter. In: Last WM, Smol JL (eds) Tracking environmental changes using lake sediments. Physical and geochemical methods, vol. 2. Kluwer-Academic, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp 239–269
Ostrom NE, Long DT, Bell EM, Beals T (1998) The origin and cycling of particulate and sedimentary organic matter and nitrate in Lake Superior. Chem Geol Isot Geosci 152:13–28
Qian J, Zhang L, Le M (1990) The determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus by digestion of persulphate. Soil 22:258–262 (in Chinese)
Qin B, Hu W, Chen W (eds) (2004) Process and mechanism of environmental changes of the Taihu Lake. Science Press, Beijing, pp 3–51 (in Chinese)
Reasoner MA (1993) Equipment and procedure improvements for a lightweight, inexpensive, percussion core sampling system. J Paleolimnol 8:273–281
Rose NL, Boyle JF, Du Y, Yi C, Dai X, Appleby PG, Bennion H, Cai S, Yu L (2004) Sedimentary evidence for changes in the pollution status of Taihu in the Jiangsu region of eastern China. J Paleolimnol 32:41–51
Rosenmeier MF, Brenner M, Kenney WF, Whitmore TJ, Taylor CM (2004) Recent eutrophication in the Southern Basin of Lake Petén Itzá, Guatemala: human impact on a large tropical lake. Hydrobiologia 511:161–172
Routh J, Meyers A, Gustafsson Ö, Baskaran M, Hallberg R, Schöldström A (2004) Sedimentary geochemical record of human-induced environmental changes in the Lake Brunnsviken watershed, Sweden. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1560–1569
Ruby EG, Jannasch HW, Deuser WG (1987) Fractionation of stable carbon isotopes during chemoautotrophic growth of sulfur oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1940–1943
Sanger JE, Gorham E (1972) Stratigraphy of fossil pigments as a guide to the post-glacial history of Kirchner Marsh, Minnesota. Limnol Oceanogr 17:840–854
Schelske CL, Hodell DA (1991) Recent changes in productivity and climate of Lake Ontario detected by isotopic analysis of sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 36:961–975
Schettler G, Qiang L, Mingram J, Negendank JFW (2006) Palaeovariations in the East-Asian Monsoon regime geochemically recorded in varved sediments of Lake Sihailongwan (NE-China Jilin province), Part 1: hydrological condition and dust flux. J Paleolimnol 35:239–270
Shen L, Lin GF, Tan JW, Shen JH (2000) Genotoxicity of surface water samples from Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, eastern China. Chemosphere 41:129–132
Smol JP (2002) Pollution of lakes and rivers: a paleoenvironmental perspective. Arnold, London, pp 280
Swain EB (1985) Measurement and interpretation of sedimentary pigments. Freshwat Biol 15:53–76
Wang S, Dou H (eds) (1998) Memoirs of Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing, pp 5–6 (in Chinese)
Wetzel RG (1970) Recent and postglacial production rates of a Marl Lake. Limnol Oceanogr 15:491–503
Wu JL, Gagan MK, Jiang X, Xia W, Wang S (2004) Sedimentary geochemical evidence for recent eutrophication of Lake Chenghai, Yunnan, China, J Paleolimnol 32:85–94
Xie H, Yu X, Zhang Y (2001) Preliminary study of the coincident relationship between water environment and human activity in Taihu Lake basin. Resour Environ Yangtze Basion 10:393–400
Yu T, Wang Z (eds) (1980) Soil analytical chemistry. Science Press, Beijing, pp 15–17 (in Chinese)
Zou H, Sheng G, Sun C, Xu O (1996) Distribution of organic contaminants in Lake Taihu. Water Res 30:2003–2008
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Hu Yaohui, Pan Hongxi, Lin Lin and Liu Jianjun for their help in the field. We are also grateful to Chen Yuwei, N. Rose and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions on the manuscript. This study was supported by the Key Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CXNIGLAS-A02-15; KZCX1-SW-12), the National Natural Science Fund of China (40673015), the National Key Project for Basic Research (2004CB720200) and the UK Royal Society/Chinese Academy of Sciences joint project on Shallow Lake Ecosystems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jinglu, W., Chengmin, H., Haiao, Z. et al. Sedimentary evidence for recent eutrophication in the northern basin of Lake Taihu, China: human impacts on a large shallow lake. J Paleolimnol 38, 13–23 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-006-9058-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-006-9058-x