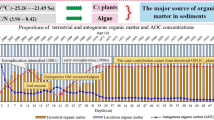
Abstract
Total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) were determined in combination with stable isotope ratios of carbon and nitrogen (δ13COrg, δ15N) in a 63 cm sediment core from Longgan Lake, located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. These geochemical and isotopic records provide a continuous history of lake productivity and trophic state of Longgan Lake since 1890. Variations of δ13COrg, TOC, TN and TP indicate that primary productivity of Longgan Lake increased continuously during the last century and that the trophic state of the lake shifted from oligotrophic to mestrotrophic conditions accordingly. Anthropogenic sources of organic carbon (OC), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) were distinguished from their natural background in the sediments using mass accumulation rates. Element mass accumulation rates suggested increased human activities in the lake’s catchment since 1950s, were especially the utilization of artificial fertilizers amplified the anthropogenic input of N and P into the lake. In the course of the improved availability of dissolved nutrients also primary productivity of Longgan Lake increased, resulting in an increase of the Suess-effect corrected organic carbon isotope ratios. δ15N of bulk sediments show a marked shift towards lower values around 1950 that has been attributed to the input of nitrogen from chemical fertilizers characterized by relatively depleted isotopic signatures into the lake.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altabet MA, Francois R (1994) Sedimentary nitrogen isotopic ratio as recorder for surface ocean nitrate utilization. Global Biogeochem Cycles 8:103–116
Altabet MA, Francois R, Murray DW, Prell WL (1995) Climate related variations in denitrification in the Arabian Sea from 15N/14N-ratios. Nature 373:506–509
Aloupi M, Angelidis MO (2001) Geochemistry of natural and anthropogenic metals in the coastal sediments of the island of Lesvos, Aegean Sea. Environ Pollut 113:211–219
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1978) The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena 5:1–8
Appleby PG, Richardson N, Nolan PJ (1992) Self-absorption corrections for well-type germanium detectors. Nucl Instrum Methods B 71:228–233
Beek J, Van Riemijk WH (1979) Interaction of Phosphate ions with soil. In Soil Chemistry B (Bolt G H, ed). 2nd Ed, 1982, Elsevier, Amsterdam. pp 459–504
Bernasconi SM, Barbieri A, Simona M (1997) Carbon and nitrogen isotope variations in sedimenting organic matter in Lake Lugano. Limnol Oceanogr 42:17855–1765
Boutton TW (1991) Stable carbon isotope ratios of natural materials: II. Atmospheric, terrestrial, marine and freshwater environments. In: Coleman DC, Fry B (eds) Carbon isotope techniques. Academic Press Inc., New York, pp 173–185
Brenner M, Whitmore TJ, Curtis JH, Hodell DA, Schelske CL (1999) Stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) signatures of sedimented organic matter as indicators of historic lake trophic state. J Paleolimnol 22:205–221
Calvert SE, Nielsen B, Fonttugne MR (1992) Evidence from nitrogen isotope ratios for enhanced productivity during formation of eastern Mediterranean sapropels. Nature 359:223–225
Cao YCh, Sun GQ, Xing G, Shi ShL (1991) Natural abundance of 15N in main N-containing chemical fertilizers of China. Pedosphere 1:377–382
Chen SY, Yu XX, Wu AQ (2005) Lake nutrients accumulation process from lacustrine records in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River. Ecol Environ 14:526–529 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dai S, Zhao F, Jin Z (1997) Inhibitory effects of cattail on algae growth and its separation technique. Environ Chem 16:268–271 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Engstorm DR, Wright HE (1984) Chemical stratigraphy of lake sediments as a record of environmental change. In: Haworth EY, Lund JWG (eds) Lake sediments and environmental history. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, pp 11–68
Gerritse RG, Wallbrink PJ, Murry AS (1998) Accumulation of Phosphorus and heavy metals in the Swan-Canning Estuary, Western Australia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 47:165–179
Golterman HL (1988) The calcium- and iron bound phosphate phase diagram. Hydrobiologia 159:149–151
He C, Ye J (1999) Inhibitory effects of Acorus tatainowii on algae growth. Acta Ecologica Sinica 19:754–758 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hodell DA, Schelske CL (1998) Production, sedimentation, and isotopic composition of organic matter in Lake Ontario. Limnol Oceanogr 43:200–214
Lehmann MF, Bernasconi SM, Barbieri A, McKenzie JA (2002) Preservation of organic matter and alternation of its carbon and nitrogen isotope composition during simulated and in situ early sedimentary diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:3573–3584
Liu J, Yang XD, Wang SM (2006) Study on the nutrient evolution and its controlling factors of Longgan Lake for the last 200 years. Sci China (Series D) 49:193–202
Longanhu Farm Records Committee (ed) Longanhu Farm Records (1956∼1985) (unpublished document)
Lücke A, Schleser GH, Zolitschka B, Negendank JFW (2003) A continuous Lateglacial and Holocene organic carbon isotope record of lacustrine palaeoproductivity and climatic change derived from varved lake sediments of Lake Holzmaar, Germany. Quaternary Sci Rev 22:569–580
Lücke A, Brauer A (2004) Biogeochemical and micro-facial fingerprints of ecosystem response to rapid Late Glacial climatic changes in varved sediments of Lake Meerfelder Maar (Germany). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 211:139–155
Meyers PA, Ishiwatari R (1993) Lacustrine organic geochemistry—an overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org Geochem 20:867–900
Meyers PA, Lallier-Vergès E (1999) Lacustrine sedimentary organic matter records of late Quaternary paleoclimates. J Paleolimnol 21:345–372
Middelburg JJ (1989) A simple rate model for organic matter decomposition in marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:1577–1581
Neumann T, Stögbauer A, Walpersdorf E, Stüben D, Kunzendorf H (2002) Stable isotopes in recent sediments of Lake Arendsee, NE Germany: response to eutrophication and remediation measures. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 178:75–90
Norrish K, Rosser H (1983) Mineral phosphate. In: Soils: an Australian viewpoint. CSIRO/Academic Press, Melbourne, Victoria, pp 335–361
Qin BQ, Zhu GW (2006) The nutrient forms, cycling and exchange flux in the sediment and overlying water system in lakes from the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Sci China (Series D) 49:1–13
Rose NL (1994) Charactersation of carbonaceous particles from lake sediments. Proceedings of the international symposium “limnology of mountain lakes” stara Lesna, Czechoslovakia. July 1–7, (1991) Hydrobiologia 274:127–132
Routh J, Meyers PA, Gustafsson Ö, Hallberg R, Baskaran M, Schöldrström A (2004) Sedimentary geochemical record of human-induced environmental changes in the Lake Brunnsviken watershed, Sweden. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1560–1569
Ruiz-Fernández AC, Hillaire-Marcel C, Ghaleb B, Soto-Jiménez M, Páez-Osuna F (2002) Recent sedimentary history of anthropogenic impacts on the Culiacan River Estuary, northwestern Mexico: Geochemical evidence from organic matter and nutrients. Environ Pollut 118:365–377
Sarazin G, Michard G (1992) Sedimentation rate and early diagenesis of particulate organic and carbon in Aydat Lake. Chem Geol 98:307–316
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer ML, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol Evol 8:275–279
Schelske CL, Hodell DA (1995) Using carbon isotopes of bulk sedimentary organic matter to reconstruct the history of nutrient loading and eutrophication of Lake Erie. Limnol Oceanogr 40:918–929
Silliman JE, Meyers PA, Bourbonniere RA (1996) Record of postglacial organic matter delievery and burial in sediments of Lake Ontario. Org Geochem 24:463–472
Struck U, Emeis KC, Voss M, Christiansen C, Kunzendorf H (2000) Records of southern and central Baltic Sea eutrophication in δ13C and δ15N of sedimentary organic matter. Mar Geol 164:157–171
Tromp TK, Cappellen PV, Key RM (1995) A global model for the early diagenesis of organic carbon and organic phosphorus in marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1259–1284
Wu YH, Wang SM, Battarbee RW, Zhu YX (2004) Temporal and spatial distribution of chemical elements in small catchment, and buffer function of wetland in Longanhu Lake, China. Chin J Geochem 23:37–45
Wu YH, Wang SM, Xia WL, Liu J, (2005) Dating recent lake sediments using spheroidal carbonaceous particle (SCP). Chin Sci Bull 50:1016–1020
Yang XD, Shen J, Dong XH, Liu EF (2006) Historical trophic evolutions and their ecological responses from shallow lakes in the middle and low reaches of the Yangtze River: case studies on Longgan Lake and Taibai Lake. Sci China (Series D) 49:51–60
Yang XD, Wang SM, Shen J, Zhu YX, Zhang ZhK, Wu YH (2002) Lacustrine environment responses to human activities in the past 300 years in Longgan Lake catchment, southeast China. Sci China (D) 45:709–718
Zimmerman AR, Canuel EA (2000) A geochemical record of eutrophication and anoxia in Chesapeake Bay sediments: anthropogenic influence on organic matter composition. Mar Chem 69:117–137
Acknowledgement
We thank Holger Wissel for stable isotope analyses. We are very grateful to Prof. John Smol and anonymous reviewers for their profitable suggestions. This work was jointly funded by Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. kzcx2-yw-319), the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.40302022), the Chinese National Key Basic Research Project (Grant No. 2002CB412303) and the Max-Planck Society, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Lücke, A. & Wang, S. Assessment of nutrient sources and paleoproductivity during the past century in Longgan Lake, middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. J Paleolimnol 39, 451–462 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-007-9123-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-007-9123-0