Abstract
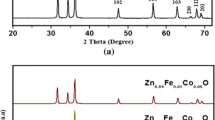
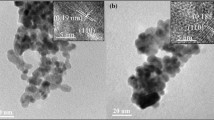
In the present work, pure ZnO, Zn 0.99Fe 0.01O (ZFO), Zn 0.99Ni 0.01O (ZNO) and Zn 0.98Fe 0.01Ni 0.01O (ZFNO) dilute magnetic semiconductors were successfully synthesized by using the wet coprecipitation method. Pure and doped samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, UV-Vis spectroscopy and vibrating sample magnetometer. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of pure and doped samples confirms the formation of a hexagonal wurtzite structure, without formation of any other secondary and impurity phases. Surface morphology of pure and doped ZnO nanoparticle samples performed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveals the formation of spherical nanocrystallites with clear and welldefined boundaries. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) indicates the successful substitution of dopant Fe 2+ and Ni 2+ in the lattice site of Zn 2+ and results in the formation of single-phase Zn 1−x−y Fe x Ni y O. The UV-visible absorption spectra of all doped samples showed blueshift in absorption edge as compared to undoped ZnO nanoparticles. The magnetic characterization reveals and confirms the roomtemperature ferromagnetism in all doped and codoped samples. Magnetization saturation is enhanced in Ni–Fe codoped sample as compare with individual Fe and Nidoped ZnO samples which further reveals that exchange interaction between Fe and Ni ions dominates over the Fe–Fe and Ni–Ni ion interaction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., Von Molnar, S., Roukes, M.L., Chichel- kanova, A.Y., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science (2001). doi:10.1126/science.1065389
Ohno, H.: Making nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science (1998). doi:10.1126/science.281.5379.951
Prinz, G.A.: Magnetoelectronics. Science (1998). doi:10.1126/science.282.5394.1660 10.1126/science.282.5394.1660
Ghosh, S., Mandal, K.: Study of Zn 1−x Co x O (0.02 <x< 0.08) dilute magnetic semiconductor prepared by mechanosynthesis route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.01.017 10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.01.017
Dietl, T., Ohno, H., Matsukura, F., Cibert, J., Ferrand, D.: Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science (2000). doi:10.1103/10.1126/science.287.5455.101 10.1103/10.1126/science.287.5455.101
Wesselinowa, J.M., Aposto, A.T.: A possibility to obtain room temperature ferromagnetism by transition metal doping of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. (2010). doi:10.1063/1.3329457
Karmakar, D., Mandal, S.K., Kadam, R.M., Paulose, P.L., Rajarajan, A.K., Nath, T.K., Das, A.K., Dasgupta, I., Das, G.P.: Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals: Experiment and theory. Phys. Rev. B (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.144404
Xingyan, X., Chuanbao, C.: Structure and ferromagnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.01.017
Martínez, B., Sandiumenge, F., Balcells, L., Arbiol, J., Sibieude, F., Monty, C.: Structure and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.72.165202 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.165202
Duan, L.B., Rao, G.H., Yu, J., Wang, Y.C.: Ferromagnetism of lightly Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. (2008). doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2008.01.014
Luo, J., Liang, J.K., Liu, Q.L., Liu, F.S., Zhang, Y., Sun, B.J., Rao, G.H.: Structure and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. (2005). doi:10.1063/1.1873058
Wang, J.B., Huang, G.J., Zhong, X.L., Sun, L.Z., Zhou, Y.C., Liu, E.H.: Raman scattering and high temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2006). doi: 10.1063/1.2208564
Jayakumar, O.D., Gopalakrishnan, I.K., Sudakar, C., Kadam, R.M., Kulshreshtha, S.K.: Magnetization and structural studies of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles: Prepared by reverse micelle method. J. Cryst. Growth (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.12.030 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2006.12.030
Bhuiyan, M.R.A., Rahman, M.K.: Synthesis and characterization of Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles. I. J. Eng. Manuf. (2014). doi:10.5815/ijem.2014.01.02
Vijayaprasath, G., Murugan, R., Ravi, G.: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni doped ZnO nanostructures prepared by co-precipitation method. In. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 6, 3385–3387 (2014)
Katoon, S., Ahmad, T.: Synthesis, optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Eng B 2(6), 325–333 (2012)
Jadhav, J., Patange, M, Biswas, S.: Ferromagnetic Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a chemical precursor method. Carbon – Sci. Tech. 5(2), 269–274 (2013)
John Kennady Vethanathan, S., Perumal, S., Meenakshi Sundar, S., Priscilla Koilpillai, D., Karpagavalli, S., Suganthi, A.: Structural and magnetic properties of nickel and cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by solvothermal route. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Tech. Res. 6(3), 856–865 (2014)
Mandal, S.K., Das, A.K., Nath, T.K., Karmakar, D., Satpati, B.: Microstructural and magnetic properties of ZnO: TM (TM = Co, Mn) diluted magnetic semiconducting nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. (2006). doi:10.1063/1.2360387
Bilecka, I., Luo, L., Djerdj, I., Rossell, M.D., Jagodi, M., Jaglicic, Z., Masubuchi, Y., Kikkawa, S., Niederberger, M.: Microwave-assisted nonaqueous sol–gel chemistry for highly concentrated ZnO-based magnetic semiconductor nanocrystals. J.Phys. Chem. C (2011). doi:10.1021/jp108050w
Yu, X., Meng, D., Liu, C., He, X., Wang, Y., Xie, J.: Structure and ferromagnetism of Fe-doped and Fe- and Co-codoped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by homogeneous precipitation method (2012). doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2012.07.040
Sharma, V.K., Najim, M., Srivastava, A.K., Varma, G.D.: Structural and magnetic studies on transition metal (Mn, Co) doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.08.061 10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.08.061
Chand, P., Gaur, A., Kumar, A.: Effect of Cr and Fe doping on the structural and optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Int. J. Chem. Nucl. Mater. Metall. Eng. 8, 1238–1241 (2014)
Wu, X., Wei, Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, C., Yang, H., Jiang, J.: Synthesis and characterization of Fe and Ni co-doped ZnO nanorods synthesized by a hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 40, 14635–14640 (2014)
Kumar, S., Kim, Y.J., Koo, B.H., Choi, H., Lee, C.G.: Ferromagnetism in chemically-synthesized Co-doped ZnO. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 55(3), 1060–1064 (2009)
Aydın, C., Abd El-Sadek, M.S., Zheng, K., Yahia, I.S., Yakuphanoglu, F.: Synthesis, diffused reflectance and electrical properties of nanocrystalline Fe-doped ZnO via sol–gel calcination technique. Opt. Laser Technol. 48, 447–452 (2013)
Morales, A.E., Mora, E.S., Pal, U.: Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Revista Mexicana de Fisica Supplement 53, 18–22 (2007)
Zhou, S., Potzger, K., Reuther, H., Kuepper, K., Skorupa, W., Helm, M., Fassbender, J.: Absence of ferromagnetism in V-implanted ZnO single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 09H109 (2007)
Sharma, V.K., Varma, G.D.: Fe clusters as origin of ferromagnetism in hydrogenated Zn 1−xFe xO (x = 0.02 & 0.05) samples. Adv. Mat. Lett. (2012). doi:10.5185/amlett.2011.7283
Bappaditya Pal, Giri, P.K.: Defect mediated magnetic interaction and high Tc ferromagnetism in Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 1–8 (2011)
Santara, B., Giri, P.K., Dhara, S., Imakita, K, Fujii, M: Oxygen vacancy-mediated enhanced ferromagnetism in undoped and Fe-doped TiO 2 nanoribbons. J. Appl. Phys. Phys. D (2014). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/47/23/235304
Das, J., Mishra, D.K., Sahu, D.R., Roul, B.K.: Influence of Ni doping on magnetic behavior of Mn doped ZnO. Mater. Lett. 65(4), 598–601 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal Singh, R.P., Hudiara, I.S., Panday, S. et al. Effect of Ni Doping on Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Fe-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 3685–3691 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3183-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3183-6