Abstract
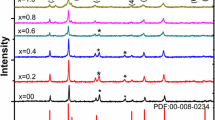
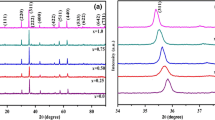
In this study, nanocrystalline Li–Zn ferrites with the chemical composition of Li0.5Zn x Fe2.5−x O4 (where 0 ≤ x≤0.5) were synthesized by glycine–nitrate combustion process using glycine as a fuel, nitrate as an oxidizer, and microwave oven as a heat source. The as-synthesized powders were characterized using an X-ray diffraction technique. X-ray diffraction patterns show that nanocrystalline Li–Zn ferrite phase with a spinel structure has been formed successfully in all samples. Dielectric properties including dielectric constants, dielectric loss, AC conductivity, and complex dielectric impedance were measured in the frequency range 20 Hz–10 MHz using a LCR meter. Results show that dielectric constant, as well as dielectric loss, decreases with increasing frequency and then becomes roughly frequency independent at high frequencies. In contrast, AC conductivity follows an upward trend with frequency. Complex impedance spectroscopic studies show the presence of only one semicircle for all samples, suggesting the predominant effect of grain boundary property of the material. It is also found that substitution of Zn for Fe ions leads to a significant decrease in electrical conductivity due to decrease of ferrous and ferric ions available for the hopping process. Similarly, both dielectric constant and dielectric loss show reduction with the increase in Zn content as a result of the reduction of Fe2+/Fe3+ ions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batoo, K.M.: Study of dielectric and impedance properties of Mn ferrites. Phys. B 406, 382–387 (2011)
Dar, M.A., Batoo, K.M., Verma, V., Siddiqui, W.A., Kotnala, R.K.: Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized pure and Al-doped lithium ferrite having high value of dielectric constant. J. Alloys Compd. 493, 553–560 (2010)
Batoo, K.M., Kumar, S., Lee, C.G., Alimuddin: Study of dielectric and ac impedance properties of Ti doped Mn ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9, 1397–1406 (2009)
Singh, N., Agarwal, A., Sanghi, S.: Dielectric relaxation, conductivity behavior and magnetic properties of Mg substituted Zn-Li ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 783–789 (2011)
Hankare, P.P., Patil, R.P., Sankpal, U.B., Jadhav, S.D., Mulla, I.S., Jadhav, K.M., Chougule, B.K.: Magnetic and dielectric properties of nano phase manganese-substituted lithium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3270–3273 (2009)
Hankare, P.P., Patil, R.P., Sankpal, U.B., Garadkar, K.M., Sasikala, R., Tripathi, A.K., Mulla, I.S.: Magnetic, dielectric and complex impedance spectroscopic studies of nanocrystalline Cr substituted Li-ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2629–2633 (2010)
Watawe, S.C., Sarwade, B.D., Bellad, S.S., Sutar, B.D., Chougule, B.K.: Microstructure, frequency and temperature-dependent dielectric properties of cobalt-substituted lithium ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 214, 55–60 (2000)
Mazen, S.A., Dawoud, H.A.: Temperature and composition dependence of dielectric properties in Li–Cu ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 557–566 (2003)
Reddy, P.V.B., Ramesh, B., Reddy, C.G.: Electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of zinc substituted lithium ferrites prepared by sol–gel method. Phys. B 405, 1852–1856 (2010)
Borhan, N., Gheisari, K.: Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline lithium–zinc ferrite synthesized by microwave-induced glycine–nitrate process. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 1483–1490 (2014)
Gheisari, K., Bhame, S.D., Oh, J.T., Javadpour, S.: Comparative studies on the structure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrite powders prepared by glycine-nitrate auto-combustion process and solid state reaction method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 477–483 (2013)
Hajarpour, S., Gheisari, Kh., Honarbakhsh Raouf, A.: Characterization of nanocrystalline Mg0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 soft ferrites synthesized by glycine-nitrate combustion process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 165–169 (2013)
Bhandare, M.R., Jamadar, H.V., Pathan, A.T., Chougule, B.K., Shaikh, A.M.: Dielectric properties of Cu substituted Ni0.5−x Zn0.3Mg0.2Fe2O4 ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 113–118 (2011)
Livingston, J.D.: Electronic Properties of Engineering Materials. Wiley, New York (1999)
Kadam, A.A., Shinde, S.S., Yadav, S.P., Patil, P.S., Rajpure, K.Y.: Structural, morphological, electrical and magnetic properties of Dy doped Ni–Co substitutional spinel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 329, 59–64 (2013)
Hussain, T., Siddiqi, S.A., Atiq, S., Awan, M.S.: Induced modify cations in the properties of Sr doped BiFeO3 multiferroics. Int. Mater. 23, 487–492 (2013)
Thakur, A., Mathur, P., Singh, M.: Study of dielectric behaviour of Mn–Zn nano ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 68, 378–381 (2007)
Venudhar, Y.C., Mohan, K. S.: Dielectric behaviour of lithium–cobalt mixed ferrites. Mater. Lett. 54, 135–139 (2002)
Hankare, P.P., Sankpal, U.B., Patil, R.P., Jadhav, A.V., Garadkar, K.M., Chougule, B.K.: Magnetic and dielectric studies of nanocrystalline zinc substituted Cu–Mn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 389–393 (2011)
Sankaranarayanan, V.K., Prakash, O., Pant, R.P., Islam, M.: Lithium ferrite nanoparticles for ferrofluid applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 252, 7–9 (2002)
Verma, K., Kumar, A., Varshney, D.: Effect of Zn and Mg doping on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of tetragonal CuFe2O4. Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 467–473 (2013)
Verma, K., Kumar, A., Varshney, D.: Dielectric relaxation behavior of A x Co1−x Fe2O4 (A = Zn, Mg) mixed ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 526, 91–97 (2012)
Ghatak, S., Sinha, M., Meikap, A.K., Pradhan, S.K.: Alternate current conductivity and dielectric properties of nonstoichiometric nanocrystalline Mg–Zn ferrite below room temperature. Phys. E 42, 1397–1405 (2010)
Gheisari, Kh., Shahriari, Sh., Javadpour, S.: Structural evolution and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline 50 permalloy powders prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 574, 71–82 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Shahid Chamran University for providing support to this research. The authors are indebted to H. Mohseni for his great assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borhan, N., Gheisari, K. & Shoushtari, M.Z. Dielectric Properties of Nanocrystalline Zn-Doped Lithium Ferrites Synthesized by Microwave-Induced Glycine–Nitrate Process. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 145–151 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3225-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3225-0