Abstract
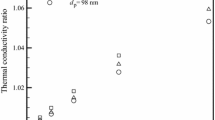
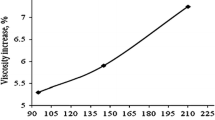
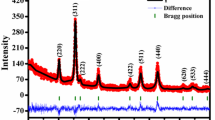
The NiFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesized and used to prepare stable water-based magnetic nanofluids of various concentrations by ultrasonically assisted two-step techniques. Thermophysical investigations are made on the nanofluids at different temperatures ranging from 20 to 80 °C. The measurements revealed that the thermal conductivity of nanofluids significantly enhances with an increase in the percentage of nanoparticle volume fraction. The thermal conductivity measurements showed that the maximum enhancement is 32.65% achieved at 1% nanoparticle volume fraction and at 80 °C. Specific heat of nanofluids was decreased with increasing nanoparticle volume fractions, and it augments with increasing temperature. Viscosity measurements showed that nanofluid had a Newtonian behavior at all nanoparticle volume fractions and temperatures considered. The viscosity of the nanofluid increased with increasing nanoparticle concentration and decreasing temperature. Experimental results revealed that the viscosity sensitivity to temperature variation is minor, while it is more sensitive to the variations of nanoparticle volume fraction. The density of nanofluids was increased with increasing nanoparticle volume fractions and decreased with increasing temperature. Lastly, efforts were made to provide a precise correlation to estimate the thermal conductivity, as well as other thermophysical properties at various temperatures and volume fractions of nanoparticles. The comparison between the results and the correlation results showed a good agreement.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farret, F.A., Simões, M.G: Integration of Renewable Sources of Energy. Wiley, New York (2017)
Sidik, N.A.C., Jamil, M.M., Japar, W.M.A.A., Adamu, I.M.: A review on preparation methods, stability and applications of hybrid nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 80, 1112–1122 (2017)
Ganvir, R., Walke, P., Kriplani, V.: Heat transfer characteristics in nanofluid—a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 75, 451–460 (2017)
Kakavandi, A., Akbari, M.: Experimental investigation of thermal conductivity of nanofluids containing of hybrid nanoparticles suspended in binary base fluids and propose a new correlation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 124, 742–751 (2018)
Wadekar, V.V.: Ionic liquids as heat transfer fluids–an assessment using industrial exchanger geometries. Appl. Therm. Eng. 111, 1581–1587 (2017)
Das, S.K., Choi, S.U., Yu, W., Pradeep, T.: Nanofluids: Science and Technology. Wiley, New York (2007)
Sundar, L.S., Sharma, K., Singh, M.K., Sousa, A.: Hybrid nanofluids preparation, thermal properties, heat transfer and friction factor—a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 68, 185–198 (2017)
Gupta, M., Singh, V., Kumar, S., Kumar, S., Dilbaghi, N., Said, Z.: Up to date review on the synthesis and thermophysical properties of hybrid nanofluids. J. Clean. Prod. 190, 169–192 (2018)
Amani, M., Amani, P., Kasaeian, A., Mahian, O., Pop, I., Wongwises, S.: Modeling and optimization of thermal conductivity and viscosity of MnFe2O4 nanofluid under magnetic field using an ANN. Sci. Rep. 7, 17369 (2017)
Chavan, A.R., Chilwar, R.R., Kharat, P.B., Jadhav, K.: Effect of annealing temperature on structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 thin films. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4565-3 (2018)
Sanna Angotzi, M., Musinu, A., Mameli, V., Ardu, A., Cara, C., Niznansky, D., Xin, H.L., Cannas, C.: Spinel ferrite core–shell nanostructures by a versatile solvothermal seed-mediated growth approach and study of their nanointerfaces. ACS Nan 11, 7889–7900 (2017)
Wei, C., Feng, Z., Baisariyev, M., Yu, L., Zeng, L., Wu, T., Zhao, H., Huang, Y., Bedzyk, M.J., Sritharan, T.: Valence change ability and geometrical occupation of substitution cations determine the pseudocapacitance of spinel ferrite XFe2O4 (X = Mn, Co, Ni, Fe). Chem. Mater. 28, 4129–4133 (2016)
Shisode, M., Kharat, P.B., Bhoyar, D.N., Vinayak, V., Babrekar, M., Jadhav, K.: Structural and multiferroic properties of Ba2 + doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles synthesized via sol-gel method. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, p 030276. AIP Publishing (2018)
Humbe, A.V., Kharat, P.B., Nawle, A.C., Jadhav, K.: Nanocrystalline Ni0.70−xCuxZn0.30Fe2O4 with 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25 prepared by nitrate-citrate route: structure, morphology and electrical investigations. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 3467–3481 (2018)
Kale, G., Humbe, A.V., Kharat, P., Bhoyar, D., Jadhav, K.: Tartaric acid a novel fuel approach: synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Bionano Frontier 8, 146–148 (2015)
Ghadikolaei, S., Yassari, M., Sadeghi, H., Hosseinzadeh, K., Ganji, D.: Investigation on thermophysical properties of TiO2–Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid transport dependent on shape factor in MHD stagnation point flow. Powder Technol. 322, 428–438 (2017)
Malvandi, A., Moshizi, S., Ganji, D.: Nanoparticle transport effect on magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection of electrically conductive nanofluids in micro-annuli with temperature-dependent thermophysical properties. Phys. E: Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 88, 35–49 (2017)
Gupta, M., Singh, V., Kumar, R., Said, Z.: A review on thermophysical properties of nanofluids and heat transfer applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 74, 638–670 (2017)
Afrand, M.: Experimental study on thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol containing hybrid nano-additives and development of a new correlation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 110, 1111–1119 (2017)
Ganesan, V., Louis, C., Damodaran, S.P.: Novel nanofluids based on magnetite nanoclusters and investigation on their cluster size-dependent thermal conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 6918–6929 (2018)
Hajmohammadi, M.: Cylindrical Couette flow and heat transfer properties of nanofluids; single-phase and two-phase analyses. J. Mol. Liq. 240, 45–55 (2017)
Karimi, A., Afghahi, S.S.S., Shariatmadar, H., Ashjaee, M.: Experimental investigation on thermal conductivity of MFe2O4 (M = Fe and Co) magnetic nanofluids under influence of magnetic field. Thermochim. Acta 598, 59–67 (2014)
Karimi, A., Sadatlu, M.A.A., Saberi, B., Shariatmadar, H., Ashjaee, M.: Experimental investigation on thermal conductivity of water based nickel ferrite nanofluids. Adv. Powder Technol. 26, 1529–1536 (2015)
Amani, M., Amani, P., Kasaeian, A., Mahian, O., Wongwises, S.: Thermal conductivity measurement of spinel-type ferrite MnFe2O4 nanofluids in the presence of a uniform magnetic field. J. Mol. Liq. 230, 121–128 (2017)
Shahsavar, A., Salimpour, M.R., Saghafian, M., Shafii, M.: Effect of magnetic field on thermal conductivity and viscosity of a magnetic nanofluid loaded with carbon nanotubes. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 30, 809–815 (2016)
Kharat, P.B., Kounsalye, J.S., Shisode, M.V., Jadhav, K.: Preparation and thermophysical investigations of CoFe2O4-based nanofluid: a potential heat transfer agent. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4711-y(2018)
Kharat, P.B., Somvanshi, S.B., Kounsalye, J.S., Deshmukh, S.S., Khirade, P.P., Jadhav, K.: Temperature dependent viscosity of cobalt ferrite/ethylene glycol ferrofluids. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, p 050044. AIP Publishing (2018)
Din, I.U., Tasleem, S., Naeem, A., Shaharun, M.S., Nasir, Q.: Study of annealing conditions on particle size of nickel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical route. Synth. React. Inorg., Met.-Org., Nano-Met. Chem. 46, 405–408 (2016)
Dolla, T.H., Pruessner, K., Billing, D.G., Sheppard, C., Prinsloo, A., Carleschi, E., Doyle, B., Ndungu, P.: Sol-gel synthesis of MnxNi1−xCo2O4 spinel phase materials: structural, electronic, and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 742, 78–89 (2018)
Kharat, P.B., JSK, A.V.H., Birajdar, S.D., Jadhav, K.: Preparation and diverse properties of cobalt ferrite ferrofluid. Int. J. Adv. Res. Basic Appl. Sci. (2), 106–109 (2017)
Kounsalye, J.S., Kharat, P.B., Chavan, A.R., Humbe, A.V., Borade, R., Jadhav, K.: Symmetry transition via tetravalent impurity and investigations on magnetic properties of Li0.5Fe2.5O4. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, p 050067. AIP Publishing (2018)
Kounsalye, J.S., Kharat, P.B., Bhoyar, D.N., Jadhav, K.: Radiation-induced modifications in structural, electrical and dielectric properties of Ti4 + ions substituted Li0.5Fe2.5O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 8601–8609 (2018)
Wang, Y., Li, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Fang, S., Li, G.: Growth kinetics, cation occupancy, and magnetic properties of multimetal oxide nanoparticles: a case study on spinel NiFe2O4. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 19467–19477 (2017)
Yadav, R.S., Kuřitka, I., Vilcakova, J., Havlica, J., Masilko, J., Kalina, L., Tkacz, J., Enev, V., Hajdúchová, M.: Structural, magnetic, dielectric, and electrical properties of NiFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey-mediated sol-gel combustion. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 107, 150–161 (2017)
Reddy, M.P., Shakoor, R., Mohamed, A.: Auto combustion synthesis, microstructural and magnetic characteristics of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 10(13). https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2017/v10i13/88034 (2017)
Aghazadeh, M., Karimzadeh, I., Ganjali, M.R.: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid capped superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles: a novel preparation method and characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 439, 312–319 (2017)
Manikandan, V., Li, X., Mane, R., Chandrasekaran, J.: Room temperature gas sensing properties of Sn-substituted nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) thin film sensors prepared by chemical co-precipitation method. J. Electron. Mater. 1–6 (2018)
Ramirez, S., Chan, K., Hernandez, R., Recinos, E., Hernandez, E., Salgado, R., Khitun, A., Garay, J., Balandin, A.: Thermal and magnetic properties of nanostructured densified ferrimagnetic composites with graphene-graphite fillers. Mater. Des. 118, 75–80 (2017)
Corner, W., Tanner, B.: Magnetic domains. Phys. Educ. 11, 356 (1976)
Hubert, A., Schäfer, R.: Magnetic domains: the analysis of magnetic microstructures. Springer Science & Business Media (2008)
Gromova, Y.A., Maslov, V.G., Baranov, M.A., Serrano-García, R., Kuznetsova, V.A., Purcell-Milton, F., Gun’ko, Y.K., Baranov, A.V., Fedorov, A.V.: Magnetic and optical properties of isolated and aggregated CoFe2O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles studied by MCD spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 11491–11497 (2018)
Carey, V.P.: Liquid Vapor Phase Change Phenomena: an Introduction to the Thermophysics of Vaporization and Condensation Processes in Heat Transfer Equipment. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2018)
Yadav, R.: Synthesis and characterization of structural and magnetic properties of electrodeposited cobalt iron thin film. Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad (2015)
Asadi, A., Asadi, M., Rezaniakolaei, A., Rosendahl, L.A., Afrand, M., Wongwises, S.: Heat transfer efficiency of Al2O3-MWCNT/thermal oil hybrid nanofluid as a cooling fluid in thermal and energy management applications: an experimental and theoretical investigation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 117, 474–486 (2018)
De Sciarra, F.M., Russo, P.: Experimental Characterization, Predictive Mechanical and Thermal Modeling of Nanostructures and Their Polymer Composites. William Andrew, New York (2018)
Cao, G.: Nanostructures & Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties & Applications. Imperial College Press, London (2004)
Priyananda, P., Sabouri, H., Jain, N., Hawkett, B.S.: Steric stabilization of γ-Fe2O3 superparamagnetic nanoparticles in a hydrophobic ionic liquid and the magnetorheological behavior of the ferrofluid. Langmuir 34, 3068–3075 (2018)
Ma, B., Banerjee, D.: A review of nanofluid synthesis. In: Advances in Nanomaterials, pp 135–176. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Kharat, P.B., Shisode, M., Birajdar, S., Bhoyar, D., Jadhav, K.: Synthesis and characterization of water based NiFe2O4 ferrofluid. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, p 050122. AIP Publishing (2017)
Li, C., Strachan, A.: Cohesive energy density and solubility parameter evolution during the curing of thermoset. Polymer 135, 162–170 (2018)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Professor John Philip, Indira Gandhi Center for Atomic Research Center, Kalpakkam, Tamilnadu, as well as Professor J. B. Naik, Head, University Institute of Chemical Technology, North Maharashtra University, Jalgaon, Maharashtra, and Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai for providing thermal conductivity and specific heat, and VSM measurement facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharat, P.B., Humbe, A.V., Kounsalye, J.S. et al. Thermophysical Investigations of Ultrasonically Assisted Magnetic Nanofluids for Heat Transfer. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 1307–1317 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4819-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4819-0