Abstract
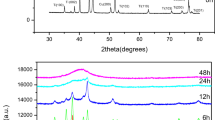
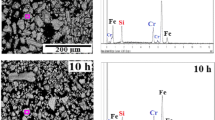
Nanostructured Ti80Ni20 material was elaborated by mechanical alloying from pure Ti and Ni powders in a planetary ball-mill P7 under argon atmosphere at ambient temperature. Morphological, microstructural, magnetic, and nanoindentation properties were studied using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, magnetic measurements, and nanoindentation test. The morphological observations show the predominance of the welding phenomenon during the milling process. The Rietveld refinement of the X-ray diffraction pattern reveals, after 4 h of milling, the formation of the disordered hcp-Ti (Ni) solid solution in addition to elemental hcp-Ti and fcc-Ni. On further milling (20 h), the interdiffusion between Ti and Ni atoms is evidenced by the formation of disordered hcp-Ti (Ni) and fcc-Ni (Ti) solid solutions. The saturation magnetization and coercivity values are about of 159.8 emu/g and 80.79 Oe, respectively, after 20 h of milling. Mr/Ms ratio indicates the existence of small magnetic particles which are typically single domains (Mr/Ms 0.1–0.5) and/or multidomain (Mr/Ms < 0.1). Nanohardness values of the sintered powders fluctuates between 1.53 and 5.98 GPa while those of the elastic modulus varies in the range 130.73 to 164.53 GPa.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y.: Recent advances in research and development of porous NiTi shape memory alloys. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 21(6), 561–569 (2007)
Geng, F., Shi, P., Yang, D.Z.: Review on the development of NiTi shape memoryalloy as a biomaterial. J. Funct. Mater. 36(1), 11–14 (2005)
Zhao, X., Ma, L., Yao, Y., Ding, Y., Shen, X.: Ti2Ni alloy: a potential candidate for hydrogen storage in nickel/metal hydride secondary batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 3(9), 1316–1321 (2010)
Slotoff, N., Liu, C., Deevi, S.: Emerging applications of intermetallics. Intermetallics. 8, 1313–1320 (2000)
K. Ebato, M. Tsuda, T. Oomori, Method of producing Ni–Ti intermetallic compounds, US Patent 5316599, 1994
Takasaki, A.: Mechanical alloying of the Ti-Ni system. Phys. Status Solidi. 169, 83–191 (1998)
Mousavi, T., Karimzadeh, F., Abbasi, M.H.: Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline NiTi intermetallic by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. 487, 46–51 (2008)
Terunuma, Y., Nagumo, M.: Structural relaxation in amorphous Ni50Ti50 alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater. Trans. e JIM. 7, 842–847 (1995)
Makifuchi, Y., Terunuma, Y., Nagumo, M.: Structural relaxation in amorphous Ni-Ti alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. 228, 312–316 (1997)
Martins, C.B., Fernandes, B.B., Ramos, E.C.T., Silva, G., Ramos, A.S.: Syntheses of the Ni3Ti, NiTi and NiTi2 compounds by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Forum. 531, 217–222 (2006)
Jiang, X., Liu, Q., Zhang, L.: Electrochemical hydrogen storage property of NiTi alloys with different Ti content prepared by mechanical alloying. Rare Metals. 30, 63–67 (2011)
L. Lutterotti, MAUD CPD Newletter, IUCR 24, 2000
Rietveld, H.M.: A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crys. 2, 45–48 (1969)
Schneider, C.A., Rasband, W.S., Eliceiri, K.W.: NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods. 7, 671–675 (2012)
Chudoba, T., Schwaller, R., Rabe, J.M., Breguet, J.M.: Comparison of nanoindentation results obtained with Berkovich and Cube Corner indenters. Philos. Mag. 86, 5265–5283 (1986)
Kittel, C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics. Wiley, New York (1966)
Nakajima, H., Koiwa, M.: Diffusion in titanium. 1ISIJ International. 31(1 991), 757–766
Radev, D.D.: Mechanical synthesis of nanostructured titanium–nickel alloys. Adv. Powder Technol. 21, 477–482 (2010)
Sakher, E., Loudjani, N., Benchiheub, M., Bououdina, M.: Influence of milling time on structural and microstructural parameters of Ni50Ti50 prepared by mechanical alloying using Rietveld analysis. Hindawi J. Nanomater. 2018, 1 (2018)
Karolus, M., Panek, J.: Nanostructured Ni-Ti alloys obtained by mechanical synthesis and heat treatment. J. Alloys. Compds. 658, 709–715 (2016)
Laves, F., Wallbaum, H.J.: Naturwissenschaften. 27–674 (1939)
Koskimaki, D., Marcinkowski, M.J., Sastri, A.S.: Trans. AIME. 245–1883 (1969)
Poole, D.M.: Hume-Rothery. J. Inst. Met. 55, 83–473 (1954)
Koch, C.C., Pathak, D., Yamada, K.: Mechanical alloying for structural applications, pp. 12–205. Mater, Park (1993)
Chen, C.W.: Amsterdam. North-Holland (1977)
Loudjani, N., Bensebaa, N., Dekhil, L., Alleg, S., Suñol, J.J.: Structural and magnetic properties of Co50Ni50 powder mixtures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 3063–3070 (2011)
Bensebaa, N., Loudjani, N., Alleg, S., Dekhil, L., Suñol, J.J., Al Sae, M., Bououdina, M.: XRD analysis and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni20Co80 alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 349, 51–56 (2014)
Souilah, S., Alleg, S., Bououdina, M., Sunol, J.J., Hlil, E.K.: Magnetic and structural properties of the nanostructured Cu50Ni50 powders. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 1927 (2017)
de Julian Fernandeza, C., Sangregorio, C., Innocenti, C., Mattei, G., Mazzoldi, P.: Inorg. Chim. Acta. 361, 4138–4142 (2008)
Zhao, H., Sheng, H.W., Lu, K.: Microstructure evolution and thermal properties in nanocrystalline Fe during machanical attrition. Acta Mater. 49, 365–375 (2001)
R. Kocich, I. Szurman, M. Kursa: The Methods of Preparation of Ti-Ni-X Alloys and Their Forming, Intech Open, Chapter 2, 2013
Ghadadimi, M., Shokuhfar, A., Rostami, H.R., Ghaffari, M.: Effects of milling and annealing on formation and structural characterization of nanocrystalline intermetallic compounds from Ni–Ti elemental powders. Mater. Lett. 80, 181–183 (2012)
Oliver, W.C., Pharr, G.M.: J. Mater. Research. 7, 1564–1583 (1992)
Qian, L., Li, M., Zhou, Z., Yang, H., Shi, X.: Surf. Coat. Technol. 195, 264–271 (2005)
Fu, Y., Du, H., Zhang, S.: Deposition of TiN layer on TiNi thin films to improve surface properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 167, 129–136 (2003)
Pogrebnjak, A., Bratushka, S., Levintant-Zayonts, N., Malikov, L.: Influence of high-dose ion implantation of NiTi equiatomic on shape memory and pseudoelastic. J. Nano Electronic Phys. 5, 61–72 (2013)
Mante, F.K., Baran, G.R., Lucas, B.: Biomaterials. 20, 1051–1055 (1999)
Britton, T.B., Liang, H., Dunne, F.P.E., Wilkinson, A.J.: Proceedings of the Royal Society, vol. 466, pp. 695–719 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Zerniz Nawel from the Laboratoire de Chimie organique, Département de Chimie, Faculté des Sciences, Université Badji-Mokhtar, Annaba, Algérie, for the elaboration of the nanostructured powders; to A.M. Mercier from the Laboratoire des Fluorures, Université du Maine, Le Mans, France, for the XRD measurements; to Beldi Mounira for sintering; and to Boulakraa Mohamed from the Unité de recherches des matériaux avancés, Annaba, Algérie, for the cold compaction.
Funding
This research work was supported by the Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique, Algérie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dekhil, L., Louidi, S., Bououdina, M. et al. Microstructural, Magnetic, and Nanoindentation Studies of the Ball-Milled Ti80Ni20 Alloy. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 3623–3636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05145-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05145-1