Abstract
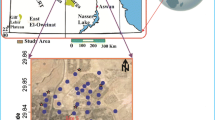
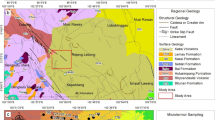
Every year, numerous casualties and a large deal of financial losses are incurred due to earthquake events. The losses incurred by an earthquake vary depending on local site effect. Therefore, in order to conquer drastic effects of an earthquake, one should evaluate urban districts in terms of the local site effect. One of the methods for evaluating the local site effect is microtremor measurement and analysis. Aiming at evaluation of local site effect across the city of Babol, the study area was gridded and microtremor measurements were performed with an appropriate distribution. The acquired data was analyzed through the horizontal-to-vertical noise ratio (HVNR) method, and fundamental frequency and associated amplitude of the H/V peak were obtained. The results indicate that fundamental frequency of the study area is generally lower than 1.25 Hz, which is acceptably in agreement with the findings of previous studies. Also, in order to constrain and validate the seismostratigraphic model obtained with this method, the results were compared with geotechnical, geological, and seismic data. Comparing the results of different methods, it was observed that the presented geophysical method can successfully determine the values of fundamental frequency across the study area as well as local site effect. Using the data obtained from the analysis of microtremor, a microzonation map of fundamental frequency across the city of Babol was prepared. This map has numerous applications in designing high-rise building and urban development plans.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birgören G, Özel O, Siyahi B (2009) Bedrock depth mapping of the coast south of Istanbul: comparison of analytical and experimental analyses. Turk J Earth Sci 18(2):315–329
Bour M, Fouissac D, Dominique P, Martin C (1998) On the use of microtremor recordings in seismic microzonation. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 17:465–474
Büyüksaraç A, Bektaş Ö, Yılmaz H, Arısoy MÖ (2013) Preliminary seismic microzonation of Sivas City (Turkey) using microtremor and refraction microtremor (ReMi) measurements. J Seismol 17(2):425–435
Chatelain JL, GuillierB CF, Duval AM, Atakan K, Bard PY (2008) Evaluation of the influence of experimental conditions on H/V results from ambient noise recordings. B Earthq Eng 6(1):33–74
Choobbasti AJ, Rezaei S, Farrokhzad F (2013) Evaluation of site response characteristics using microtremors. Gradevinar 65(8):731–741
Choobbasti AJ, Rezaei S, Farrokhzad F, Heidarzadeh Azar P (2014) Evaluation of site response characteristics using nonlinear method (case study: Babol, Iran). Front Struct Civ Eng 8(1):69–82
Dikmen Ü, Mirzaoglu M (2005) The seismic microzonation map of Yenisehir-Bursa, NW of Turkey by means of ambient noise measurements. J Balk Geophys Soc 8(2):53–62
Fäh D, Kind F, Giardini D (2001) A theoretical investigation of average H/V ratios. Geophy J Int 145(2):535–549
Field EH, Clement AC, Aharonian V, Friberg PA, Carroll L, Babaian TO, Karapetian SS, Hovanessian SM, Abramian HA (1995) Earthquake site response study in Giumri (formerly Leninakan), Armenia, using ambient noise observations. Bull Seismol Soc Am 85:349–353
Galea P, D'Amico S, Farrugia D (2014) Dynamic characteristics of an active coastal spreading area using ambient noise measurements—Anchor Bay, Malta. Geophy J Int 199(2):1166–1175
Galgaro A, Boaga J, Rocca M (2014) HVSR technique as tool for thermal-basin characterization: a field example in NE Italy. Environ Earth Sci 71(10):4433–4446
Gosar A (2007) Microtremor HVSR study for assessing site effects in Bovec basin (NW Slovenia) related to 1998 Mw 5.6 and 2004 Mw 5.2 earthquakes. Eng Geol 91:178–193
Guo Z, Aydin A, Kuszmaul JS (2014) Microtremor recordings in northern Mississippi. Eng Geol 179:146–157
Haque MN, Keramat M, Shahid S, Mohsenipour M, Wang XJ (2016) Groundwater dynamics and balance in the western part of greater Kushtia district of Bangladesh. KSCE J Civ Eng 21:1595–1606
Kanai K, Takana T (1961) On microtremors. VIII. Bull Earthq Inst 39:97–114
Kockar MK, Akgun H (2012) Evaluation of the site effects of the Ankara basin, Turkey. J Appl Geophys 83:120–134
Kolat C, Ulusay R, Lutfi Suzen M (2012) Development of geotechnical microzonation model for Yenisehir (Bursa, Turkey) located at a seismically active region. Eng Geol 127:36–53
Konno K, Omachi T (1998) Ground motion characteristics estimated from spectral ratio between horizontal and vertical components of microtremors. Bull Seismol Soc Am 88(1):228–241
Lachet C, Bard PY (1994) Numerical and theoretical investigations on the possibilities and limitations of Nakamura's technique. J Phys Earth 42(5):377–397
Lermo JF, Chavez-Garcia FJ (1994) Are microtremors useful in site response evaluation. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84(5):1350–1364
Macau A, Benjumea B, Gabàs A, Figueras S, Vilà M (2015) The effect of shallow quaternary deposits on the shape of the H/V spectral ratio. Surv Geophys 36(1):185–208
Mahajan AK, Slob S, Ranjan R, Sporry R, van Westen CJ (2007) Seismic microzonation of Dehradun City using geophysical and geotechnical characteristics in the upper 30 m of soil column. J Seismol 11(4):355–370
Matassoni L, Fiaschi A, Silengo MC, Lotti A, Saccorotti G (2015) Preliminary seismic microzonation in a mountain municipality of Tuscany (Italy). Open Geosci 7:559–571
Microzonation of Babol city (technical report) (2012) Babol University of Technology (In Persian)
Milana G, Azzara RM, Bertrand E, Bordoni P, Cara F, Cogliano R, Cultrera G, Di Giulio G, Duval AM, Fodarella A, Marcucci S, Puccilo S, Regnier J, Riccio G (2011) The contribution of seismic data in microzonation studies for downtown L’Aquila. Bull Earthq Eng 9(3):741–759
Mundepi AK, Galiana-Merino JJ, Lindholm C (2010) Soil characteristics and site effect assessment in the city of Delhi (India) using H/V and f–k methods. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30(7):591–599
Nakamura Y (1989) A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface. QR RTRI 30:25–33
Natarajan T, Rajendran K (2016) Site responses based on ambient vibrations and earthquake data: a case study from the meizoseismal area of the 2001 Bhuj earthquake. J Seismol 1–13
Navarro M, García-Jerez A, Alcalá FJ, Vidal F, Enomoto T (2014) Local site effect microzonation of Lorca town (SE Spain). Bull Earthq Eng 12(5):1933–1959
Ojeda A, Escallon J (2000) Comparison between different techniques for evaluation of predominant periods using strong ground motion records and microtremorss in Pereira Colombia. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 20:137–143
Paolucci E, Albarello D, D'Amico S, Lunedei E, Martelli L, Mucciarelli M, Pileggi D (2015) A large scale ambient vibration survey in the area damaged by May–June 2012 seismic sequence in Emilia Romagna, Italy. Bull Earthq Eng 13(11):3187–3206
Pastén C, Sáez M, Ruiz S, Leyton F, Salomón J, Poli P (2016) Deep characterization of the Santiago Basin using HVSR and cross-correlation of ambient seismic noise. Eng Geol 201:57–66
Purnachandra Rao N, Rabi Kumar M, Seshunarayana T, Shukla AK, Suresh G, Pandey Y, Dharma Raju R, Pimprikar SD, Chandra D, Kalpna G, Mishra PS, Harsh G (2011) Site amplification studies towards seismic microzonation in Jabalpur urban area, central India. Phys Chem Earth 36(16):1247–1258
Rezaei S, (2014) Assessing the site effects and estimation of strong ground motion specification by using microtremor data and compare its results with simulation of soil profile (case study: western part of Babol city). MSc thesis, Babol University of Technology
Rezaei S, Choobbasti AJ (2014) Liquefaction assessment using microtremor measurement, conventional method and artificial neural network (case study: Babol, Iran). Front Struct Civ Eng 8(3):292–307
Rezaei S, Choobbasti AJ, Soleimani Kutanaei S (2015) Site effect assessment using microtremor measurement, equivalent linear method and artificial neural network (case study: Babol, Iran). Arab J Geosci 8:1453–1466
Rezaei S, Choobbasti AJ (2017) Application of the microtremor measurements to a site effect study. Earthq Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-017-0187-2
SESAME (2004) Guidelines for the implementation of the H/V spectral ratio technique on ambient vibrations measurements. Processing and Interpretation, Sesame European research project WP12 – Deliverable D23.12
Singh AP (2015) Seismic hazard evaluation in Anjar city area of western India: microtremor array measurement. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 71:143–150
Sivaram K, Mahesh P, Rai SS (2012) Stability assessment and quantitative evaluation of H/V spectral ratios for site response studies in Kumaon Himalaya, India using ambient noise recorded by a broadband seismograph network. Pure Appl Geophys 169(10):1801–1820
Tezcan S, Kaya E, Bal IE, Ozdemir Z (2002) Seismic amplification at Avcilar, Istanbul. Eng Struct 24:661–667
The Technical Committee for earthquake geotechnical engineering, TC4, ISSMGE (1999) Manual for zonation on seismic geotechnical hazards (revised version). Japanese Geotechnical Society
Ullah I, Prado RL (2017) Soft sediment thickness and shear-wave velocity estimation from the H/V technique up to the bedrock at meteorite impact crater site, Sao Paulo city, Brazil. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 94:215–222
Vella A, Galea P, D'Amico S (2013) Site frequency response characterization of the Maltese islands based on ambient noise H/V ratios. Eng Geol 163:89–100
Yalcinkaya E, Tekebas S, Pinar A (2013) Analysis of ambient noise in Yalova, Turkey: discrimination between artificial and natural excitations. J Seismol 17(3):1021–1039
Yamanaka H, Gamero MSQ, Chimoto K, Saguchi K, Calderon D, La Rosa FL, Bardales ZA (2016) Exploration of deep sedimentary layers in Tacna city, southern Peru, using microtremors and earthquake data for estimation of local amplification. J Seismol 20(1):107–116
Yanger Walling M, Mohanaty William K, Nath Sankar K, Mitra S, John A (2009) Microtremor survey in Talchir, India to ascertain its basin characteristics in terms of predominant frequency by Nakamura’s ratio technique. Eng Geol 106:123–132
Acknowledgments
We would like to take this opportunity to express our profound gratitude to Yashar Tavangar, for constant cooperation throughout the duration of the project. The authors are also grateful to two anonymous reviewers that significantly helped in improving the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, S., Choobbasti, A.J. Evaluation of local site effect from microtremor measurements in Babol City, Iran. J Seismol 22, 471–486 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-017-9718-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-017-9718-5