Abstract
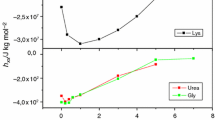
The apparent molar volumes, Vφ,2, of glycine, alanine, α-amino-n-butyric acid, valine, leucine, and lysine monohydrochloride have been determined in aqueous solutions of 0.05, 0.1, and 0.4 mol-kg−1 Triton X-100 (TX-100), and the partial specific volume, v0, of hen-egg-white lysozyme in 0.4 mol-kg−1 TX-100 by density measurements at 298.15 K. These data have been used to calculate the infinite dilution apparent molar volumes, V2,m0, for the amino acids in aqueous TX-100 solutions and the standard partial molar volumes of transfer, Δtr V2,m0, of the amino acids from water to the aqueous surfactant solutions. The linear correlation of V2,m0 for a homologous series of amino acids has been utilized to calculate the contribution of the charged end groups (NH3+, COO−), CH2 group and other alkyl chains of the amino acids to V2,m0. The results on Δ tr V2,m0, of amino acids from water to aqueous TX-100 solutions have been interpreted in terms of ion–ion, ion–polar, hydrophilic–hydrophilic and hydrophobic–hydrophobic group interactions. For all the six amino acids studied, the values of Δtr V2,m0 from water to all the studied concentrations of aqueous TX-100 are small in spite of their different hydrophobic content, indicating an overall balance in interactions of zwitterionic/hydrophilic groups of amino acids with the hydrophilic groups of TX-100, and of hydrophobic and ionic/hydrophilic groups of the amino acids with hydrophobic groups of TX-100. Comparison of the interactions of the amino acids with nonionic, anionic and cationic surfactants has also been made and discussed. The partial specific volume of transfer of lysozyme from water to aqueous TX-100 solutions also indicates a balance of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions in the protein–nonionic surfactant system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Lynne, P. Collins, and M. R. J. Salton, (1979)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 553, 40 .
T. L. Reddy and M. M. Weber, (1986)J. Bacteriol. 167, 1 .
T. G. Warner, L. M. Dambach, J. H. Shin, and J. S. O’Brien, (1981)J. Biol. Chem. 256, 2952.
O. J. Bjerrum, S. Bhakdi, and K. Rieneck, (1980)J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 3, 355 .
T. Saitoh, N. Hattori, and M. Hiraide, (2004)J. Chromatogr. A 1028, 149 .
Z. Wang, F. Zhao, X. Hao, D. Chen, and D. Li, (2004)J. Mol. Catal. B 27, 147.
T. Cserhati, E. Forgacs, Z. Deyl, I. Miksik, and A. Echardt, (2001)J. Chromatogr. A 910, 137 .
B. Wang and H. Liu, (1999)Acta Biophys. Sin. 15, 456 .
Z. Bi and A. W. Neumann, (1998)Acta Phys. Chem. Sin. 14, 649 .
Y. Zhang, P. Chen, and H. Zhou, (1994)Acta Biophys. Sin. 10, 181 .
L. Huizhou, Y. Weijing, and C. Jiayong, (1996)Biochem. Eng. J. 2, 187.
Y. Moriyama and K. Takeda, (1999)Langmuir 15, 2003.
K. Takeda and Y. Moriyama, (1997)Curr. Topics Colloids Interface 1, 109.
E. L. Gelamo and M. Tabak, (2000)Spectrochim. Acta., Part A 56, 2255.
M. Vasilescu, D. Angelescu, M. Almgren, and A. Valstar, (1999)Langmuir 15, 2635 .
D. Kelley and D. J. McClements, (2003)Food Hydrocolloids 17, 74.
S. Deep and J. C. Ahluwalia, (2001)Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3, 4583.
A. D. Nielsen, K. Borch, and P. Westh, (2000)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1479, 321.
M. Yamasaki, T. Yamashita, H. Yano, K. Tatsumi, and K. Aoki, (1996)Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 19, 241.
S. K. Singh, A. Kundu, and N. Kishore, (2004)J. Chem. Thermodyn. 36, 7.
F. E. Jones, (1978)J. Res. Natl. Bur. Std. (U.S.) 83, 419.
D. G. Archer, (1992)J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 21, 793.
S. K. Singh and N. Kishore, (2003)J. Solution Chem. 32, 117.
A. K. Mishra and J. C. Ahluwalia, (1984)J. Phys. Chem. 88, 86 .
J. E. Desnoyers, (1982)Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 1469 .
G. R. Hedwig, J. F. Reading, and T. H. Lilley, (1991)J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 87, 1751 .
R. K. Wadi and R. K. Goyal, (1992)J. Solution Chem. 21, 163 .
Z. Yau, J. Wang, H. Zheng, and D. Liu, (1998)J. Solution Chem. 27, 473 .
J. Wang, Z. Yau, K. Zhuo, and J. Liu, (1999)Biophys. Chem. 80, 179 .
A. W. Hakin, M. M. Duke, J. L.Marty, and K. E. Presuss, (1994)J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 90, 2027 .
A. W. Hakin, M. M. Duke, L. L. Groft, J. L. Marty, and M. L. Rashfeldt, (1995)Can. J. Chem. 73, 725 .
F. J. Millero, A. L. Surdo, and C. Shin, (1978)J. Phys. Chem. 82, 784 .
E. Berlin and M. J. Pallansch, (1968)J. Phys. Chem. 72, 1887 .
F. Franks, M. A. Quickenden, D. S. Reid, and B. Watson, (1970)Trans Faraday Soc. 66, 582 .
A. Bondi, (1964)J. Phys. Chem. 68, 441 .
A. Bondi, (1954)J. Phys. Chem. 58, 929 .
F. Shahidi, P. G. Farrell, and J. T. Edwards, (1976)J. Solution Chem. 5, 807 .
K. Hara, H. Kuwabara, O. Kajimoto, and K. Bhattachrayya, (1999)J. Photochem. Photobiol. 124, 159 .
E. Haque, A. R. Das, and S. P. Moulick, (1995)J. Chem. Phys. Chem. 99, 14032 .
R. W. Gurney, Ionic Process in Solutions (McGraw Hill, New York, 1953).
H. S. Frank and M. W. Evan, (1945)J. Chem. Phys. 13, 507 .
H. Z. Yuan, G. Z. Cheng, S. Zhao, X. J. Miao, J. Y. Yu, L. F. Shen, and Y. R. Du, (2000)Langmuir 16, 3030 .
C. A. Bunton, H. J. Foroudian, N. D. Gillitt, and C. R. Whiddon, (1999)J. Colloid Interface Sci. 215, 64 .
L. A. Bulavin, V. M. Garamus, T. V. Karmazina, and S. P. Shtanko, (1995)J. Colloid (Trans. Kolloidn. Zh.) 57, 856 .
V. L. Alekseev, G. A. Evmenenko, and A. T. Dembo, (1997)Colloid J. 59, 267 .
P. S. Goyal, S. V. G. Menon, B. A. Dasannacharya, and P. Thiyagarajan, (1995)Physica B 213–214, 610 .
P. Sen, S. Mukherjee, A. Halder, and K. Bhattacharyya, (2004)Chem. Phys. Lett. 385, 361 .
H.-J. Hinz, (ed.) Thermodynamic Data for Biochemistry and Biotechnology (Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo, 1986).
K. Sasahara, M. Sakurai, and K. Nitta, (1999)J. Mol. Biol. 291, 693 .
W. Kauzmann, (1959)Adv. Protein Chem. 14, 1 .
T. V. Chalikian, V. S. Gindikin, and K. J. Breslauer, (1995)J. Mol Biol 250, 291 .
F. M. Richards, (1977)Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 6, 151 .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.K., Kishore, N. Volumetric Properties of Amino Acids and Hen-Egg White Lysozyme in Aqueous Triton X-100 at 298.15 K. J Solution Chem 33, 1411–1427 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-004-1056-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-004-1056-x