Abstract
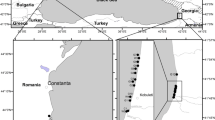
The ambient dose rate distribution, measured along the Southern sector of Romanian Black Sea shore, between Vama Veche in South and Chituc sandbank in North gave, with some notable exception, values between 34 and 54 nSv/h, lower than the 90 nSv/h, the average value for Romania. The experimental dose rates increase northward, reaching a maximum in the vicinity the Chituc sandbank, i.e. at the Vadu and Corbu beaches. According to gamma ray measurements performed in the Slanic-Prahova Low-Background Radiation Laboratory on the sand collected from the same location, the natural radionuclides have a major contribution to observes dose rate while the contribution of the anthropogenic 137Cs, 26 years after Chernobyl accident, remains almost negligible. By taking into account both activity concentrations of radionuclides and the contribution of cosmic rays, we have calculated the local values of dose rate, which showed to be, within experimental uncertainties, coincident with the experimental ones. Moreover, on Chituc sandbank, we have noticed the presence of some local maxima, two to three times higher than the average ones. Further investigations showed an increased content of natural radionuclides, most probably accumulated in the heavy minerals fraction—a common occurrence in the vicinity of Danube Delta.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2012) Monthly Stat Bull 9: pp. 94, National Institute of Statistics, Bucharest, Romania, http://www.insse.ro/cms/files/arhiva_buletine2012/bsl_9.pdf (last accessed 10.01.2013)
Giosan L, Bokuniewicz H, Panin N, Postolache I (1993) Longshore sediment transport pattern along Romanian Danube delta coast, Geo-Eco-Marina 2:11-23; http://www.geoecomar.ro/website/publicatii/Nr.2-1997/2.GiosanL.pdf (last accessed 10.01.2013)
UNECE (2007) Our Waters: joining hands across borderd: first assessment of transboundary rivers, lakes and groundwaters, convention on the protection and use of transboundary watercourses and international lakes, United Nations, New York, http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/env/water/blanks/assessment/black.pdf (last accessed 10.01.2013)
PRIS (2012) power reactor information system, international atomic energy agency, Vienna; http://www.iaea.org/pris/ (Last accessed 10.01.2013)
OECD Chernobyl (2003) Assessment of Radiological and Health Impacts OECD Papers 3:3-155, OECD Publications, 2, rue Andr-Pascal, 75775 Paris Cedex 16 ; http://caliban.sourceoecd.org/vl=99967460/cl=11/nw=1/rpsv/cgi-bin/fulltextew.pl?prpsv=/ij/oecdjournals/16091914/v3n1/s1/p1l.idx (last accessed 10.01.2013)
Pennington W, Tutin TG, Cambray RS (1973) Observations on lake sediments using fallout 137Cs as a tracer. Nature 242:324–326 doi:10.1038/242324a0
Florea N, Cristache C, Oaie G, Duliu OG (2011) Concordant 210Pb and 137Cs ages of Black Sea anoxic unconsolidated sediments Geochronometria 38:101-106 doi:10.2478/s13386-011-0022-9
Peev TM, Mitov IG (1999) Some investigations of sea sands from the Black Sea coastline. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 241:169–172 doi:10.1007/BF02347305
Filippidis A, Misaelides P, Clouvas A, Godelitsas A, Barbayiannis N, Anousis I (1997) Mineral, chemical and radiological investigation of a black sand at Touzla Cape, near Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ Geochem Health 19:83–88 doi:10.1023/A:1018498404922
Nada A, Abd EL-Maksoud TM, Abu Zeid H, El-Asy IE, Mostafa SM Im Abc El-Azeem SA (2012) Correlation between radionuclides associated with zircon and monazite in beach sand of Rosetta, Egypt. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291:601–610 doi:10.1007/s10967-011-1430-2
Vasconcelos DC, Pereira C, Oliveira AH, Santos TO, Rocha Z, de B C Menezes M (2011) Determination of natural radioactivity in beach sand in the extreme south of Bahia, Brazil, using gamma spectrometry. Rad Prot Environ 34:178–84 doi:10.4103/0972-0464.101714
Mallik TK, Vasudevan V, Aby Verghese P, Machado T (1987) The black sand placer deposits of Kerala beach, southwest India. Mar Geol 77:129150 doi:10.1016/0025-3227(87)90088-0
Margineanu R, Simion C, Bercea S, Duliu OG, Gheorghiu D, Stochioiu A, Matei M (2008) The Slanic-Prahova (ROMANIA) underground low-background radiation laboratory. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1501-6 doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2008.04.002
Hult M, Preusse W, Gasparro J, Khlerc M (2006) Underground gamma-ray spectrometry: Minireview. Acta Chim Slov 53:17
Semkow TM, Parekh PP, Schwenker CD, Khan AJ, Bari A, Colaresi JF, Tench OK, David G, Guryn GW (2002) Low-background gamma spectrometry for environmental radioactivity. Appl Radiat Isot 57:213223 doi:10.1016/S0969-8043(02)00085-4
Laubenstein M, Hult J, Gasparro D, Arnold S, Neumaier G, Heusser M Kohler, P. Povinec, JL, Reyss, M. Schwaiger, P. Theodorsson, (2004) Underground measurements of radioactivity. Appl Radiat Isot 61:167172 doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2004.03.039
Koehler M, Degering AD, Laubenstein M, Quirin P, Lampert M-O, Hult M, Arnold D, Neumaier S, Reyss J-L (2009) A new low-level γ-ray spectrometry system for environmental radioactivity at the underground laboratory Felsenkelle. Appl Radiat Isot 67:736740 doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2009.01.027
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation, vol I,The UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Vienna, Austria
Rasolonjatovo DA, Suzuki H, Hirabayashi N, Nunomiya T, Nakamura T, Nakao N (2002) Measurement of the dose-rates of the cosmic-ray components on the ground. J Radiat Res 43 sup: S27–S33; https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jrr/43/S/43_S_S27/_pdf (Last accessed 10.01.2012)
UNSCEAR (1993) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation, annex A: exposures from natural sources of radiation pp. 65 The UNSCEAR 1993 Report to the General Assembly, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Vienna
Ergul HA, Topcuoglu S, Olmez E, Krbasoglu C (2006) Radionuclides in a sediment trap and bottom sediment samples from the eastern Turkish coast of the Black Sea. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 268:133136241 doi:10.1556/JRNC.268.2006.1.22
Kam E, Bozkurt A (2007) Environmental radioactivity measurements in Kastamonu region of northern Turkey. Appl Radiat Isot 65:440444 doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2006.11.005
Celik N, Cevik U, Celik A, Koz B (2009) Natural and artificial radioactivity measurements in Eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. J Hazard Mater 162: 146–153 doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.017
Samad OEl, Baydoun R, Nsouli B, Darwish T (2013) Determination of natural and artificial radioactivity in soil at North Lebanon province. J Environ Radioact Article (in press) doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2013.02.010
Uosif MAM,El-Taher A, Abbady AGE (2008) Radiological significance of beach sand used for climatotherapy from Safaga, Egypt. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 131:331–339 doi:10.1093/rpd/ncn175
Salahel Din K, Vesterbacka P (2012) Radioactivity levels in some sediment samples from Red Sea and Baltic Sea. Radiation Protection Dosimetry 148:101–106 doi:10.1093/rpd/ncq591
Panin N, Jipa DC, Gomoiu MT, Secrieru D (1999) Importance of Sedimentary processes in environmental changes: lower river Danube - Danube Delta–Western Black Sea System, Environmental Degradation of the Black Sea: Challenges and Remedies, NATO Science Series 56:23–41; doi:10.1007/978-94-011-4568-8_3
Mihai SA, Mather JD (2003) Role of mineralogical structure of sediments in accumulation of radionuclides and trace elements. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 256:425–430 doi:10.1023/A:1024587313309
Frihy OE (2007) The Nile Delta: Process of heavy minerals sorting and depositional patterns. Dev Sedimentol 58:49–74 doi:10.1016/S0070-4571(07)58002-7
Acknowledgments
This work was done within the BS ERA NET 041 project in the frame of BS-ERA.NET Pilot Joint CAll 2010/2011. We wish to thank Ms. Mariana Marinescu for her help in reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Margineanu, R.M., Duliu, O.G., Blebea-Apostu, A.M. et al. Environmental dose rate distribution along the Romanian Black Sea Shore. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298, 1191–1196 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-013-2545-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-013-2545-4